
How to Use plug: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with plug in Cirkit Designer
Design with plug in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A plug is an essential electronic component that serves as the interface between an electrical device and the power source. It is designed to connect safely and securely to a corresponding receptacle, allowing for the transfer of electrical power. Plugs are ubiquitous in electronic systems and are used in a variety of applications ranging from household appliances to industrial machinery.
Explore Projects Built with plug

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer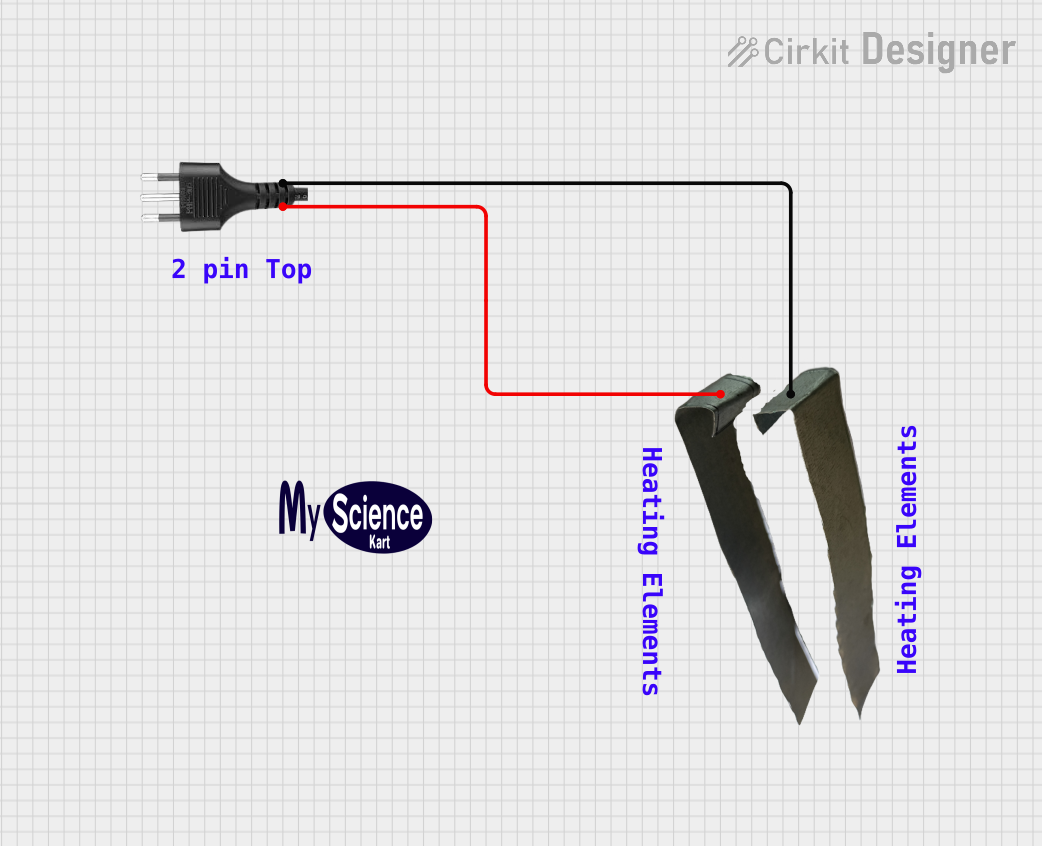
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with plug

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering household appliances like TVs, refrigerators, and lamps.
- Providing power to office equipment such as computers, printers, and photocopiers.
- Connecting power tools and machinery in industrial settings.
- Charging portable devices when used with adapters.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Voltage Rating | The maximum voltage the plug can handle, typically 110-240V AC. |
| Current Rating | The maximum current the plug can carry, often between 2.5A to 20A. |
| Power Rating | The maximum power the plug can transmit, calculated as Voltage x Current. |
| Number of Pins | The number of conductive pins or prongs, usually 2 or 3. |
| Pin Material | The conductive material used for pins, commonly brass or copper. |
| Insulation Material | The material used to insulate the plug, such as PVC or rubber. |
| Safety Standards | Compliance with international standards like IEC, UL, or CE. |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Live (L) - Carries the current to the device. |
| 2 | Neutral (N) - Completes the circuit by carrying current back. |
| 3 | Earth (E) - Safety ground to prevent electric shock (if applicable). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Plug in a Circuit
- Inspect the Plug: Before use, inspect the plug for any damage or wear.
- Check Ratings: Ensure the plug's voltage and current ratings match the device and power source.
- Wiring: Connect the wires from the device to the correct pins of the plug. Typically, live (L) is brown, neutral (N) is blue, and earth (E) is green-yellow.
- Secure Connections: Tighten any screws or clamps to secure the wires in place.
- Insulation: Ensure that the wiring is properly insulated to prevent short circuits.
- Insertion: Gently insert the plug into the corresponding receptacle.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always disconnect the power before working on any electrical components.
- Use a plug that matches the receptacle type and electrical standards of the region.
- Do not overload the plug beyond its specified ratings.
- Ensure proper grounding for devices that require a three-pin plug.
- Regularly check the condition of the plug and replace it if it shows signs of damage.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Plug Does Not Fit: Ensure the plug type matches the receptacle. Different countries have different standards.
- No Power: Check if the plug is fully inserted into the receptacle and that there is power at the source.
- Overheating: If the plug overheats, it may be due to overloading or poor connections. Disconnect immediately.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Loose Connections: Tighten any loose screws and ensure wires are securely attached to the plug pins.
- Damaged Plug: Replace the plug if it is cracked, burnt, or otherwise damaged.
- Circuit Breaker Tripped: Reset the breaker or replace the fuse in your home's distribution board.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a plug with a higher rating on a lower-powered device? A: Yes, using a plug with a higher rating is generally safe. However, the device and receptacle must not exceed the plug's ratings.
Q: What does polarized or non-polarized mean for a plug? A: A polarized plug has one prong wider than the other, ensuring it is inserted into the receptacle in one direction. Non-polarized plugs can be inserted either way.
Q: Is it safe to use an adapter to fit a different type of receptacle? A: It can be safe if the adapter is properly rated and certified, but it's always best to use a plug that directly fits the receptacle.
Q: How do I know if my plug is grounded? A: A grounded plug will have a third pin (earth) that connects to the grounding system of the electrical installation.
Note: If you are unsure about any aspect of using or installing a plug, consult a qualified electrician.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
// This section is not typically applicable to a plug as it is a passive component
// without direct interaction with microcontrollers like the Arduino UNO. However,
// if the plug is part of a device that communicates with an Arduino, the code
// would pertain to the device's functionality rather than the plug itself.
Remember: Always ensure that any electrical work complies with local regulations and safety standards.