
How to Use SPI-Display 1.8 128X160: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with SPI-Display 1.8 128X160 in Cirkit Designer
Design with SPI-Display 1.8 128X160 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The SPI-Display 1.8 128X160 is a compact color display module with a resolution of 128x160 pixels. It utilizes the Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) for fast and efficient communication with microcontrollers. This display is ideal for embedded projects, graphical user interfaces, and applications requiring a small, vibrant screen. Its small form factor and low power consumption make it a popular choice for hobbyists and professionals alike.
Explore Projects Built with SPI-Display 1.8 128X160
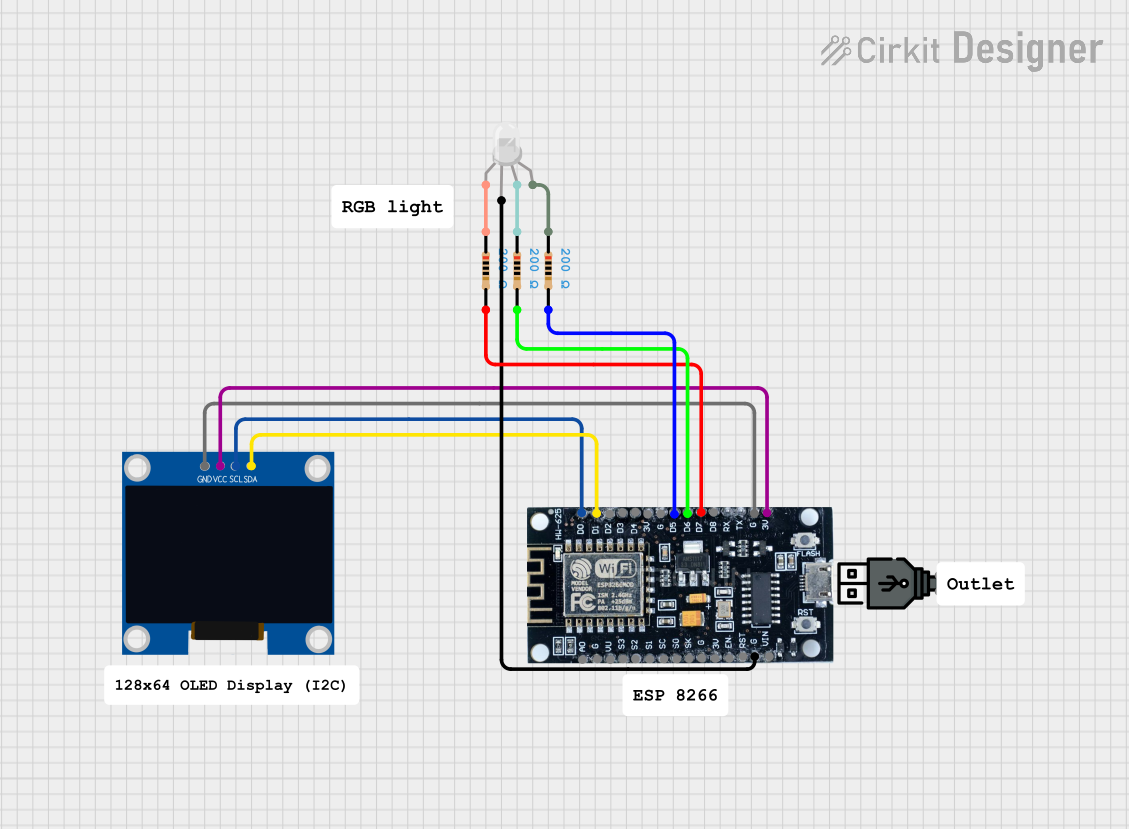
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer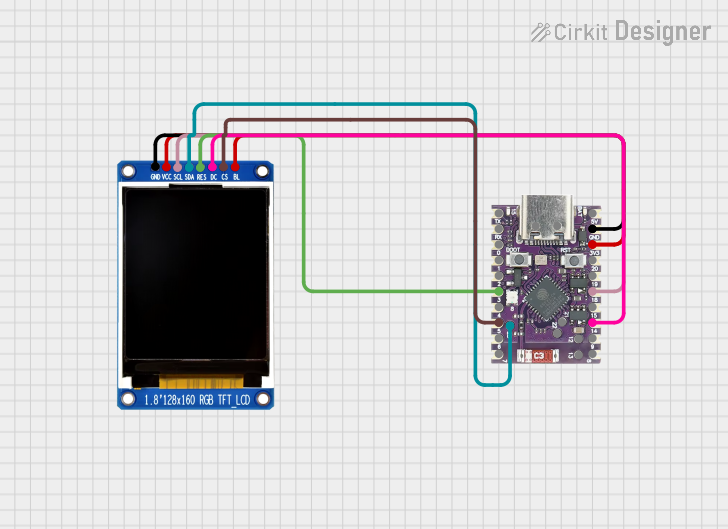
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer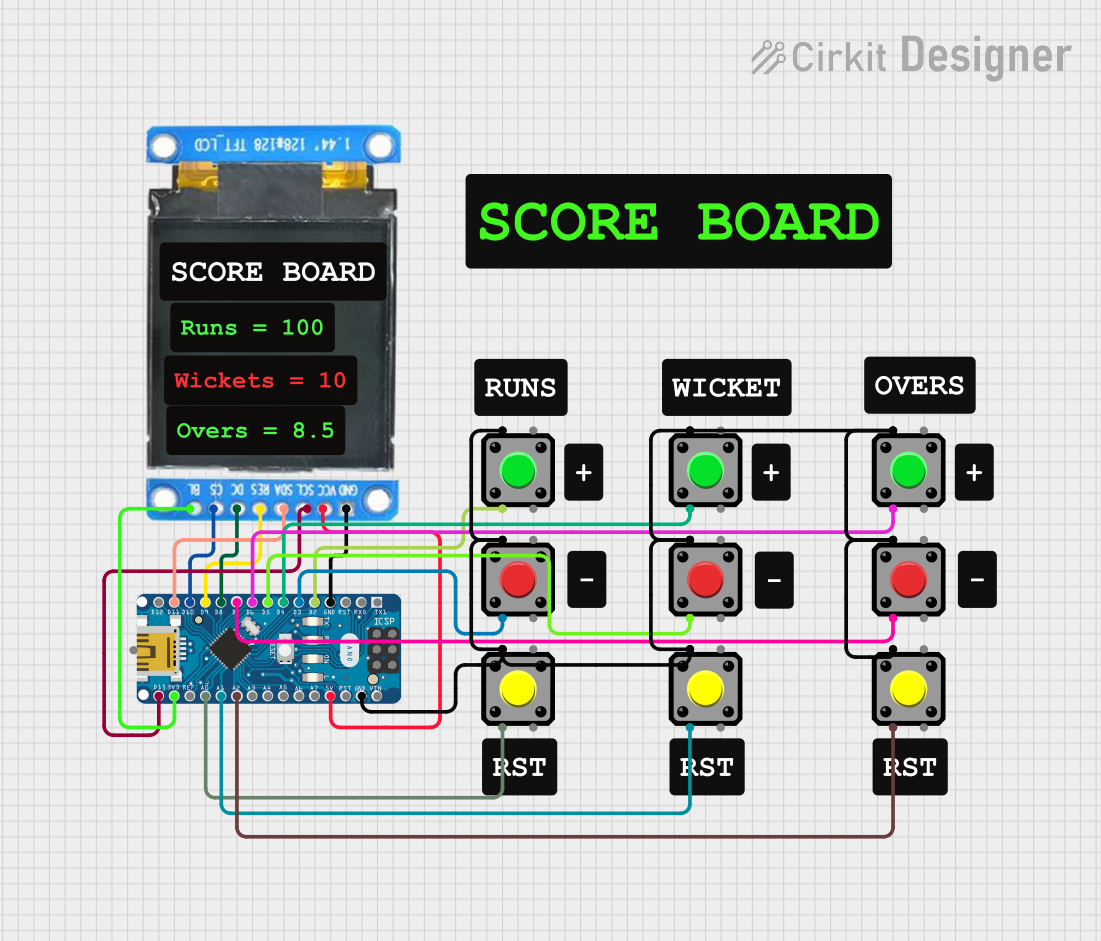
