
How to Use BMI270: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
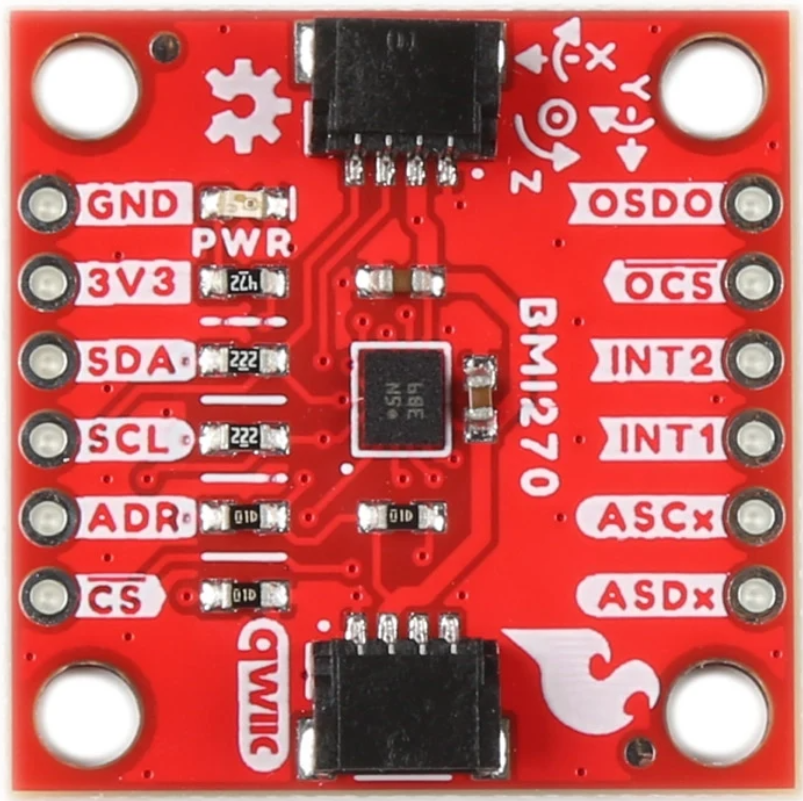
 Design with BMI270 in Cirkit Designer
Design with BMI270 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The BMI270 is a low-power, 6-axis inertial measurement unit (IMU) manufactured by Sparkfun. It integrates a 3-axis accelerometer and a 3-axis gyroscope into a single compact package. This component is designed for motion sensing applications, offering high accuracy and low power consumption. Its advanced features make it particularly suitable for wearable devices, fitness trackers, augmented reality (AR) systems, and Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
The BMI270 is equipped with intelligent power management and motion-triggered interrupt features, enabling efficient operation in battery-powered devices. It supports various communication protocols, making it easy to integrate into a wide range of systems.
Explore Projects Built with BMI270
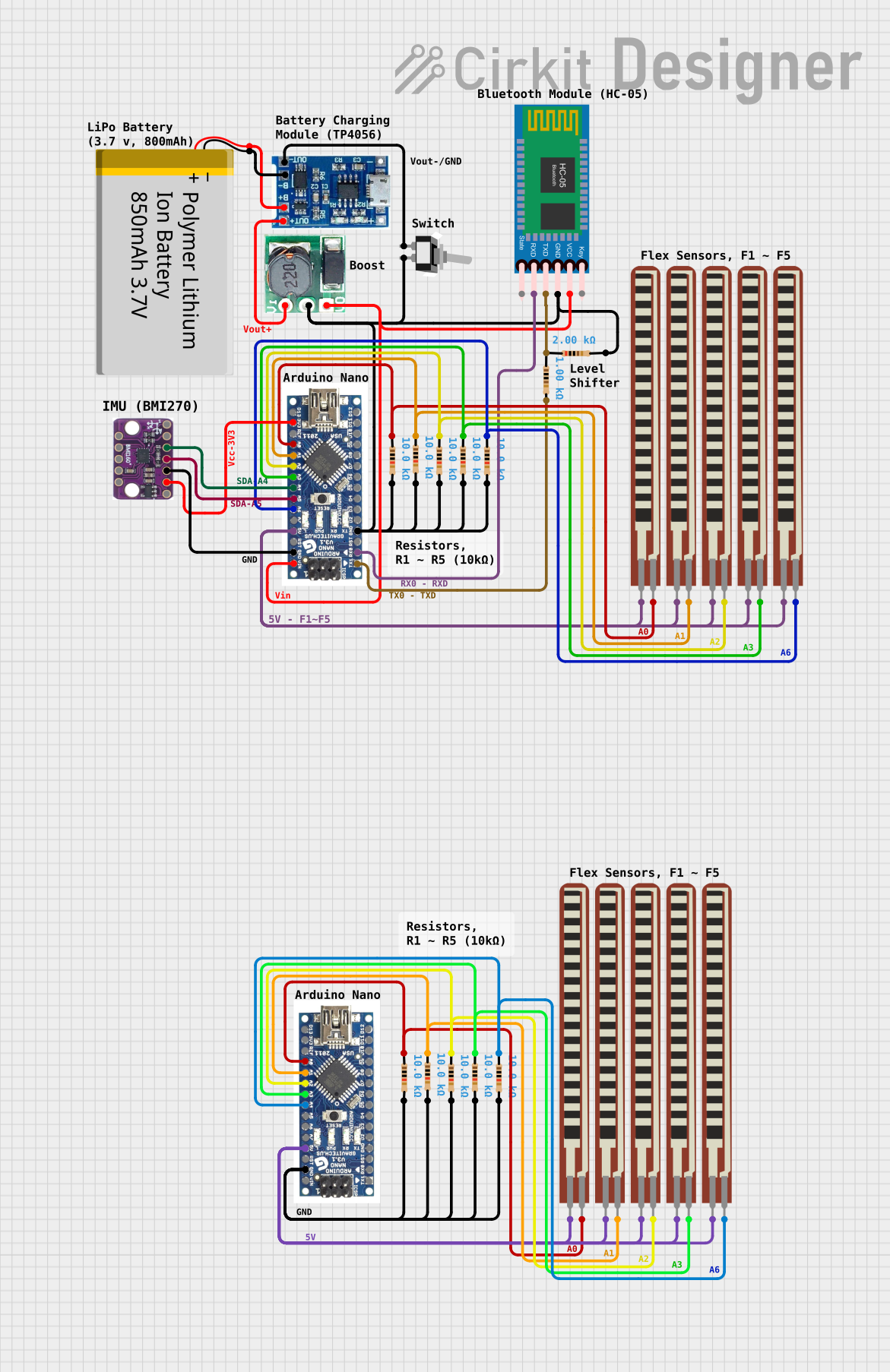
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer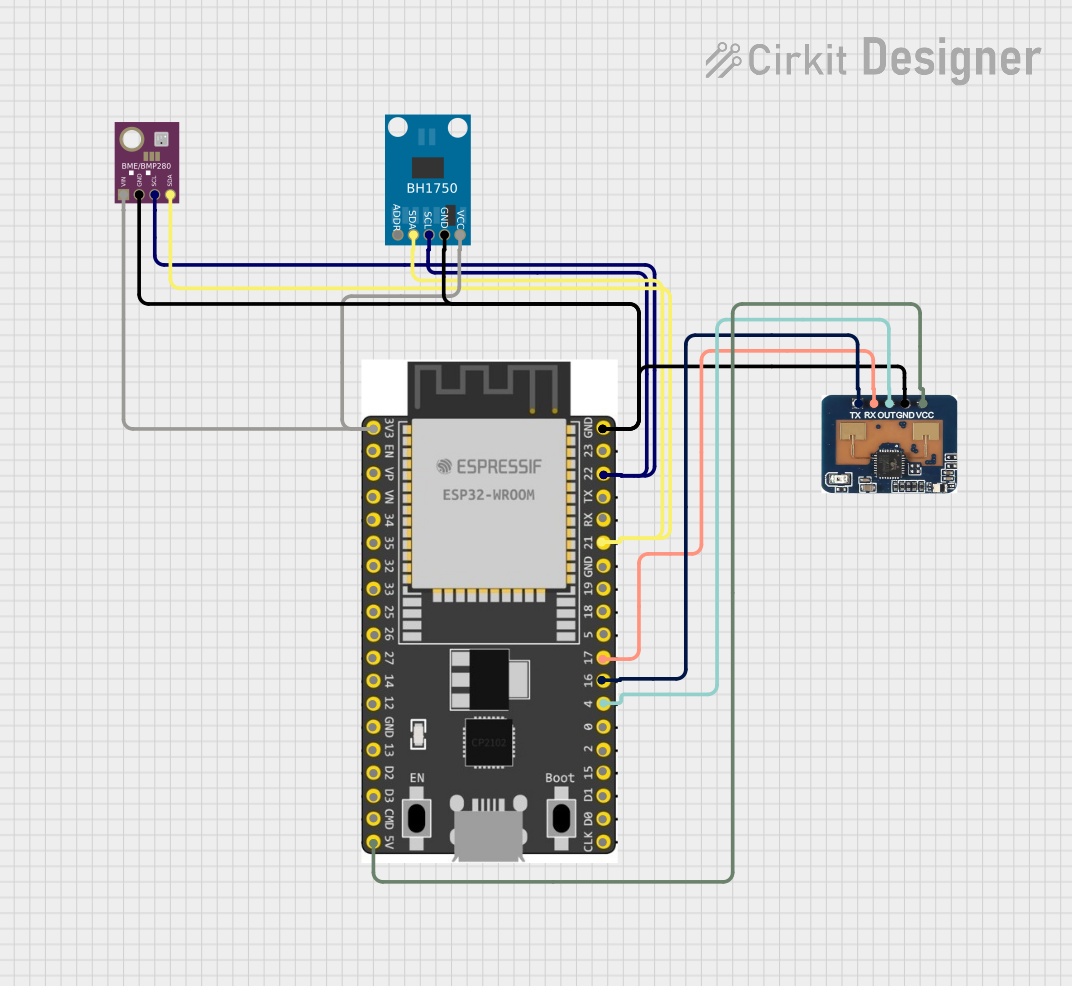
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer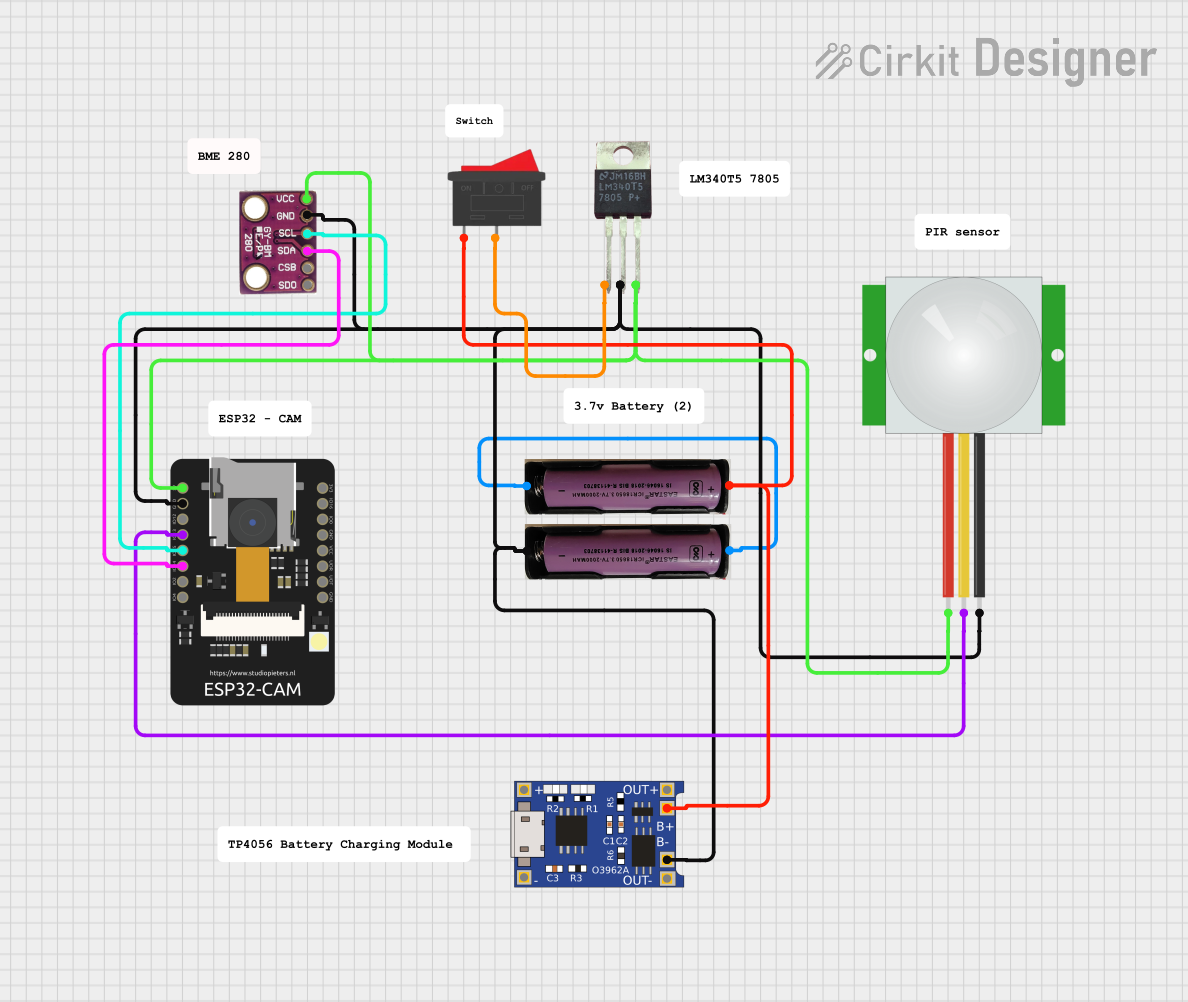
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with BMI270

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Manufacturer: Sparkfun
- Type: 6-axis IMU (3-axis accelerometer + 3-axis gyroscope)
- Supply Voltage: 1.71V to 3.6V
- Current Consumption:
- Accelerometer: 30 µA (typical)
- Gyroscope: 800 µA (typical)
- Measurement Range:
- Accelerometer: ±2g, ±4g, ±8g, ±16g
