
How to Use Dual Op Amp: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
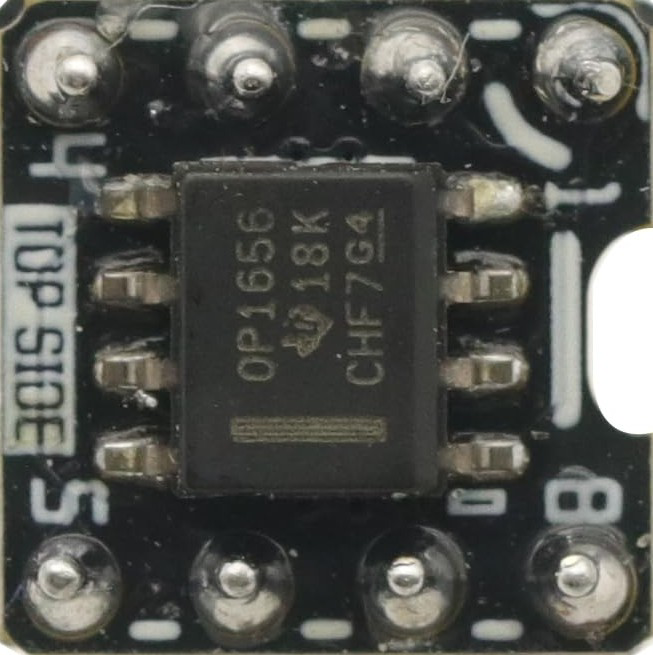
 Design with Dual Op Amp in Cirkit Designer
Design with Dual Op Amp in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The OPA1656, manufactured by GODIYMODULES, is a high-performance dual operational amplifier (op-amp) that integrates two independent, high-gain, frequency-compensated amplifiers into a single package. This component is widely used in analog circuits for applications such as signal conditioning, active filtering, and mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, and integration. Its low noise, high precision, and wide bandwidth make it ideal for audio processing, instrumentation, and other precision analog applications.
Explore Projects Built with Dual Op Amp
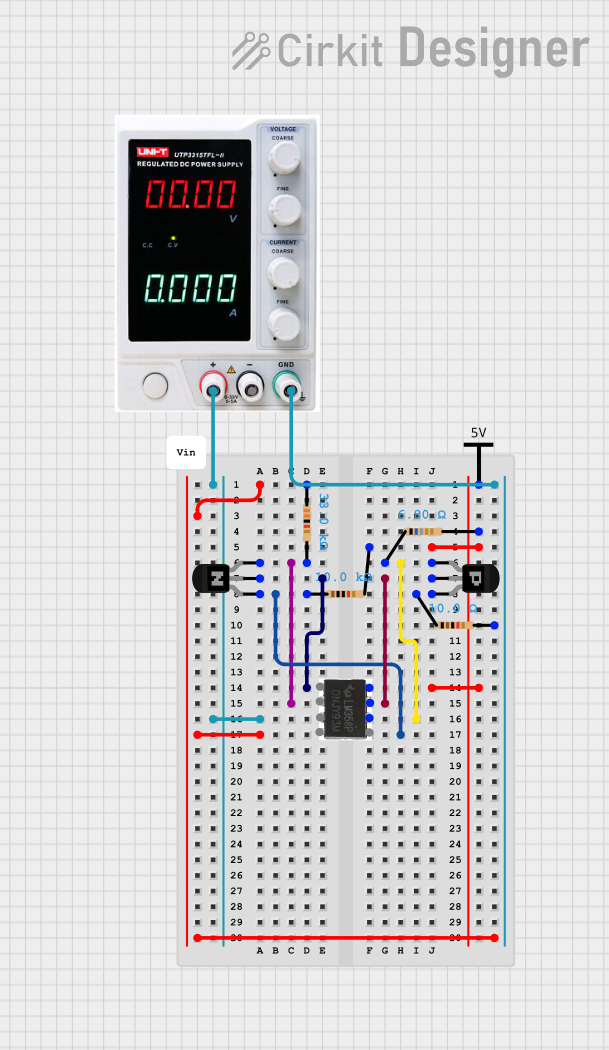
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer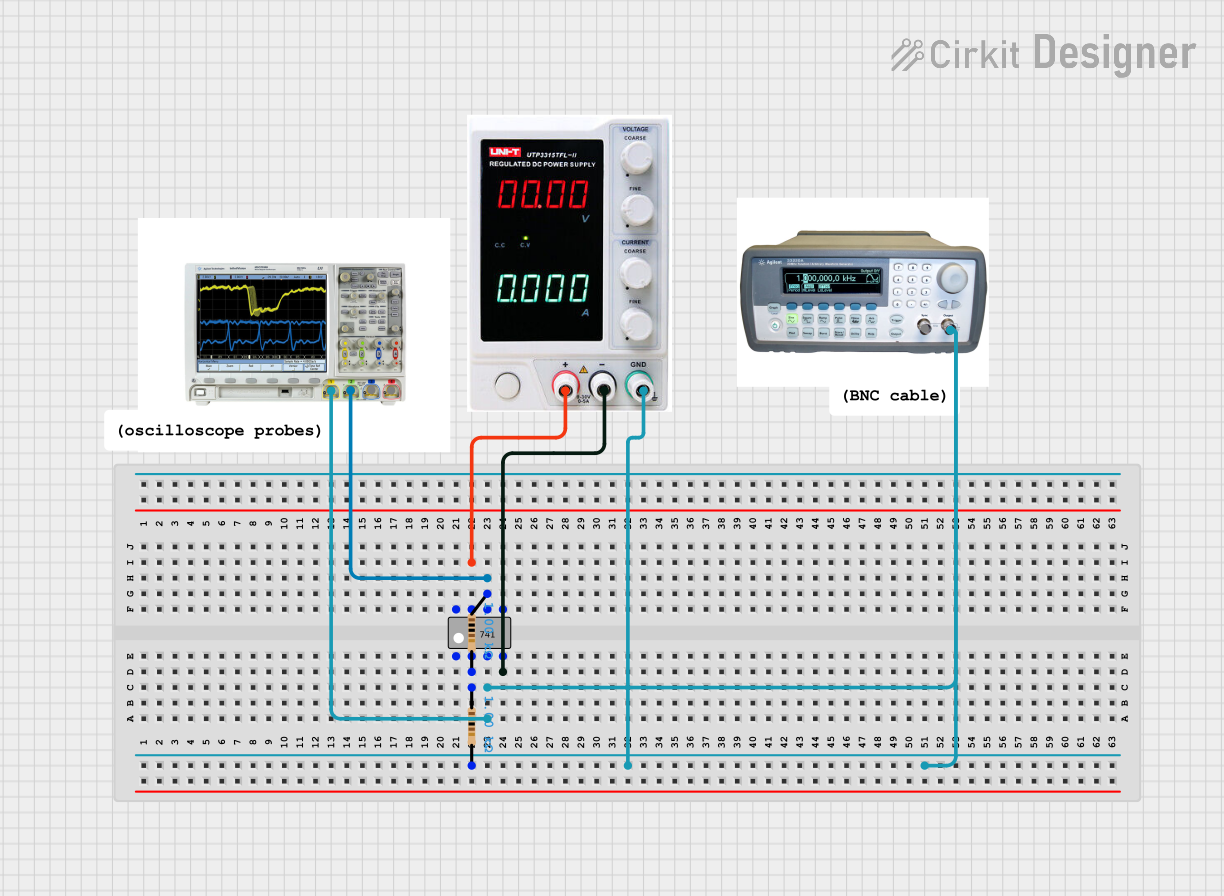
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer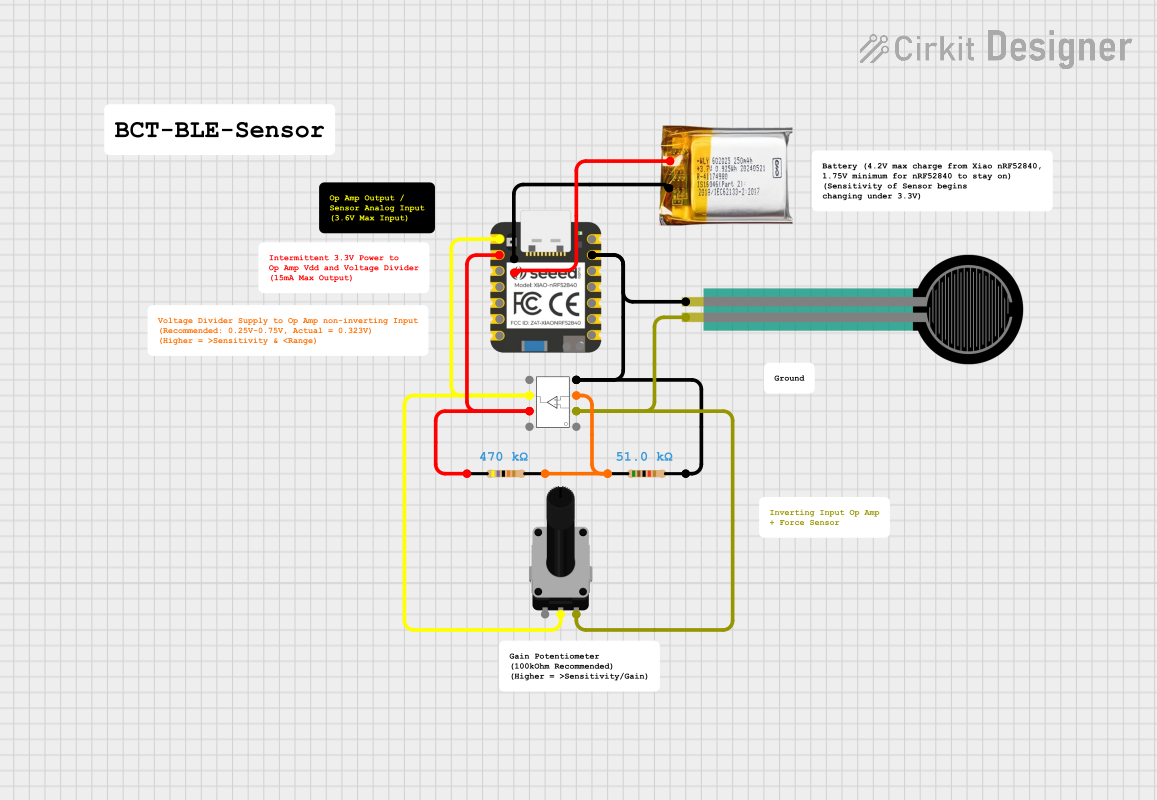
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer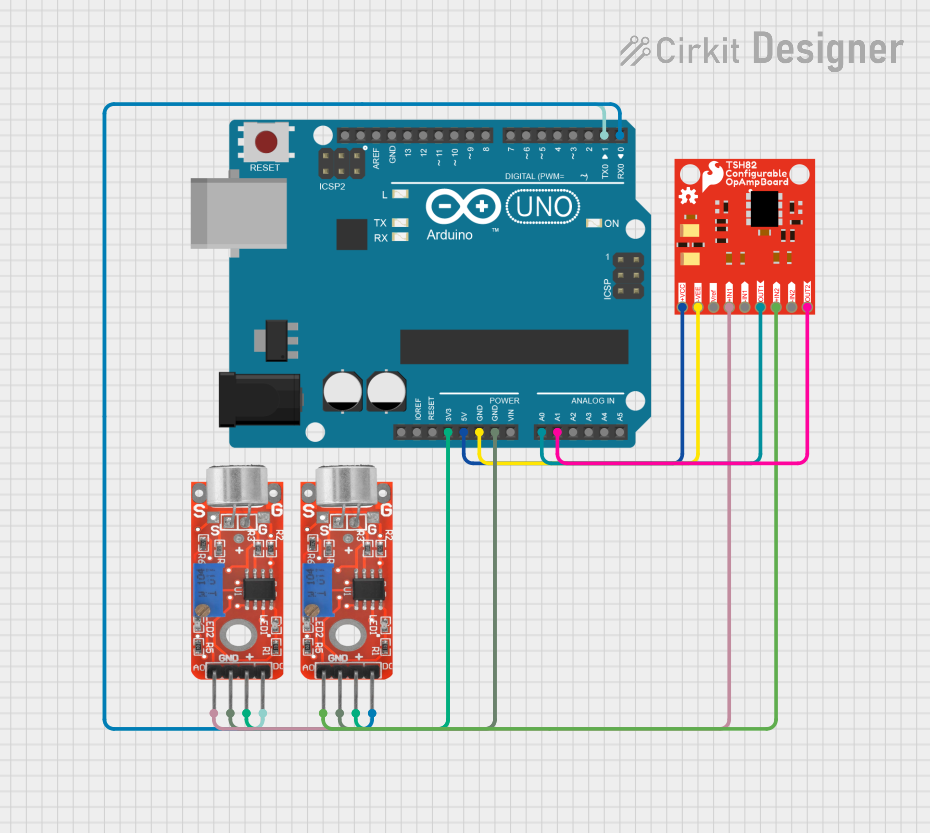
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Dual Op Amp

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Audio signal processing and amplification
- Active filters (low-pass, high-pass, band-pass)
- Analog mathematical operations (e.g., summing, integration, differentiation)
- Sensor signal conditioning
- Data acquisition systems
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | GODIYMODULES |
| Part Number | OPA1656 |
| Supply Voltage Range | ±2.5V to ±18V (dual supply) or 5V to 36V (single supply) |
