
How to Use RS-485 Breakout Board for XIAO: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
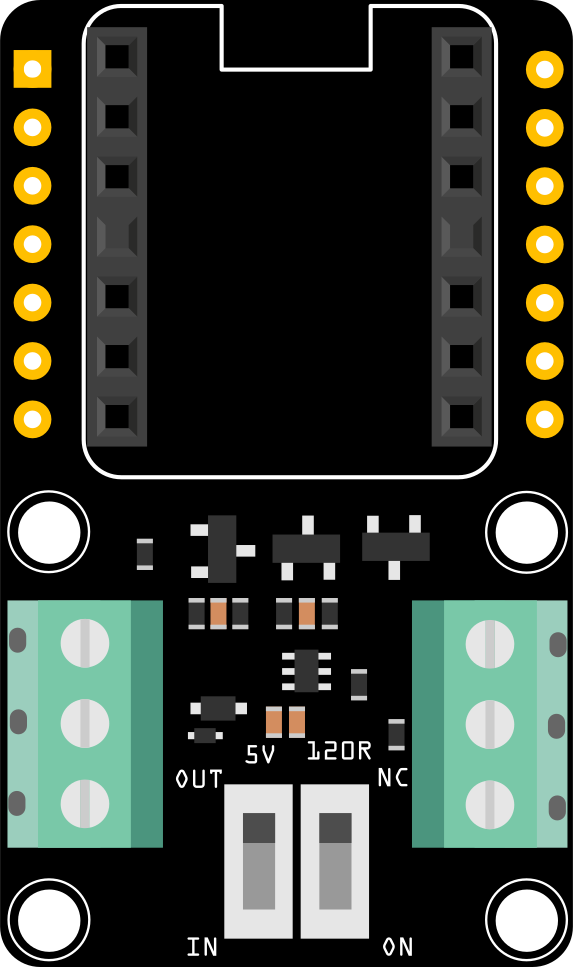
 Design with RS-485 Breakout Board for XIAO in Cirkit Designer
Design with RS-485 Breakout Board for XIAO in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The RS-485 Breakout Board for XIAO is a compact and efficient module designed to enable RS-485 communication for the Seeed Studio XIAO microcontroller series. RS-485 is a robust communication standard that supports long-distance, high-speed, and reliable data transmission using differential signaling. This breakout board simplifies the integration of RS-485 communication into your projects, making it ideal for industrial automation, IoT applications, and other scenarios requiring noise-resistant data transfer over extended distances.
Explore Projects Built with RS-485 Breakout Board for XIAO
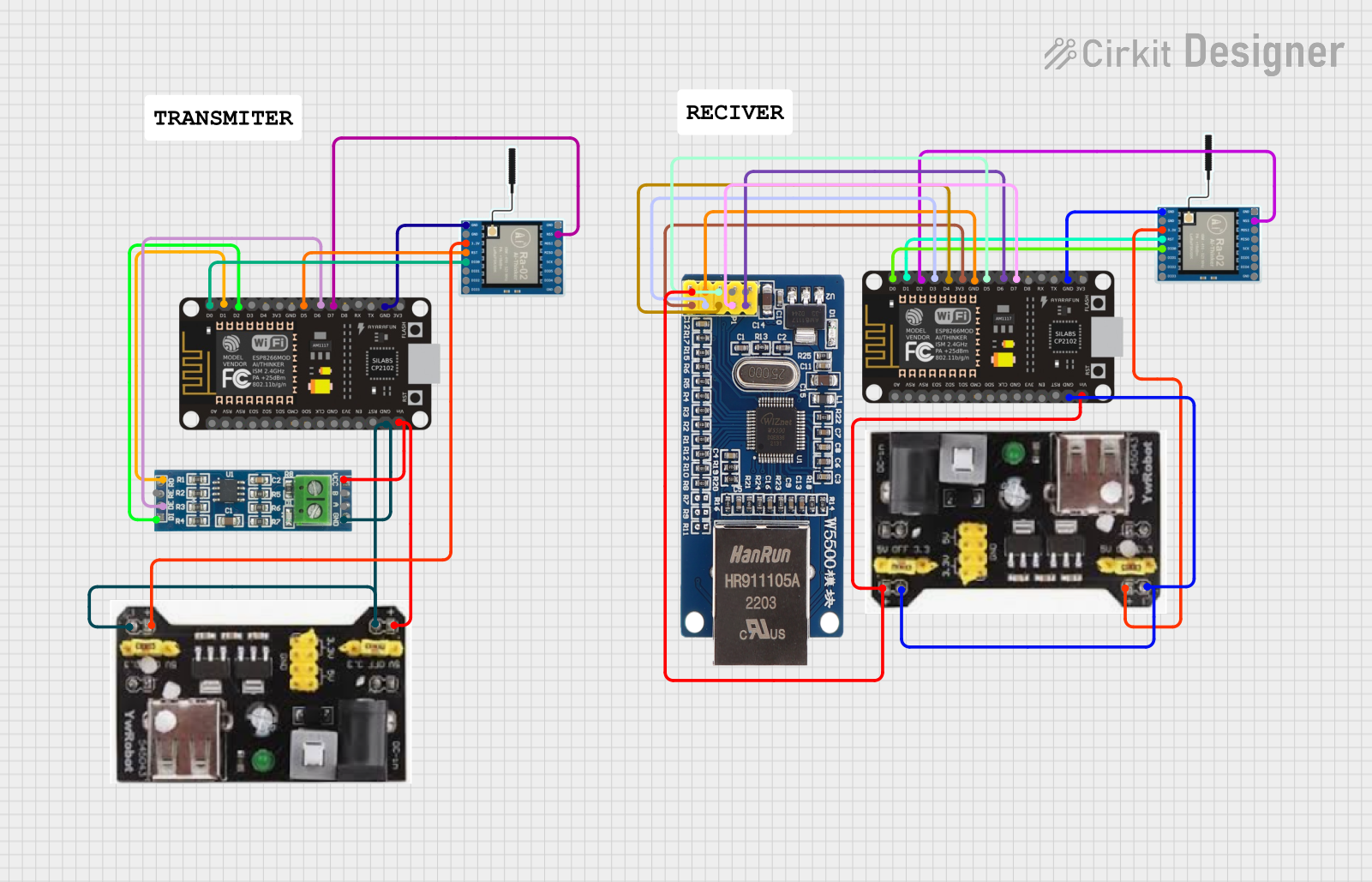
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer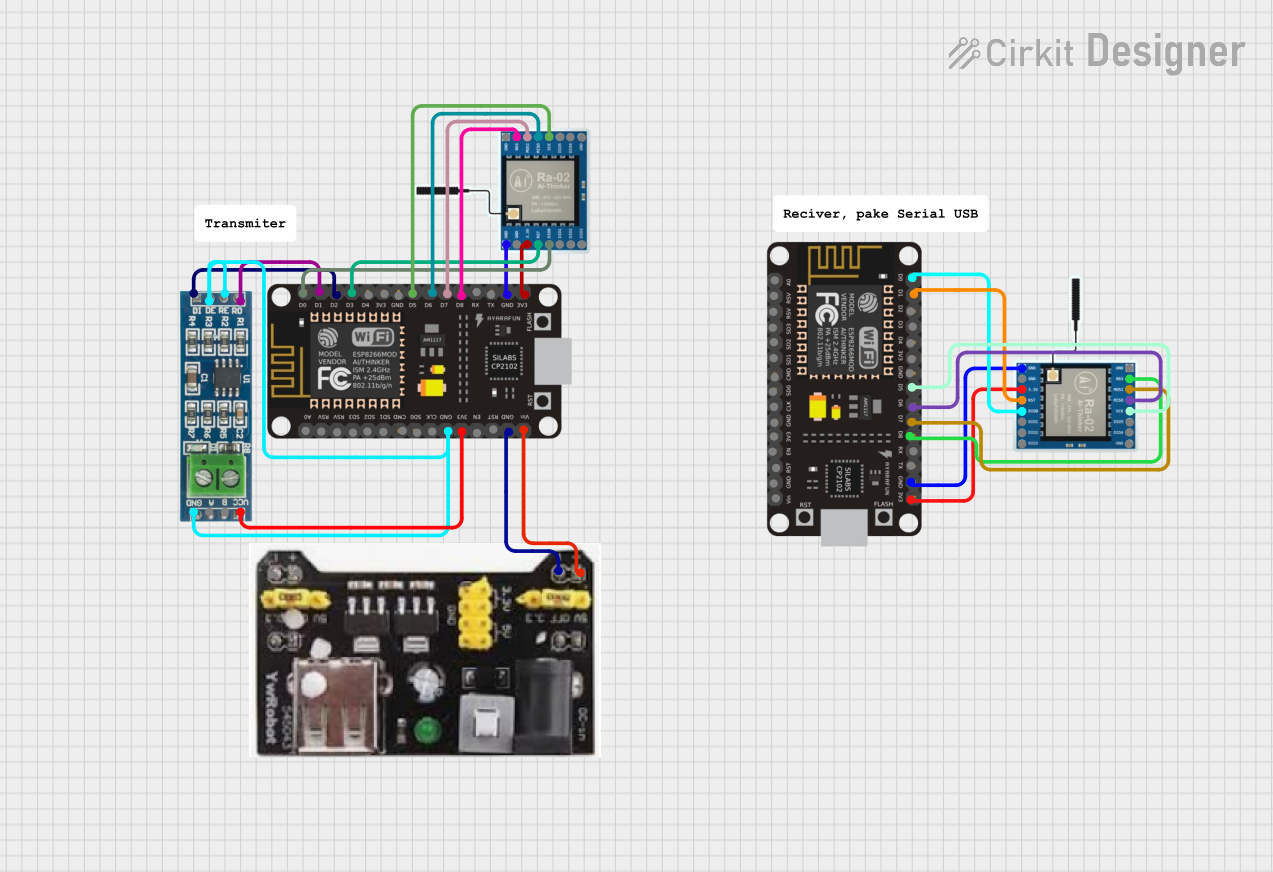
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer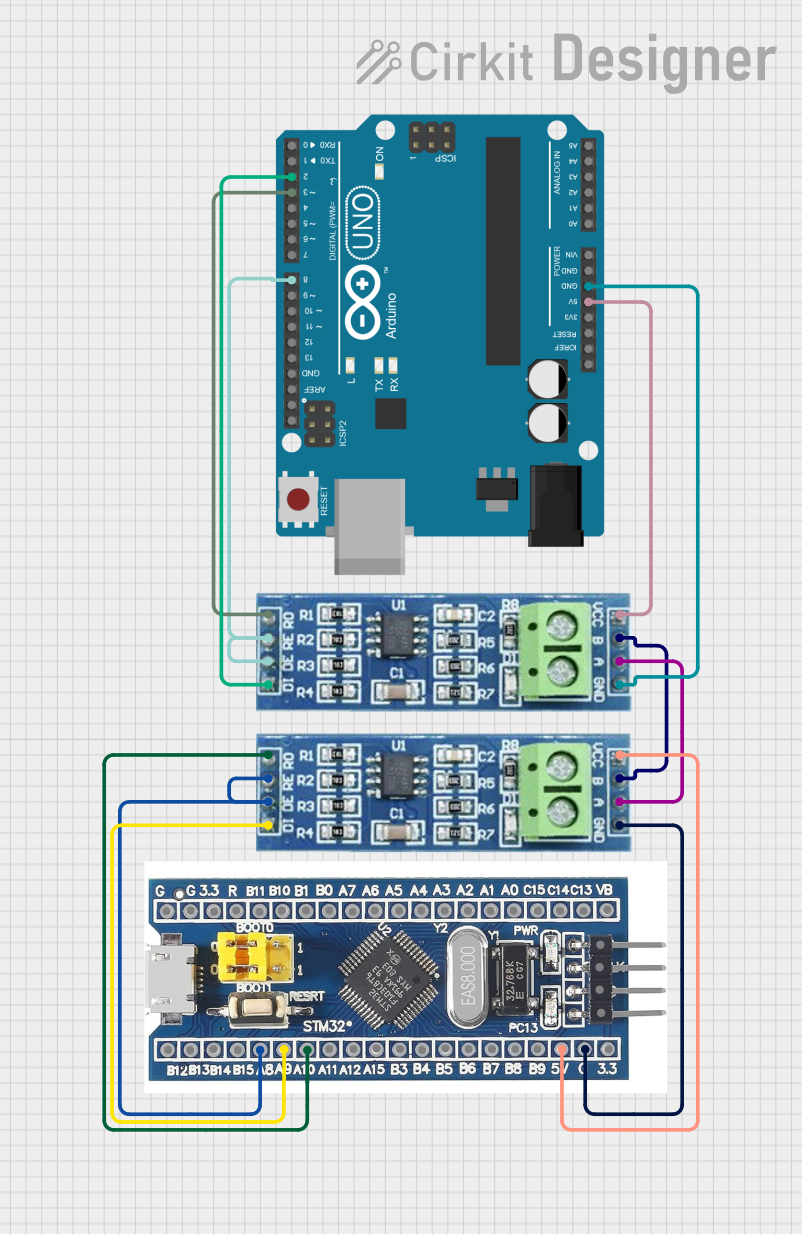
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with RS-485 Breakout Board for XIAO

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Industrial automation and control systems
- IoT networks with long-distance communication
- Building management systems (e.g., HVAC, lighting control)
- Robotics and sensor networks
- Data acquisition systems