- Gyroscope: ±125°/s, ±250°/s, ±500°/s, ±1000°/s, ±2000°/s
- Communication Interfaces: I²C, SPI
- Operating Temperature: -40°C to +85°C
- Package: LGA-16 (2.5mm x 3.0mm x 0.8mm)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The BMI270 comes in an LGA-16 package with the following pinout:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VDD | Power supply (1.71V to 3.6V) |
| 2 | VDDIO | I/O voltage supply |
| 3 | GND | Ground |
| 4 | CS | Chip select for SPI (active low) |
| 5 | SDO/SA0 | SPI data out / I²C address selection |
| 6 | SCL/SCK | I²C clock / SPI clock |
| 7 | SDA/SDI | I²C data / SPI data in |
| 8 | INT1 | Interrupt 1 output |
| 9 | INT2 | Interrupt 2 output |
| 10-16 | NC | Not connected (leave floating) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the BMI270 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VDD pin to a 1.8V to 3.3V power source and the GND pin to ground. Ensure the VDDIO pin is connected to the same voltage level as the microcontroller's I/O voltage.
- Communication Interface:
- For I²C: Connect the SCL and SDA pins to the corresponding I²C pins on the microcontroller. Use pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ) on both lines.
- For SPI: Connect the SCK, SDI, and CS pins to the corresponding SPI pins on the microcontroller. The SDO pin can be used for data output.
- Interrupts: If required, connect the INT1 and/or INT2 pins to the microcontroller for motion-triggered interrupts.