| Input Offset Voltage | 0.3 mV (typical) |
| Input Bias Current | 10 pA (typical) |
| Gain Bandwidth Product | 22 MHz |
| Slew Rate | 17 V/µs |
| Output Voltage Swing | Rail-to-rail |
| Noise Density | 2.9 nV/√Hz |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +125°C |
| Package Options | SOIC-8, VSSOP-8 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The OPA1656 is typically available in an 8-pin SOIC or VSSOP package. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | OUT A | Output of Op Amp A |
| 2 | IN- A | Inverting input of Op Amp A |
| 3 | IN+ A | Non-inverting input of Op Amp A |
| 4 | V- (GND) | Negative power supply or ground |
| 5 | IN+ B | Non-inverting input of Op Amp B |
| 6 | IN- B | Inverting input of Op Amp B |
| 7 | OUT B | Output of Op Amp B |
| 8 | V+ | Positive power supply |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the OPA1656 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the OPA1656 to a suitable power supply. For dual-supply operation, connect
V+to the positive voltage (e.g., +15V) andV-to the negative voltage (e.g., -15V). For single-supply operation, connectV+to the positive voltage (e.g., +5V) andV-to ground. - Input Connections: Connect the input signal to the
IN+(non-inverting) orIN-(inverting) pins, depending on the desired configuration (e.g., inverting or non-inverting amplifier). - Output Load: Connect the load or the next stage of the circuit to the
OUTpin. Ensure the load impedance is within the recommended range to avoid distortion or instability. - Bypass Capacitors: Place decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1 µF ceramic and 10 µF electrolytic) close to the power supply pins to reduce noise and improve stability.
