
How to Use Small Bulb with holder: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Small Bulb with holder in Cirkit Designer
Design with Small Bulb with holder in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A small bulb with a holder is a compact lighting component that combines a bulb (either incandescent or LED) with a holder for easy installation and electrical connection. The holder ensures secure mounting and provides terminals for connecting the bulb to a power source. These components are widely used in low-power lighting applications, such as indicator lights, decorative lighting, and small-scale DIY electronics projects.
Explore Projects Built with Small Bulb with holder

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer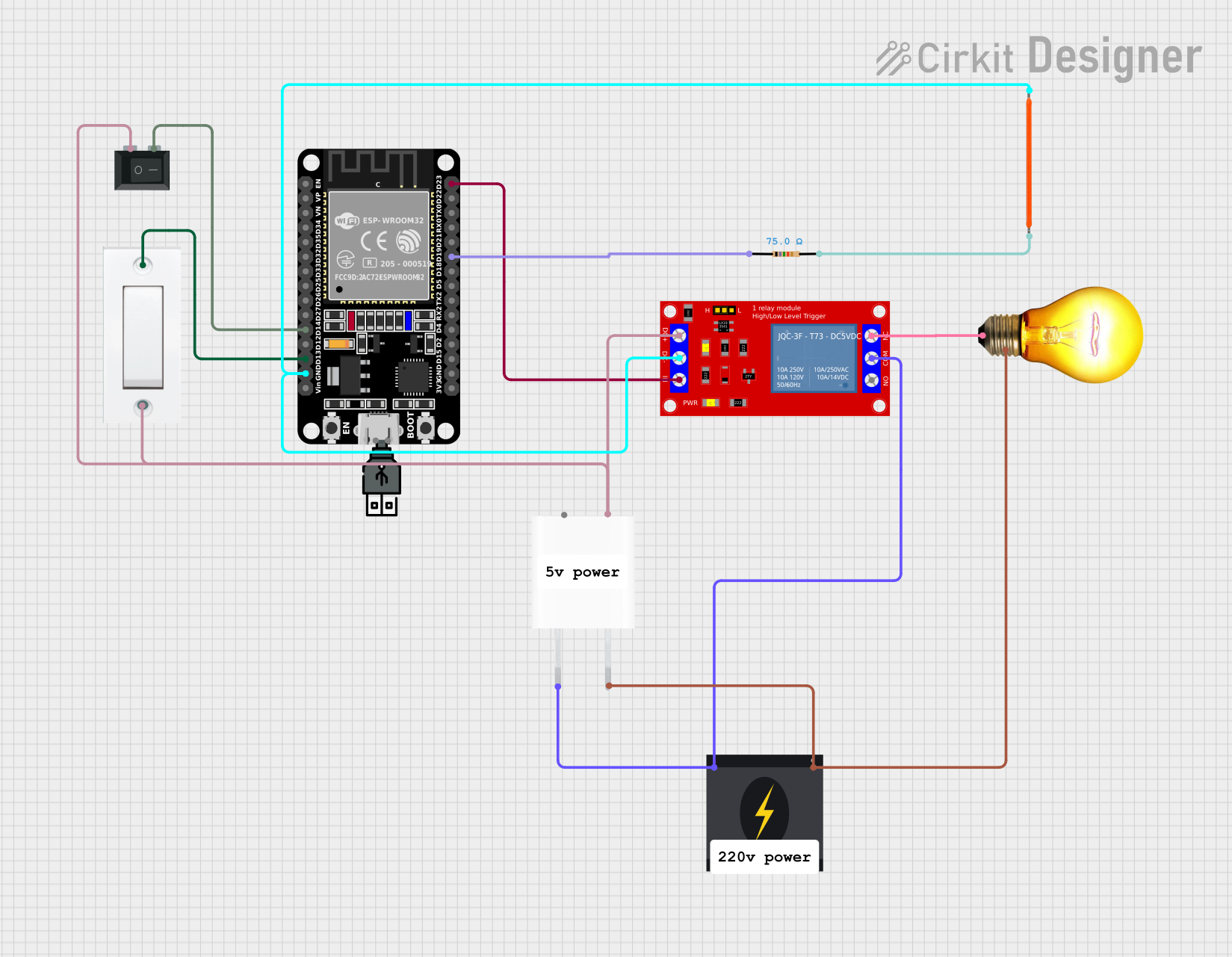
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer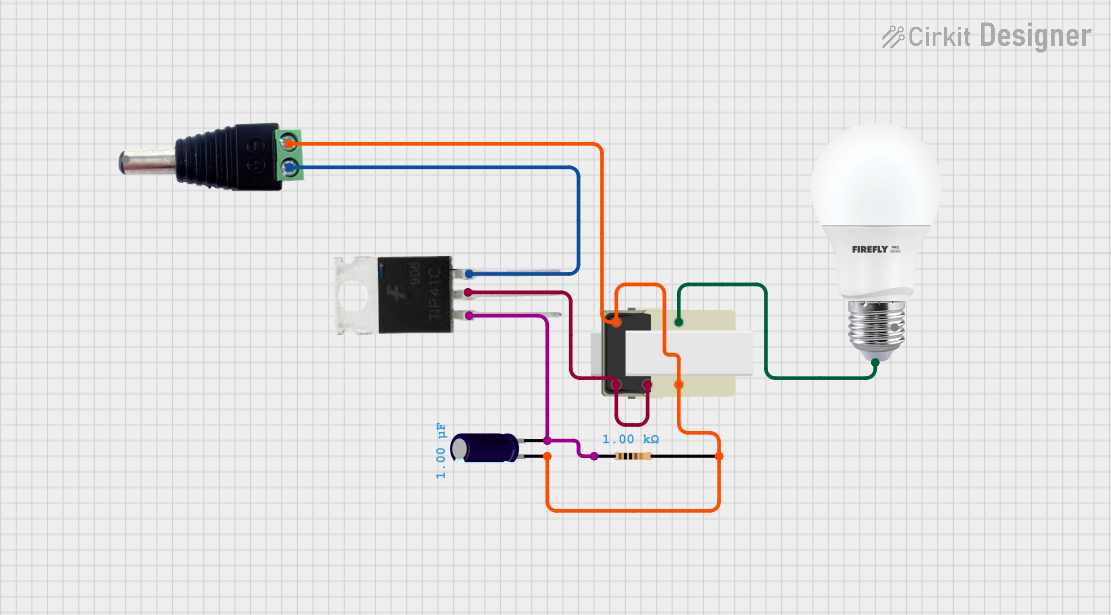
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Small Bulb with holder

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications:
- Indicator lights in control panels or appliances
- Decorative lighting in hobby projects
- Educational electronics kits
- Low-power lighting in model-making or prototypes
Technical Specifications
General Specifications:
| Parameter | Value/Range |
|---|---|
| Bulb Type | Incandescent or LED |
| Voltage Rating | 3V, 6V, 12V, or 24V (varies by model) |
| Current Rating | Typically 20mA to 100mA |
| Power Rating | 0.06W to 2.4W |
| Holder Material | Plastic or metal |
| Holder Mounting Type | Screw, clip, or panel mount |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions:
| Pin/Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive (+) | Connects to the positive terminal of the power source |
| Negative (-) | Connects to the negative terminal (ground) of the power source |
Note: The polarity is critical for LED bulbs but not for incandescent bulbs.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit:
- Identify the Voltage Rating: Check the bulb's voltage rating to ensure compatibility with your power source.
- Connect the Terminals:
- For LED bulbs, connect the positive terminal of the holder to the positive side of the power source and the negative terminal to the ground.
- For incandescent bulbs, polarity does not matter; connect the terminals to the power source.
- Secure the Holder: Mount the holder securely using screws, clips, or a panel mount, depending on the design.
- Power the Circuit: Turn on the power source to illuminate the bulb.
Important Considerations and Best Practices:
- Voltage Matching: Always use a power source that matches the bulb's voltage rating to avoid damage.
