
How to Use G5: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with G5 in Cirkit Designer
Design with G5 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Garmin G5 is a versatile relay designed for use in electronic circuits to control the flow of current. It operates by using an electromagnetic coil to open or close a set of contacts, enabling the automation of electrical devices. Relays like the G5 are essential in applications where low-power control signals are used to manage high-power circuits.
Explore Projects Built with G5
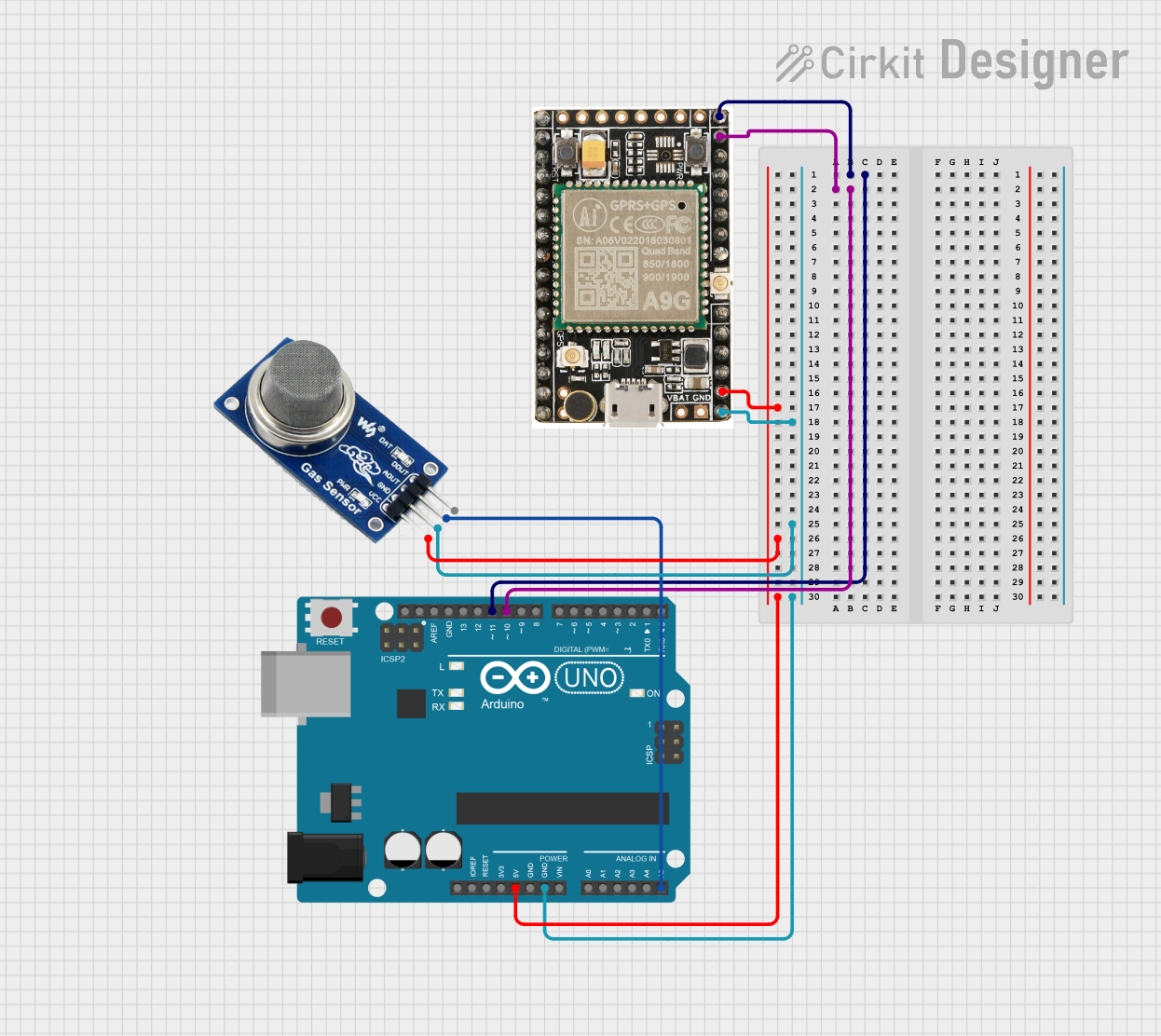
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer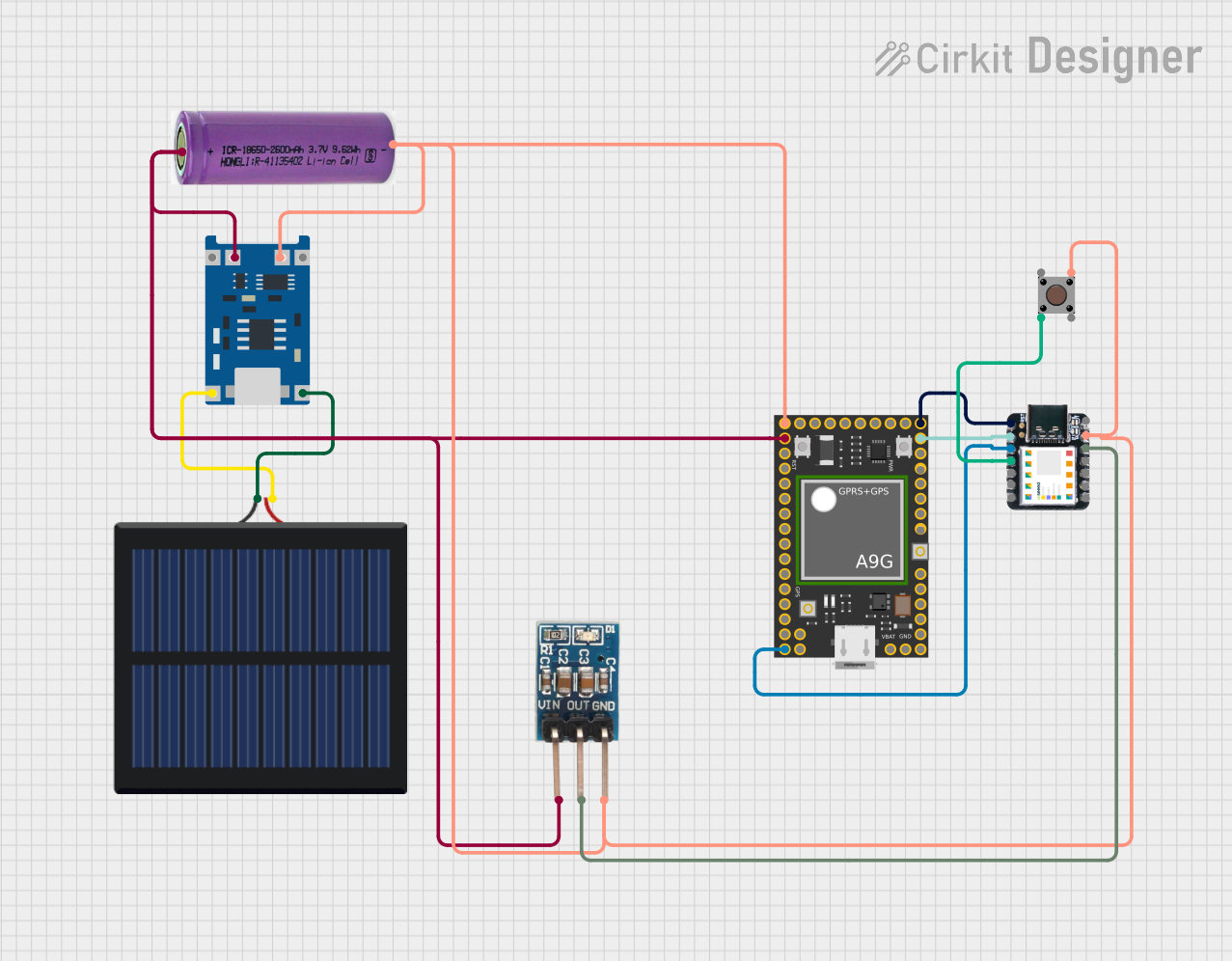
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with G5

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Home automation systems
- Industrial control panels
- Automotive electronics
- Power supply switching
- Motor control circuits
- Signal isolation between high- and low-voltage systems
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Manufacturer: Garmin
- Part ID: G5
- Type: Electromechanical relay
- Coil Voltage: 5V DC (typical)
- Contact Configuration: SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw)
- Contact Rating: 10A at 250V AC or 10A at 30V DC
- Coil Resistance: 70Ω ±10%
- Switching Time: 10ms (operate) / 5ms (release)
- Dielectric Strength: 1500V AC (coil to contacts)
- Insulation Resistance: ≥100MΩ at 500V DC
- Operating Temperature Range: -40°C to +85°C
- Dimensions: 28mm x 12mm x 15mm
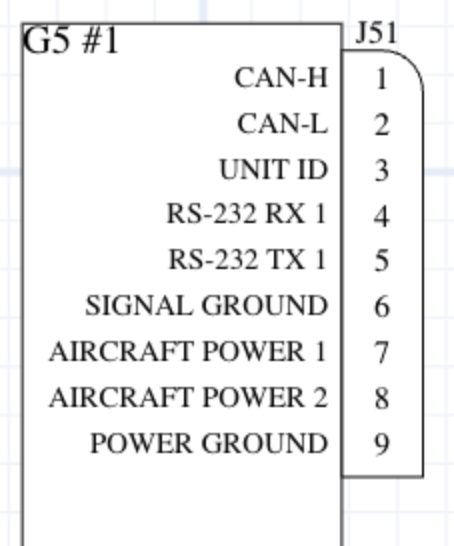
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The G5 relay typically has 5 pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Coil (+) | Positive terminal of the relay coil. Connect to the control voltage source. |