Technical Specifications
The RS-485 Breakout Board for XIAO is designed to work seamlessly with the XIAO microcontroller series. Below are the key technical details:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Communication Standard | RS-485 |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V / 5V (XIAO compatible) |
| Data Transmission Rate | Up to 10 Mbps |
| Communication Distance | Up to 1200 meters (4000 feet) |
| Connector Type | Screw terminals for RS-485 |
| Dimensions | Compact, XIAO-compatible size |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The breakout board connects directly to the XIAO microcontroller and provides screw terminals for RS-485 communication. Below is the pin configuration:
XIAO Pinout
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power input (3.3V or 5V) |
| GND | Ground |
| TX | Transmit data (connected to DI pin) |
| RX | Receive data (connected to RO pin) |
RS-485 Screw Terminal Pinout
| Terminal Name | Description |
|---|---|
| A (D+) | Non-inverting RS-485 signal (Data+) |
| B (D-) | Inverting RS-485 signal (Data-) |
| GND | Ground |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power the Board: Connect the VCC and GND pins of the breakout board to the corresponding pins on the XIAO microcontroller.
- Connect RS-485 Terminals: Use the screw terminals to connect the A (D+), B (D-), and GND lines to your RS-485 network.
- Connect TX and RX: Link the TX and RX pins of the XIAO to the DI (Driver Input) and RO (Receiver Output) pins of the RS-485 transceiver on the breakout board.
- Termination Resistor: If the breakout board is at the end of the RS-485 bus, ensure a 120-ohm termination resistor is connected between A (D+) and B (D-).
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Compatibility: Ensure the XIAO microcontroller and the breakout board share the same operating voltage (3.3V or 5V).
- Bus Topology: RS-485 requires a daisy-chain topology with termination resistors at both ends of the bus.
- Signal Integrity: Use twisted-pair cables for the A (D+) and B (D-) lines to minimize noise and signal degradation.
- Grounding: Ensure all devices on the RS-485 network share a common ground to avoid communication issues.
Example Code for Arduino UNO (with XIAO)
Below is an example of how to use the RS-485 Breakout Board for XIAO with the Arduino IDE. This code demonstrates basic RS-485 communication.
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define RS-485 pins
#define RS485_TX_PIN 1 // XIAO TX pin connected to DI
#define RS485_RX_PIN 0 // XIAO RX pin connected to RO
// Create a SoftwareSerial object for RS-485 communication
SoftwareSerial RS485Serial(RS485_RX_PIN, RS485_TX_PIN);
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication
Serial.begin(9600); // For debugging via USB
RS485Serial.begin(9600); // RS-485 communication baud rate
Serial.println("RS-485 Communication Initialized");
}
void loop() {
// Send data over RS-485
RS485Serial.println("Hello, RS-485!");
// Check for incoming data
if (RS485Serial.available()) {
String receivedData = RS485Serial.readString();
Serial.print("Received: ");
Serial.println(receivedData);
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before sending the next message
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
No Communication on RS-485 Bus:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or missing termination resistors.
- Solution: Verify the connections and ensure 120-ohm resistors are installed at both ends of the RS-485 bus.
Data Corruption or Noise:
- Cause: Long cable runs or improper grounding.
- Solution: Use twisted-pair cables and ensure all devices share a common ground.
XIAO Not Responding:
- Cause: Incorrect pin connections or mismatched baud rates.
- Solution: Double-check the TX and RX connections and ensure the baud rate in the code matches the RS-485 network.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Use a multimeter to check continuity and voltage levels on the RS-485 lines.
- Test the breakout board with a shorter cable to rule out signal degradation over long distances.
- If using multiple devices on the RS-485 bus, ensure each device has a unique address or identifier in your communication protocol.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the RS-485 Breakout Board for XIAO into your projects and achieve reliable long-distance communication.