
How to Use 895 motor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
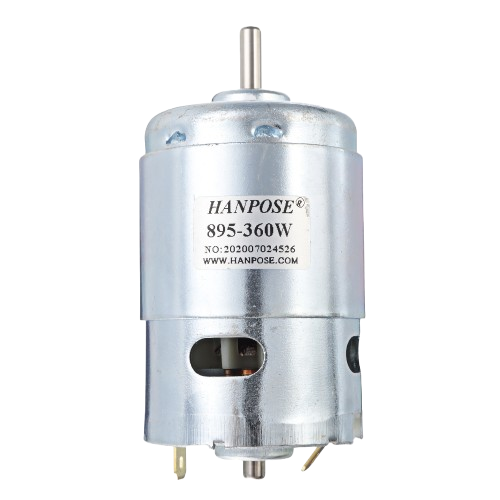

 Design with 895 motor in Cirkit Designer
Design with 895 motor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 895 motor is a type of brushed DC motor widely used in robotics, small machinery, and other applications requiring compact size and efficient performance. Manufactured by various companies, this motor is known for its high torque-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for tasks that demand both power and portability. Its robust design and versatility allow it to be used in a variety of projects, including electric vehicles, conveyor belts, and DIY robotics.
Explore Projects Built with 895 motor
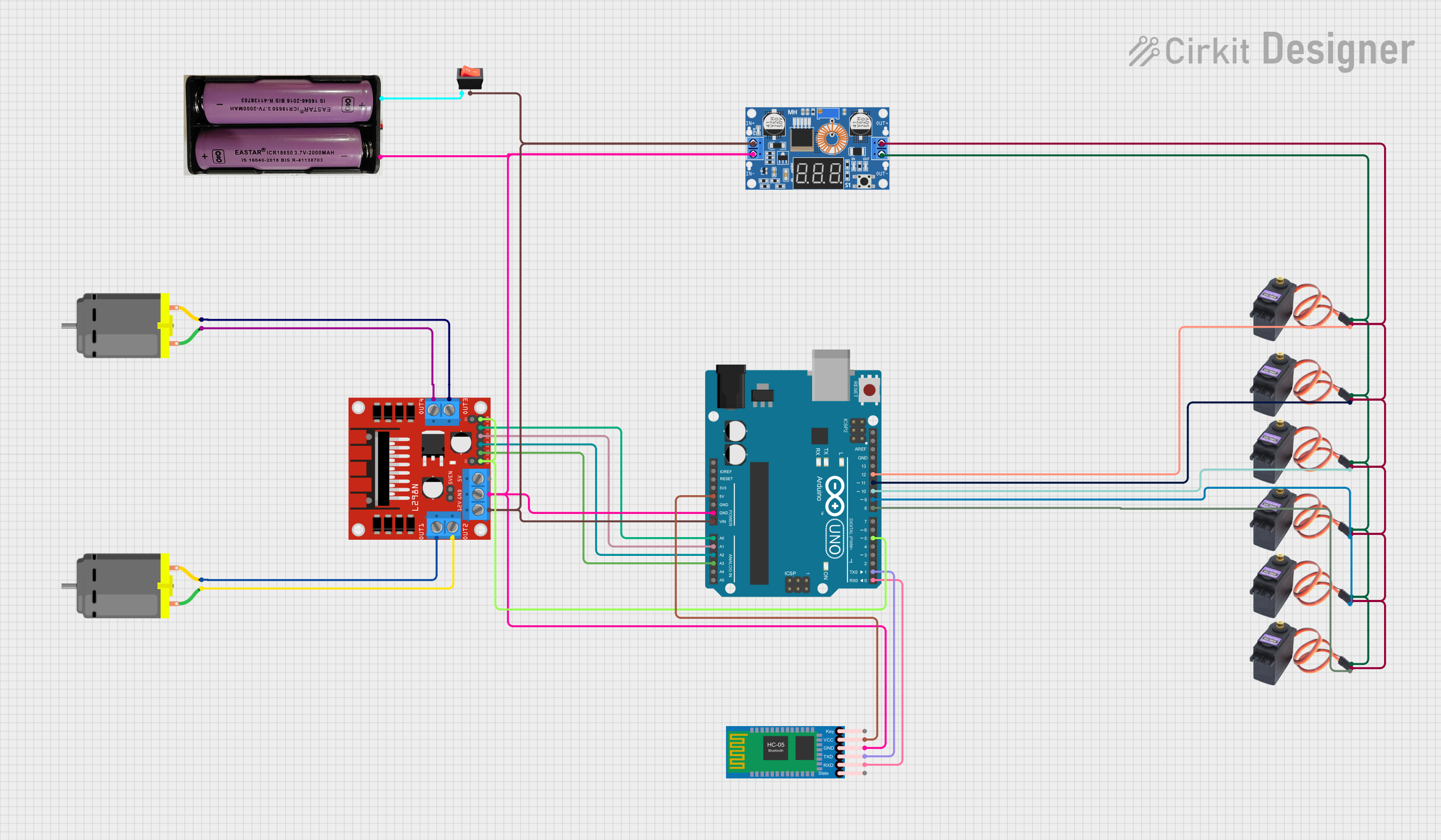
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer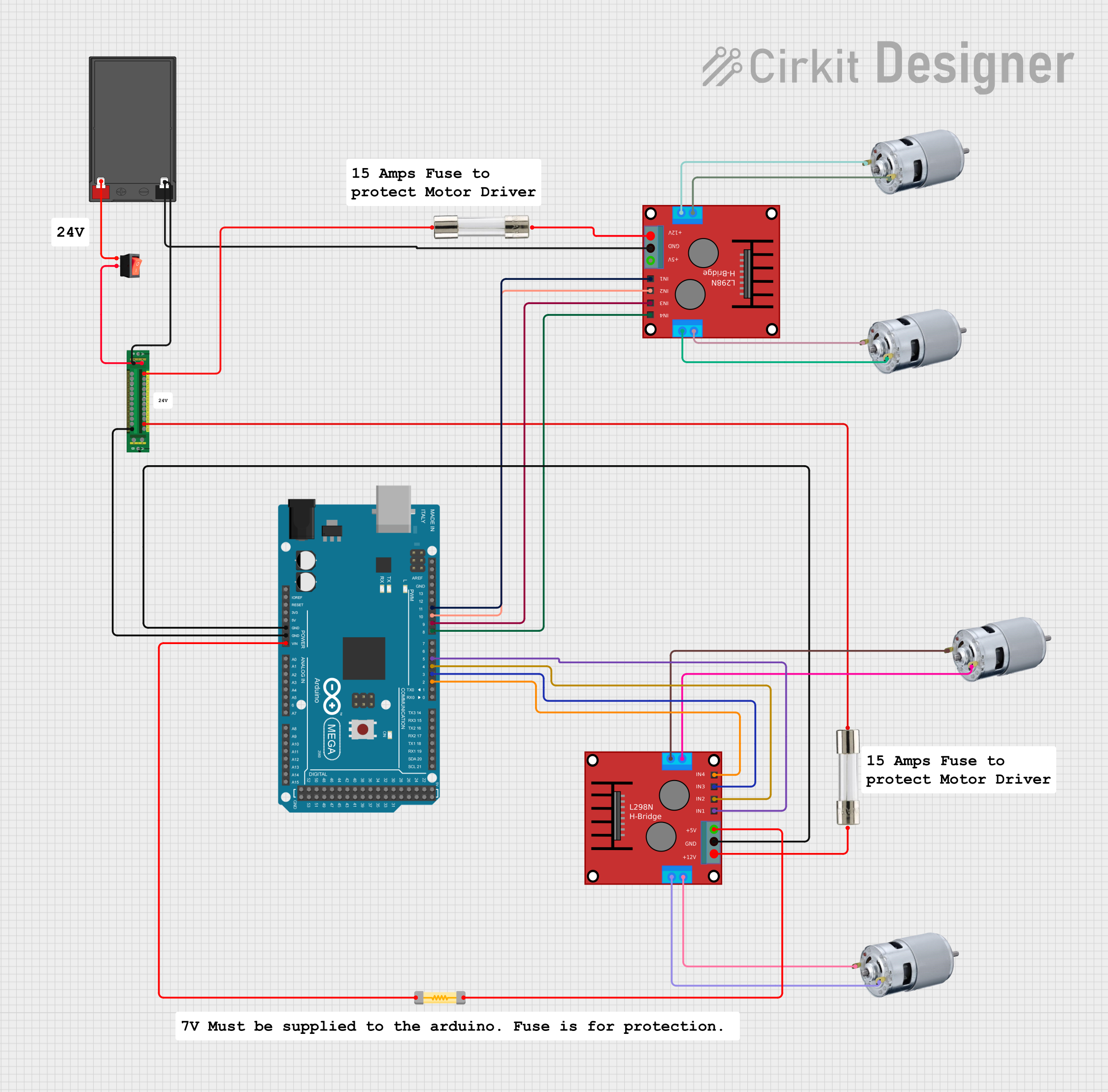
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer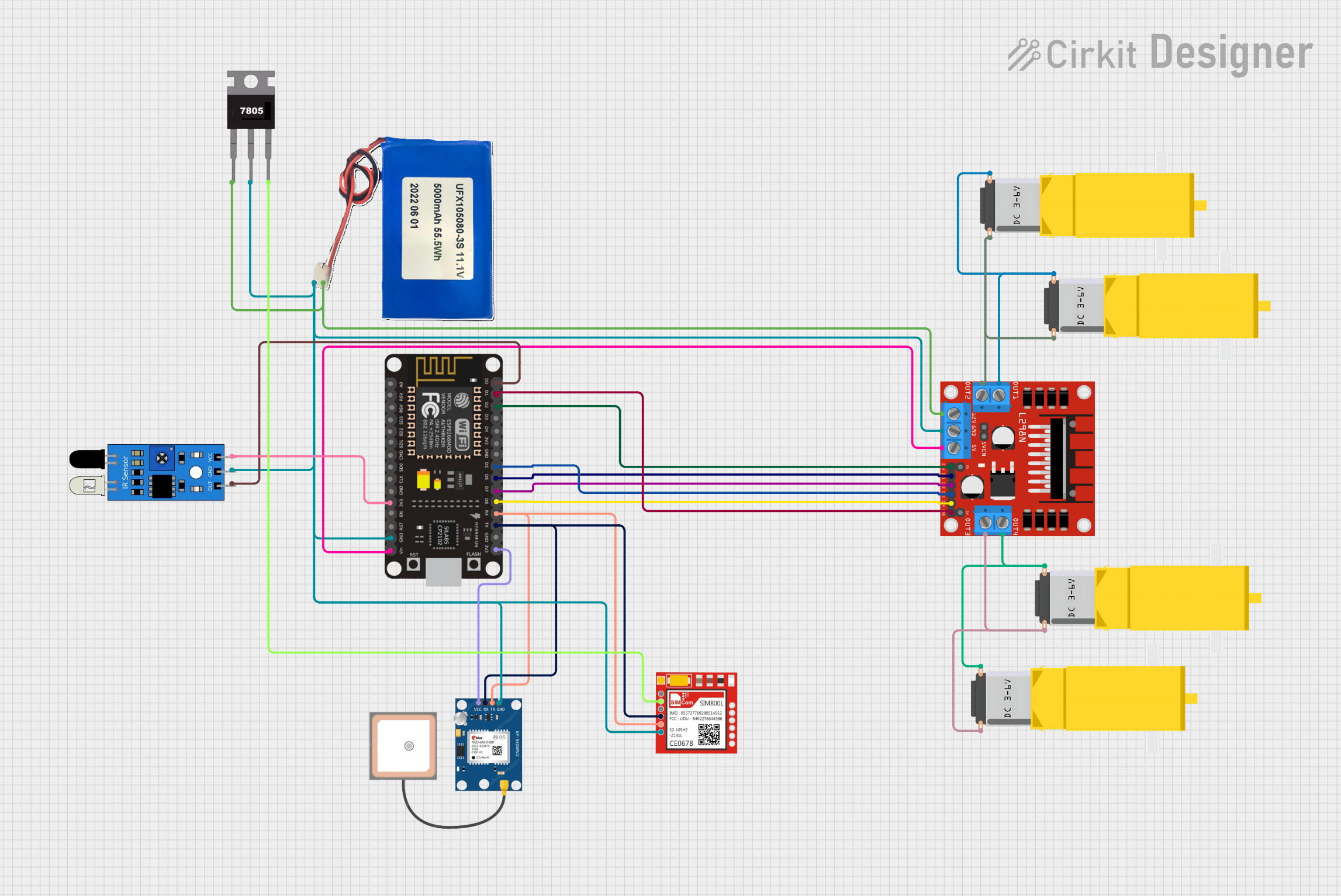
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer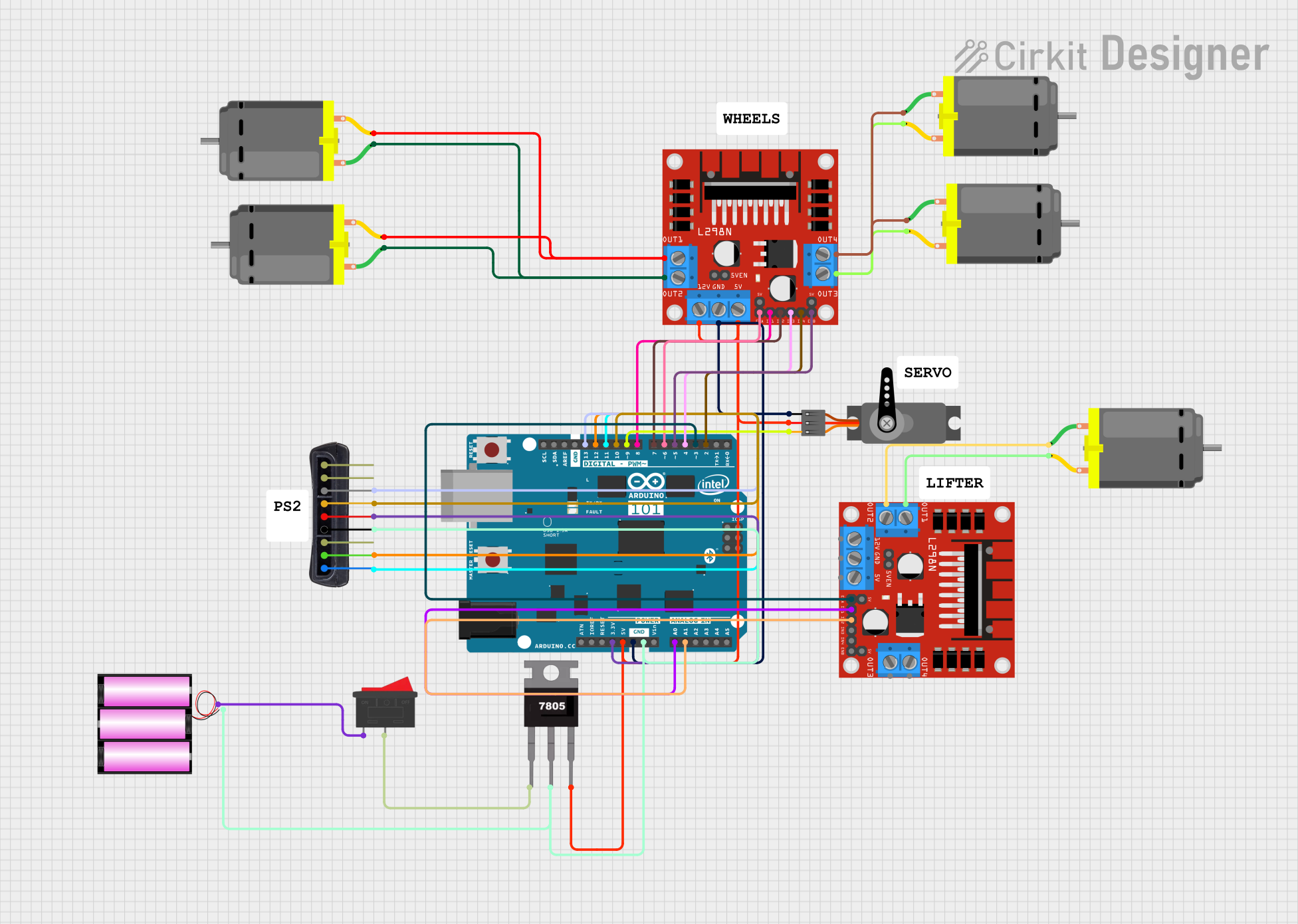
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 895 motor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Robotics (e.g., robotic arms, mobile robots)
- Electric vehicles (e.g., e-bikes, scooters)
- Small machinery (e.g., drills, saws, and pumps)
- Conveyor systems
- DIY projects and hobbyist applications
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for the 895 motor:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer Part ID | 895 |
| Motor Type | Brushed DC Motor |
| Operating Voltage | 6V to 24V |
| Rated Voltage | 12V |
| No-Load Speed | ~3000 to 12000 RPM (varies by model) |
| Stall Torque | ~1.5 Nm (varies by model) |
| Rated Current | ~1.5A to 3A |
| Stall Current | ~10A |
| Shaft Diameter | 5 mm |
| Motor Dimensions | ~68 mm (length) x 38 mm (diameter) |
| Weight | ~300 g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 895 motor typically has two terminals for electrical connections:
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| + | Positive terminal (connect to Vcc) |
| - | Negative terminal (connect to GND) |
Note: The polarity of the connections determines the direction of rotation. Reversing the polarity will reverse the motor's rotation.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 895 Motor in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Ensure the motor is powered within its operating voltage range (6V to 24V). A 12V DC power supply is commonly used.
