
How to Use PLUG: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with PLUG in Cirkit Designer
Design with PLUG in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A plug is a device used to connect an electrical appliance to a power source. It typically features prongs that fit into a corresponding socket, enabling the flow of electricity to power the connected device. Plugs are essential components in electrical systems, ensuring a safe and reliable connection between appliances and power outlets.
Explore Projects Built with PLUG

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer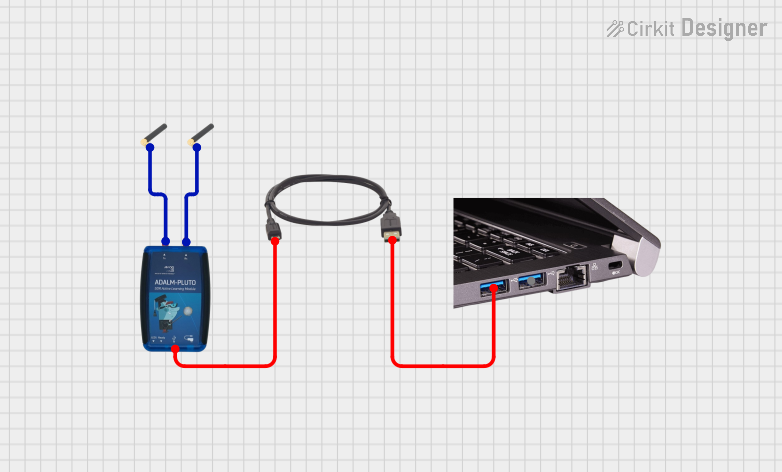
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer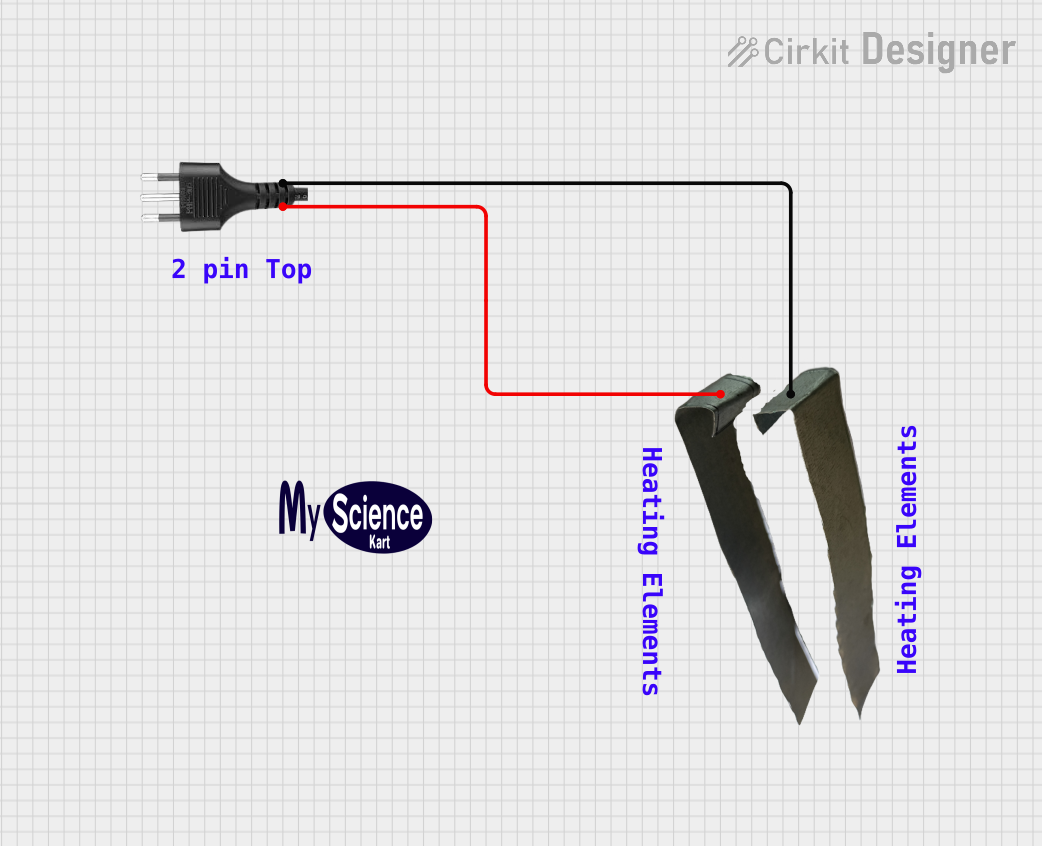
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with PLUG

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering household appliances such as lamps, televisions, and kitchen devices.