- Bypass Unused Pins: Leave the NC pins floating as they are not connected internally.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Use decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1µF) close to the VDD and VDDIO pins to reduce noise.
- Ensure proper PCB layout to minimize noise and interference, especially for high-speed SPI communication.
- Configure the BMI270's accelerometer and gyroscope ranges based on the application's requirements to optimize accuracy and power consumption.
- Use the BMI270's built-in motion detection features to reduce the need for continuous polling, saving power in battery-operated devices.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to interface the BMI270 with an Arduino UNO using the I²C protocol:
#include <Wire.h> // Include the Wire library for I²C communication
#define BMI270_I2C_ADDRESS 0x68 // Default I²C address of the BMI270
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I²C communication
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
// Configure the BMI270
Wire.beginTransmission(BMI270_I2C_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x7E); // Register address for command register
Wire.write(0x11); // Command to initialize accelerometer and gyroscope
Wire.endTransmission();
Serial.println("BMI270 initialized.");
}
void loop() {
// Read accelerometer data
Wire.beginTransmission(BMI270_I2C_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x12); // Register address for accelerometer data
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(BMI270_I2C_ADDRESS, 6); // Request 6 bytes (X, Y, Z)
if (Wire.available() == 6) {
int16_t accelX = (Wire.read() | (Wire.read() << 8));