- Motor Driver: Use a motor driver (e.g., L298N, BTS7960) to control the motor. Directly connecting the motor to a microcontroller is not recommended due to high current requirements.
- Connections:
- Connect the motor terminals to the output pins of the motor driver.
- Connect the motor driver to the power supply and control pins to the microcontroller.
- Control: Use Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signals from the microcontroller to control the motor's speed and direction.
Important Considerations
- Heat Dissipation: The motor can generate significant heat during operation. Use a heat sink or cooling fan if necessary.
- Current Limiting: Ensure the power supply and motor driver can handle the motor's stall current to avoid damage.
- Load Matching: Avoid overloading the motor to prevent overheating or reduced lifespan.
- Polarity: Double-check the polarity of connections to avoid reverse rotation or damage.
Example: Controlling the 895 Motor with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control the 895 motor using an Arduino UNO and an L298N motor driver:
// Example: Controlling an 895 motor with Arduino UNO and L298N motor driver
// Define motor driver pins
const int ENA = 9; // PWM pin for speed control
const int IN1 = 8; // Direction control pin 1
const int IN2 = 7; // Direction control pin 2
void setup() {
// Set motor driver pins as outputs
pinMode(ENA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN2, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Rotate motor in forward direction
digitalWrite(IN1, HIGH); // Set IN1 HIGH
digitalWrite(IN2, LOW); // Set IN2 LOW
analogWrite(ENA, 150); // Set speed (0-255)
delay(3000); // Run motor for 3 seconds
// Rotate motor in reverse direction
digitalWrite(IN1, LOW); // Set IN1 LOW
digitalWrite(IN2, HIGH); // Set IN2 HIGH
analogWrite(ENA, 150); // Set speed (0-255)
delay(3000); // Run motor for 3 seconds
// Stop the motor
digitalWrite(IN1, LOW); // Set IN1 LOW
digitalWrite(IN2, LOW); // Set IN2 LOW
analogWrite(ENA, 0); // Set speed to 0
delay(3000); // Wait for 3 seconds before repeating
}
Note: Adjust the analogWrite value to control the motor speed. A value of 0 stops the motor, while 255 runs it at full speed.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Does Not Spin:
- Check the power supply voltage and ensure it is within the operating range.
- Verify the motor driver connections and ensure the control signals are correct.
- Inspect the motor terminals for loose or damaged connections.
Motor Overheats:
- Ensure the motor is not overloaded or stalled.
- Use a heat sink or cooling fan to dissipate heat.
- Verify that the power supply and motor driver can handle the motor's current requirements.
Motor Spins in the Wrong Direction:
- Reverse the polarity of the motor terminals.
- Adjust the control signals from the microcontroller.
Motor Vibrates but Does Not Rotate:
- Check for mechanical obstructions or excessive load on the motor shaft.
- Ensure the motor driver is functioning correctly and providing sufficient current.
FAQs
Q: Can the 895 motor be powered directly by a battery?
A: Yes, the motor can be powered directly by a battery within its operating voltage range. However, using a motor driver is recommended for better control and protection.
Q: What is the maximum load the 895 motor can handle?
A: The maximum load depends on the specific model and operating conditions. Refer to the stall torque specification (~1.5 Nm) and avoid exceeding it to prevent damage.
Q: Can the 895 motor be used for continuous operation?
A: Yes, but ensure proper cooling and avoid overloading to prevent overheating during continuous operation.
Q: How do I reduce motor noise?
A: Use capacitors (e.g., 0.1 µF) across the motor terminals to suppress electrical noise. Additionally, ensure the motor is mounted securely to reduce mechanical vibrations.