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer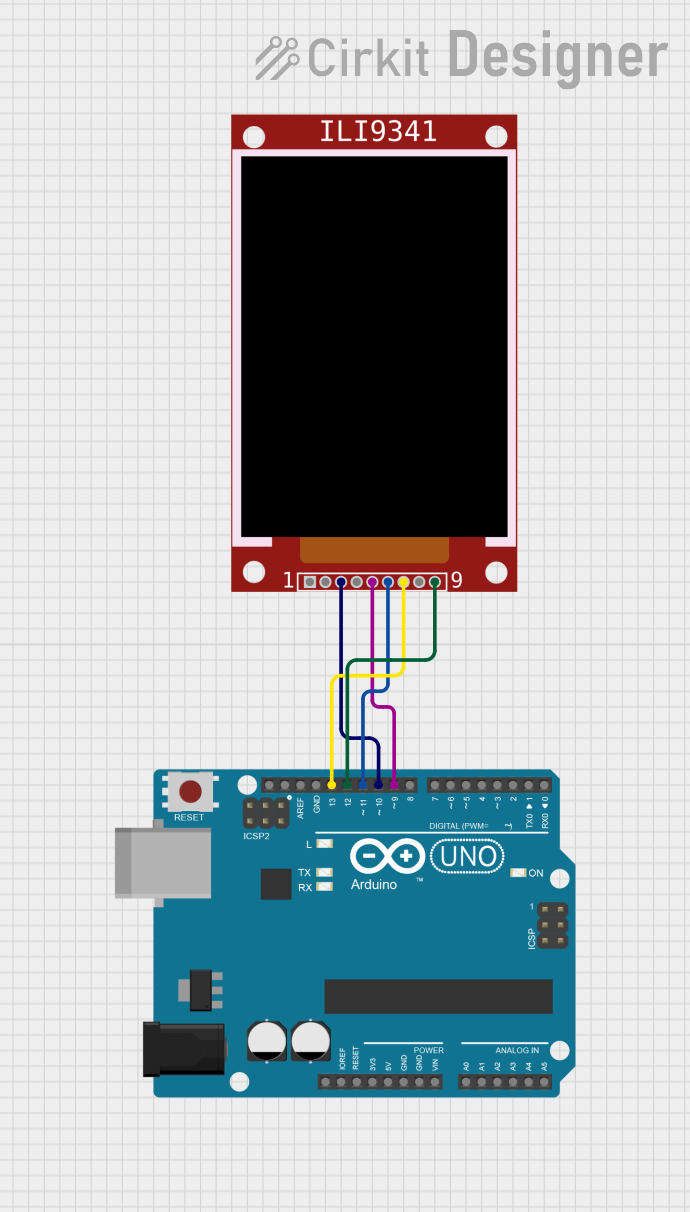
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with SPI-Display 1.8 128X160

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Wearable devices and portable electronics
- Graphical user interfaces for embedded systems
- IoT dashboards and data visualization
- Gaming devices and retro-style displays
- Educational and prototyping projects
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the SPI-Display 1.8 128X160 module:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Display Type | TFT LCD (Thin Film Transistor) |
| Resolution | 128x160 pixels |
| Communication Protocol | SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) |
| Color Depth | 18-bit (262,144 colors) |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V (logic level) |
| Backlight Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Current Consumption | ~20mA (typical) |
| Dimensions | 1.8 inches (diagonal) |
| Controller IC | ST7735 |
Pin Configuration
The SPI-Display 1.8 128X160 module typically has the following pinout:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply input (3.3V or 5V) |
| GND | Ground connection |
| SCL (CLK) | SPI clock signal |
| SDA (MOSI) | SPI data input (Master Out Slave In) |
| RES (RST) | Reset pin (active low) |
| DC (A0) | Data/Command control pin (High = Data, Low = Command) |
| CS | Chip Select (active low) |
| BLK (LED) | Backlight control (connect to 3.3V or PWM pin) |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the SPI-Display 1.8 128X160 to an Arduino UNO
To use the SPI-Display 1.8 128X160 with an Arduino UNO, follow these steps:
Wiring the Display: Connect the display module to the Arduino UNO as shown below:
Display Pin Arduino UNO Pin VCC 3.3V or 5V GND GND SCL (CLK) D13 (SCK) SDA (MOSI) D11 (MOSI) RES (RST) D8 DC (A0) D9 CS D10 BLK (LED) 3.3V or PWM pin Install Required Libraries:
- Install the Adafruit GFX Library and Adafruit ST7735 Library from the Arduino Library Manager.