int16_t accelY = (Wire.read() | (Wire.read() << 8));
int16_t accelZ = (Wire.read() | (Wire.read() << 8));
Serial.print("Accel X: "); Serial.print(accelX);
Serial.print(" Y: "); Serial.print(accelY);
Serial.print(" Z: "); Serial.println(accelZ);
}
delay(500); // Delay for readability
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Communication with the BMI270:
- Ensure the correct I²C address (default: 0x68) is being used.
- Check the wiring for loose or incorrect connections.
- Verify that pull-up resistors are present on the I²C lines.
Incorrect or No Data Output:
- Confirm that the BMI270 is properly initialized by writing the correct configuration commands.
- Check the power supply voltage and ensure it is within the specified range.
- Verify that the accelerometer and gyroscope ranges are configured correctly.
High Noise in Measurements:
- Ensure proper PCB layout to minimize noise.
- Use filtering techniques in software to smooth the data.
FAQs
Q: Can the BMI270 operate in low-power mode?
A: Yes, the BMI270 has intelligent power management features, including low-power and suspend modes, to conserve energy.Q: What is the maximum sampling rate of the BMI270?
A: The BMI270 supports a maximum output data rate (ODR) of 1600 Hz for the accelerometer and 3200 Hz for the gyroscope.Q: Can the BMI270 detect free-fall or tap events?
A: Yes, the BMI270 includes built-in motion detection features, such as free-fall, tap, and step detection.
By following this documentation, users can effectively integrate the BMI270 into their projects and troubleshoot common issues.