| 2 | Coil (-) | Negative terminal of the relay coil. Connect to ground. |
| 3 | Common (COM) | Common terminal for the relay contacts. |
| 4 | Normally Closed (NC) | Contact that is connected to COM when the relay is not energized. |
| 5 | Normally Open (NO) | Contact that is connected to COM when the relay is energized. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the G5 in a Circuit
- Power the Coil: Connect the coil pins (1 and 2) to a 5V DC power source. Use a current-limiting resistor if necessary to prevent overloading the coil.
- Control the Load: Connect the load to the COM (pin 3) and either the NC (pin 4) or NO (pin 5) terminal, depending on whether you want the load to be powered when the relay is de-energized or energized.
- Switching Logic: Apply a control signal to the coil to energize the relay. This will switch the connection between the COM and NO terminals, allowing current to flow through the load.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Diode Protection: Place a flyback diode across the coil terminals to protect the circuit from voltage spikes caused by the collapsing magnetic field when the relay is de-energized.
- Contact Ratings: Ensure the load does not exceed the relay's contact rating (10A at 250V AC or 30V DC).
- Isolation: Use optocouplers or transistors to isolate the control circuit from the relay if necessary.
- Mounting: Secure the relay in a socket or PCB to prevent mechanical stress on the pins.
Example: Connecting the G5 to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control the G5 relay using an Arduino UNO:
// Define the pin connected to the relay's coil
const int relayPin = 7;
void setup() {
// Set the relay pin as an output
pinMode(relayPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Turn the relay ON
digitalWrite(relayPin, HIGH);