Example Code: Use the following example code to display text and graphics on the screen:
// Include necessary libraries #include <Adafruit_GFX.h> // Core graphics library #include <Adafruit_ST7735.h> // ST7735 driver library #include <SPI.h> // SPI library // Define pins for the display #define TFT_CS 10 // Chip Select pin #define TFT_RST 8 // Reset pin #define TFT_DC 9 // Data/Command pin // Initialize the display object Adafruit_ST7735 tft = Adafruit_ST7735(TFT_CS, TFT_DC, TFT_RST); void setup() { // Initialize the display tft.initR(INITR_BLACKTAB); // Initialize with ST7735 settings tft.fillScreen(ST77XX_BLACK); // Clear the screen with black color // Display some text tft.setTextColor(ST77XX_WHITE); // Set text color to white tft.setTextSize(1); // Set text size to 1 tft.setCursor(0, 0); // Set cursor to top-left corner tft.println("Hello, World!"); // Print text to the screen // Draw a red rectangle tft.fillRect(10, 20, 50, 30, ST77XX_RED); } void loop() { // Nothing to do here }
Important Considerations
- Voltage Levels: Ensure the logic level of your microcontroller matches the display's requirements (3.3V). If using a 5V microcontroller, use level shifters for the SPI pins.
- Backlight Control: The backlight pin (BLK) can be connected to a PWM pin for brightness control or directly to 3.3V for full brightness.
- SPI Speed: Adjust the SPI clock speed in your code if you encounter communication issues.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Display Not Turning On:
- Verify all connections and ensure the VCC and GND pins are properly connected.
- Check if the backlight pin (BLK) is connected to 3.3V or a PWM pin.
No Output on the Screen:
- Ensure the correct pins are defined in the code for CS, DC, and RST.
- Verify that the Adafruit GFX and ST7735 libraries are installed and up to date.
Flickering or Distorted Display:
- Reduce the SPI clock speed in the code.
- Check for loose or poor connections in the wiring.
Partial or Incorrect Graphics:
- Ensure the correct initialization command (
INITR_BLACKTAB) is used in the code. - Verify that the display module is compatible with the ST7735 driver.
- Ensure the correct initialization command (
FAQs
Q: Can I use this display with a 5V microcontroller?
A: Yes, but you must use level shifters for the SPI pins to avoid damaging the display.
Q: How do I control the brightness of the backlight?
A: Connect the BLK pin to a PWM-capable pin on your microcontroller and use analogWrite() to adjust brightness.
Q: Can I display images on this screen?
A: Yes, you can display BMP images by using the Adafruit ST7735 library. Refer to the library's documentation for details.
Q: What is the maximum SPI clock speed supported?
A: The display typically supports SPI clock speeds up to 15 MHz, but this may vary depending on your setup and wiring quality.