
How to Use TP4056: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
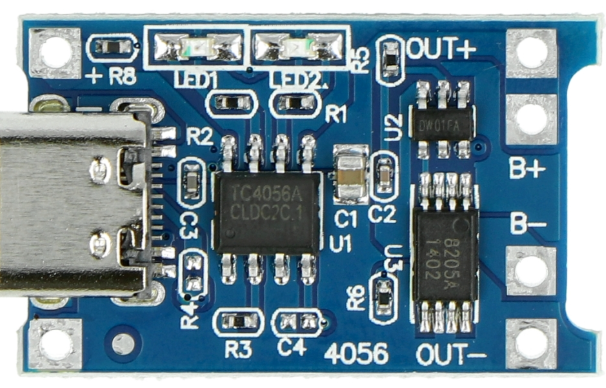
 Design with TP4056 in Cirkit Designer
Design with TP4056 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TP4056 is a lithium-ion battery charger IC designed for single-cell lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries. It provides a constant current/constant voltage (CC/CV) charging profile, ensuring safe and efficient charging. The IC integrates several safety features, including thermal regulation, over-voltage protection, and automatic charge termination. Its compact design and ease of use make it a popular choice for portable electronics, DIY projects, and battery-powered devices.
Explore Projects Built with TP4056

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer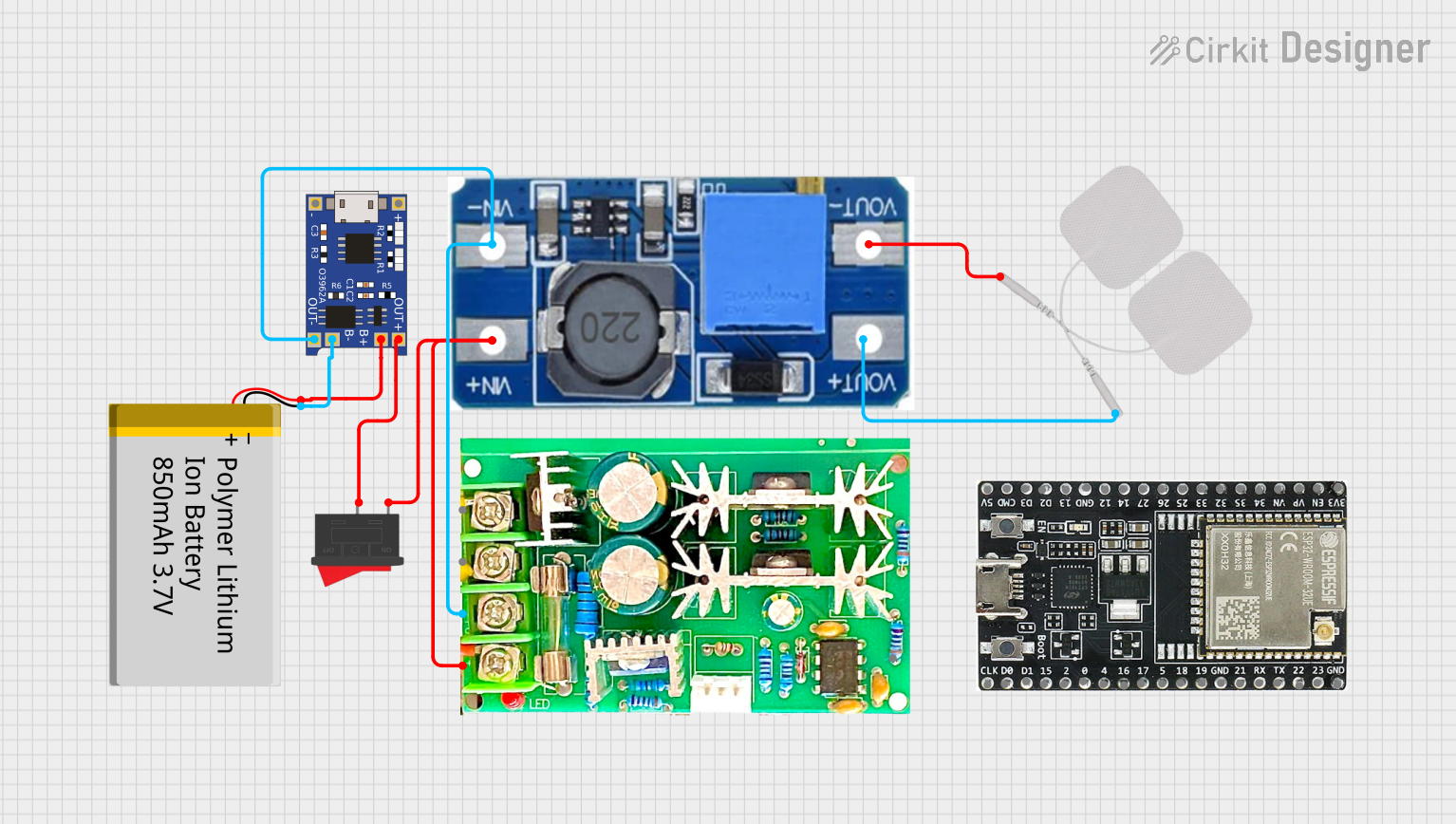
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TP4056

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Charging single-cell lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries
- Power banks and portable chargers
- Wearable devices
- DIY electronics projects
- Battery management systems
Technical Specifications
The TP4056 is a versatile and reliable charging IC. Below are its key technical details:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 4.0V to 8.0V |
| Charging Voltage | 4.2V ± 1% |
| Maximum Charging Current | 1A (adjustable via external resistor) |
| Charging Method | Constant Current/Constant Voltage (CC/CV) |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +85°C |
| Standby Current | < 2µA |
| Battery Overvoltage Protection | 4.3V |
| Thermal Regulation | 120°C (reduces charging current) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The TP4056 is typically available in an 8-pin SOP package. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Name | Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BAT | 1 | Battery connection pin. Connect to the positive terminal of the lithium battery. |
| GND | 2 | Ground pin. Connect to the system ground. |
| VCC | 3 | Input voltage pin. Connect to a 4.0V–8.0V power source. |
| PROG | 4 | Charging current programming pin. Connect a resistor to set the charging current. |
| CHRG | 5 | Charging status indicator (active low). Connect to an LED for charge indication. |
| STDBY | 6 | Standby status indicator (active low). Connect to an LED for standby indication. |
| TEMP | 7 | Temperature monitoring pin. Connect to an NTC thermistor for thermal protection. |
| CE | 8 | Chip enable pin. Pull low to enable charging, pull high to disable. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the TP4056 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect a 5V DC power source (e.g., USB) to the VCC pin. Ensure the input voltage is within the 4.0V–8.0V range.
- Battery Connection: Connect the positive terminal of the lithium-ion battery to the BAT pin and the negative terminal to GND.
- Set Charging Current: Use a resistor (Rprog) between the PROG pin and GND to set the charging current. The charging current can be calculated using the formula: [ I_{CHG} = \frac{1000}{R_{PROG}} ] For example, a 1.2kΩ resistor sets the charging current to approximately 833mA.