delay(1000); // Keep the relay ON for 1 second
// Turn the relay OFF
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW);
delay(1000); // Keep the relay OFF for 1 second
}
Note: Use a transistor (e.g., 2N2222) to drive the relay if the Arduino pin cannot supply enough current. Place a flyback diode (e.g., 1N4007) across the relay coil to protect the transistor and Arduino.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Relay Not Switching:
- Cause: Insufficient voltage or current to the coil.
- Solution: Verify the power supply voltage and ensure it matches the relay's coil voltage (5V DC). Check for loose connections.
Contacts Not Conducting:
- Cause: Load exceeds the relay's contact rating.
- Solution: Ensure the load current and voltage are within the specified limits (10A at 250V AC or 30V DC).
Coil Overheating:
- Cause: Continuous overvoltage applied to the coil.
- Solution: Use a regulated power supply and verify the coil voltage does not exceed 5V DC.
Noise or Chattering:
- Cause: Unstable control signal or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Use a capacitor to stabilize the power supply and ensure the control signal is steady.
FAQs
Q: Can the G5 relay handle DC loads?
A: Yes, the G5 relay can handle DC loads up to 10A at 30V DC.Q: Is the G5 relay suitable for high-frequency switching?
A: No, the G5 is not designed for high-frequency switching. It is best suited for low-frequency applications.Q: Can I use the G5 relay with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, but you will need a transistor to drive the relay, as the coil requires 5V DC to operate.Q: How do I protect the relay from voltage spikes?
A: Use a flyback diode (e.g., 1N4007) across the coil terminals to suppress voltage spikes when the relay is de-energized.