- Connecting industrial equipment to power supplies.
- Charging electronic devices like smartphones and laptops.
- Temporary connections for portable tools and devices.
Technical Specifications
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Voltage Rating | Typically 110V-240V AC (varies by region) |
| Current Rating | Commonly 6A, 10A, or 15A |
| Frequency | 50Hz or 60Hz |
| Material | Plastic (insulation) and metal (prongs) |
| Safety Standards | Varies by region (e.g., UL, CE, or BIS) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Live (L) | Carries the current from the power source to the appliance. |
| Neutral (N) | Completes the circuit by returning current to the power source. |
| Earth (E) | Provides a safety path for fault currents to prevent electric shock. |
Note: The number of pins and their configuration may vary depending on the plug type (e.g., Type A, Type B, Type C, etc.).
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Plug in a Circuit
- Inspect the Plug: Ensure the plug is free from damage, such as frayed wires or bent prongs.
- Connect to Appliance: Attach the plug to the appliance's power cord securely.
- Insert into Socket: Align the prongs with the socket and insert them fully to establish a connection.
- Power On: Turn on the appliance or power source as needed.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Compatibility: Verify that the plug's voltage rating matches the power source and appliance.
- Grounding: Use plugs with an earth pin for devices requiring grounding to enhance safety.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the plug's current rating to prevent overheating or damage.
- Inspect Regularly: Check for wear and tear, and replace damaged plugs immediately.
- Regional Standards: Use plugs designed for the specific socket type and voltage in your region.
Example: Connecting a Plug to an Arduino UNO Power Supply
If you are using a plug to power an Arduino UNO via an adapter, ensure the adapter's output matches the Arduino's input requirements (e.g., 9V DC, 1A). Below is an example Arduino sketch for a simple LED blink program:
// Example Arduino code to blink an LED connected to pin 13
// Ensure the Arduino is powered via a properly connected plug and adapter
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output pin
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Plug Does Not Fit the Socket:
- Cause: Mismatch between plug type and socket type.
- Solution: Use an appropriate adapter or replace the plug with a compatible one.
Appliance Does Not Power On:
- Cause: Loose connection, damaged plug, or faulty socket.
- Solution: Check the plug for damage, ensure it is securely inserted, and test with a different socket.
Overheating Plug:
- Cause: Overloading or poor contact between plug and socket.
- Solution: Reduce the load on the circuit and ensure the plug is properly inserted.
Sparks When Plugging In:
- Cause: Faulty socket or plug, or high inrush current.
- Solution: Inspect and replace damaged components, and avoid plugging in devices while they are powered on.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a plug designed for 110V in a 220V region?
A: No, using a plug with an incompatible voltage rating can damage the appliance and pose safety risks. Always use plugs rated for the voltage in your region.
Q: How do I know if my plug is grounded?
A: Grounded plugs typically have three prongs, with the third prong (earth pin) being larger or differently shaped. Ensure the socket also supports grounding.
Q: Can I repair a damaged plug?
A: Yes, but only if you have the necessary skills and tools. Otherwise, replace the plug to ensure safety and compliance with standards.
Q: Why does my plug feel warm during use?
A: A slightly warm plug is normal, but excessive heat indicates overloading or poor contact. Address the issue immediately to prevent hazards.