- Feedback Network: Use appropriate resistors and capacitors in the feedback loop to set the gain and bandwidth of the amplifier.
Example: Connecting the OPA1656 to an Arduino UNO
The OPA1656 can be used to amplify an analog signal before feeding it into the Arduino's ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter). Below is an example of a non-inverting amplifier configuration:
Circuit Diagram
- Connect
V+to +5V andV-to GND. - Connect the input signal to
IN+ Athrough a coupling capacitor. - Use a resistor divider in the feedback loop to set the gain.
Arduino Code Example
// Example: Reading an amplified signal from the OPA1656 with Arduino UNO
// The OPA1656 is configured as a non-inverting amplifier with a gain of 10.
const int analogPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the OPA1656 output
int sensorValue = 0; // Variable to store the ADC reading
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
sensorValue = analogRead(analogPin); // Read the amplified signal
float voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0); // Convert ADC value to voltage
Serial.print("Amplified Voltage: ");
Serial.println(voltage); // Print the voltage to the Serial Monitor
delay(500); // Wait for 500 ms before the next reading
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Stability: Ensure proper feedback network design to avoid oscillations.
- Input Impedance: Use high input impedance to minimize loading effects on the signal source.
- Thermal Management: Operate the OPA1656 within its specified temperature range to ensure reliable performance.
- Power Supply Decoupling: Always use bypass capacitors close to the power pins to reduce noise and improve stability.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Issue: The output signal is distorted or clipped.
- Solution: Check the power supply voltage and ensure it is within the specified range. Verify that the input signal amplitude and gain settings do not exceed the output voltage swing.
Issue: The amplifier oscillates or produces noise.
- Solution: Add bypass capacitors near the power supply pins. Verify the feedback network design and ensure proper grounding.
Issue: No output signal.
- Solution: Check all connections, especially the power supply and input signal. Ensure the load impedance is not too low.
FAQs
Q: Can the OPA1656 operate with a single power supply?
A: Yes, the OPA1656 can operate with a single supply voltage (e.g., 5V to 36V). However, ensure the input and output signals are biased appropriately to stay within the operating range.
Q: What is the maximum gain I can achieve with the OPA1656?
A: The maximum gain depends on the feedback network and the bandwidth of the amplifier. For high gains, ensure the gain-bandwidth product (22 MHz) is not exceeded.
Q: Can I use the OPA1656 for audio applications?
A: Yes, the OPA1656 is well-suited for audio applications due to its low noise and high precision.
Q: How do I protect the OPA1656 from damage?
A: Use proper decoupling capacitors, avoid exceeding the maximum voltage ratings, and ensure the input signals are within the specified range.