- Current Limiting for LEDs: If using an LED bulb, include a current-limiting resistor in series to prevent overcurrent. Use the formula ( R = \frac{V_{supply} - V_{LED}}{I_{LED}} ) to calculate the resistor value.
- Heat Management: Incandescent bulbs can generate heat; ensure proper ventilation to avoid overheating.
- Polarity Check: For LED bulbs, ensure correct polarity to avoid damage.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
You can use a small LED bulb with a holder as an indicator light in an Arduino project. Below is an example circuit and code:
Circuit:
- Connect the positive terminal of the bulb holder to a digital pin on the Arduino (e.g., pin 13) through a 220-ohm resistor.
- Connect the negative terminal of the bulb holder to the Arduino's GND pin.
Code:
// Small LED bulb example with Arduino UNO
// This code blinks the bulb connected to pin 13 every second.
const int bulbPin = 13; // Define the pin connected to the bulb
void setup() {
pinMode(bulbPin, OUTPUT); // Set the bulb pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(bulbPin, HIGH); // Turn the bulb ON
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(bulbPin, LOW); // Turn the bulb OFF
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues:
Bulb Does Not Light Up:
- Cause: Incorrect voltage or loose connections.
- Solution: Verify the power source voltage matches the bulb's rating and check all connections.
LED Bulb Flickers:
- Cause: Insufficient current or unstable power supply.
- Solution: Add a current-limiting resistor and ensure a stable power source.
Bulb Overheats:
- Cause: Excessive voltage or prolonged use without ventilation.
- Solution: Use the correct voltage and ensure proper ventilation.
LED Bulb Does Not Work:
- Cause: Incorrect polarity.
- Solution: Reverse the connections to the LED bulb.
FAQs:
Q: Can I use a 12V bulb with a 5V power source?
A: No, the bulb will not light up properly. Always match the bulb's voltage rating with the power source.Q: Do I need a resistor for an incandescent bulb?
A: No, resistors are not required for incandescent bulbs, but they are necessary for LED bulbs to limit current.Q: Can I use this component outdoors?
A: Only if the holder and bulb are rated for outdoor use and protected from moisture.Q: How do I calculate the resistor value for an LED bulb?
A: Use the formula ( R = \frac{V_{supply} - V_{LED}}{I_{LED}} ), where ( V_{supply} ) is the power source voltage, ( V_{LED} ) is the LED's forward voltage, and ( I_{LED} ) is the LED's current rating.
This documentation provides all the necessary details to effectively use a small bulb with a holder in various applications.