- Status Indicators: Connect LEDs to the CHRG and STDBY pins for visual charging status. Use a current-limiting resistor (e.g., 1kΩ) in series with each LED.
- Thermal Protection: Optionally, connect an NTC thermistor to the TEMP pin for temperature monitoring. If unused, connect TEMP to GND.
Important Considerations
- Battery Compatibility: Ensure the battery is a single-cell lithium-ion or lithium-polymer type with a nominal voltage of 3.7V.
- Heat Dissipation: The TP4056 may generate heat during operation. Use proper heat sinking or ensure adequate ventilation.
- Input Voltage: Avoid exceeding the maximum input voltage of 8.0V to prevent damage to the IC.
- Reverse Polarity: Ensure correct polarity when connecting the battery to avoid damage.
Example: Using TP4056 with Arduino UNO
The TP4056 can be used in conjunction with an Arduino UNO to monitor battery voltage. Below is an example code snippet:
// Example: Monitor battery voltage using Arduino UNO
// Connect the BAT pin of TP4056 to an analog pin (e.g., A0) on Arduino
const int batteryPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to TP4056 BAT pin
float voltageDividerRatio = 2.0; // Adjust if using a voltage divider
float referenceVoltage = 5.0; // Arduino reference voltage (5V for UNO)
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int rawValue = analogRead(batteryPin); // Read analog value from BAT pin
float batteryVoltage = (rawValue / 1023.0) * referenceVoltage * voltageDividerRatio;
// Print battery voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before next reading
}
Note: If the battery voltage exceeds the Arduino's analog input range, use a voltage divider to scale it down.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Charging Current
- Cause: Incorrect Rprog resistor value or damaged IC.
- Solution: Verify the Rprog resistor value and ensure it is properly connected. Check the input voltage and replace the IC if necessary.
Overheating
- Cause: High input voltage or insufficient heat dissipation.
- Solution: Ensure the input voltage is within the 4.0V–8.0V range. Add a heatsink or improve ventilation.
LED Indicators Not Working
- Cause: Incorrect LED connections or damaged LEDs.
- Solution: Verify the LED polarity and current-limiting resistor values. Replace damaged LEDs.
Battery Not Charging
- Cause: Faulty battery connection or incompatible battery type.
- Solution: Check the battery connections and ensure the battery is a single-cell lithium-ion or lithium-polymer type.
FAQs
Can I use the TP4056 to charge multiple batteries in series?
- No, the TP4056 is designed for single-cell batteries only. Charging multiple cells in series requires a dedicated battery management system.
What happens if the input voltage exceeds 8.0V?
- Exceeding 8.0V can damage the IC. Use a regulated power supply to prevent overvoltage.
Can I adjust the charging voltage?
- No, the charging voltage is fixed at 4.2V ± 1%. It cannot be adjusted.
Is the TP4056 suitable for fast charging?
- The TP4056 supports charging currents up to 1A, which is suitable for most single-cell batteries. For higher currents, consider alternative ICs.
By following this documentation, you can safely and effectively use the TP4056 in your projects.