
How to Use BME BMP280: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with BME BMP280 in Cirkit Designer
Design with BME BMP280 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The BME BMP280 is a high-precision, low-power barometric pressure and temperature sensor. It is widely used in weather monitoring, altitude measurement, and environmental sensing applications. The sensor is designed for both I2C and SPI communication, making it versatile and easy to integrate into various microcontroller-based projects.
Common applications include:
- Weather stations
- Altimeters for drones and other vehicles
- IoT environmental monitoring systems
- HVAC systems for indoor climate control
Explore Projects Built with BME BMP280
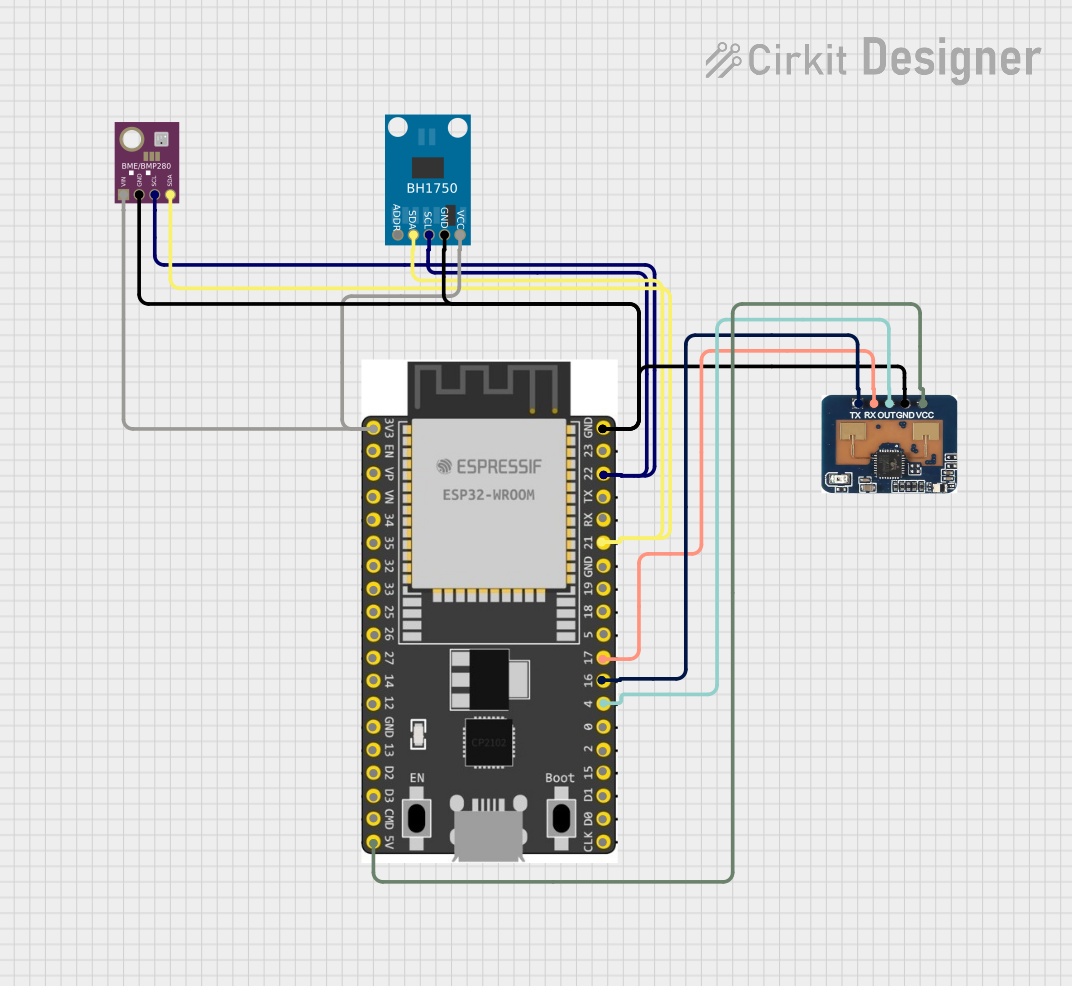
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer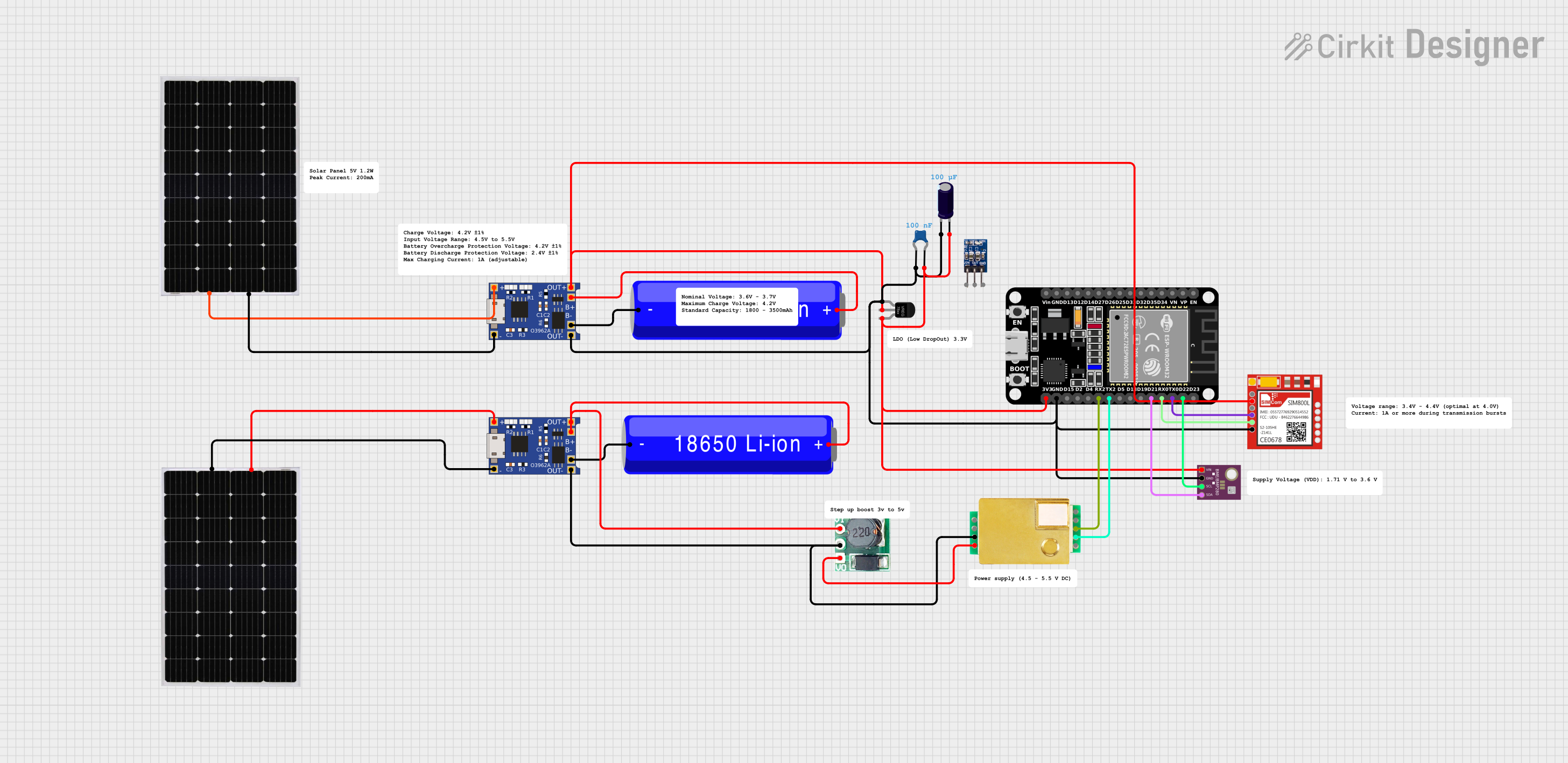
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer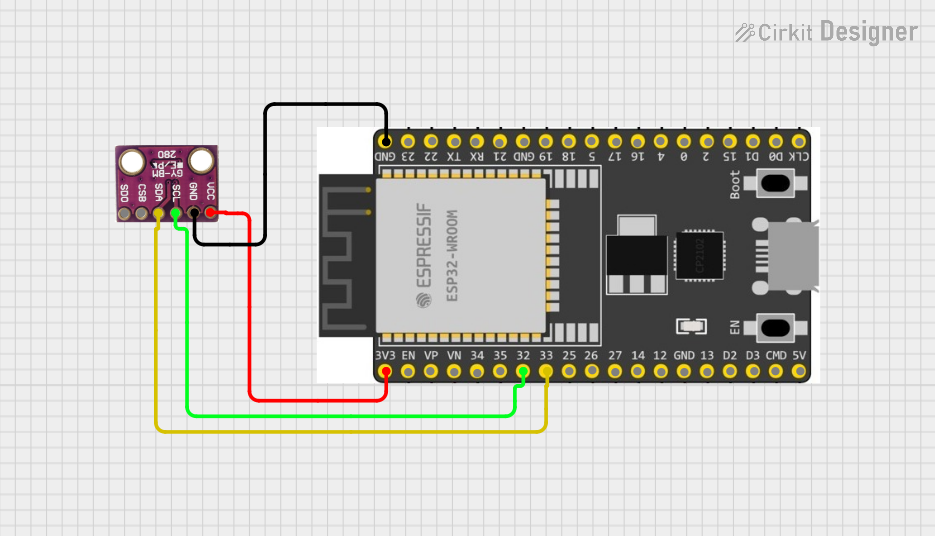
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer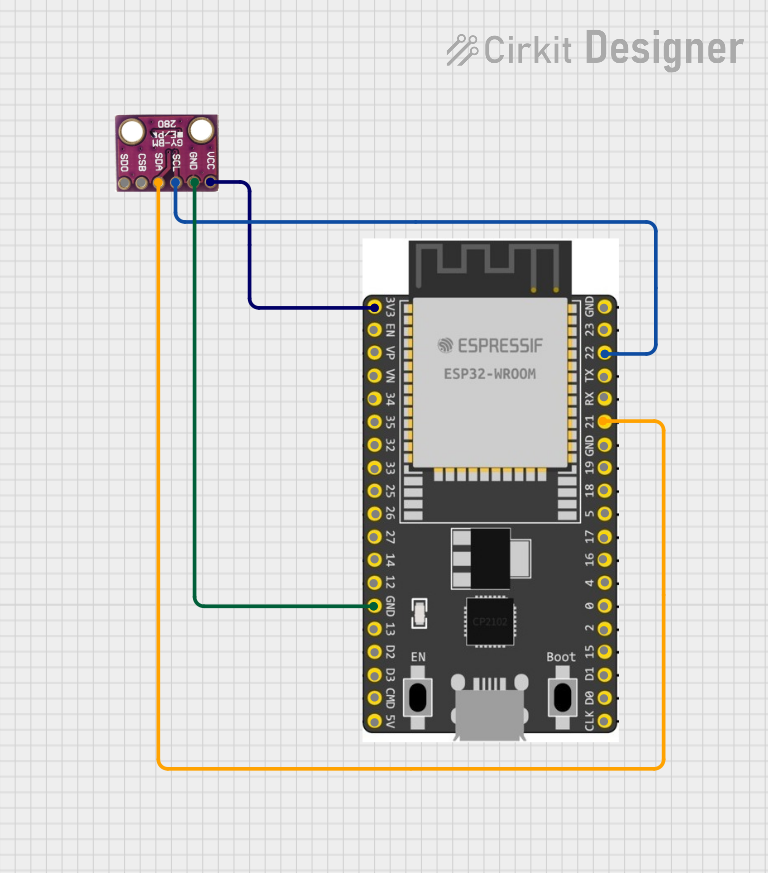
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with BME BMP280

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
The BME BMP280 sensor offers the following key specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 1.71V to 3.6V |
| Interface | I2C (up to 3.4 MHz) / SPI |
| Pressure Measurement | 300 hPa to 1100 hPa |
| Temperature Measurement | -40°C to +85°C |
| Pressure Resolution | 0.16 Pa |
| Temperature Resolution | 0.01°C |
| Power Consumption | 2.7 µA (in normal mode) |
| Dimensions | 2.0 mm x 2.5 mm x 0.95 mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The BME BMP280 typically comes in a breakout board format. Below is the pinout for the sensor:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply pin (1.71V to 3.6V). Connect to the 3.3V pin of your microcontroller. |
| GND | Ground pin. Connect to the ground of your circuit. |
| SCL | Serial Clock Line for I2C or SPI clock input. |
| SDA | Serial Data Line for I2C or SPI data input/output. |
| CSB | Chip Select for SPI communication. Pull high for I2C mode. |
| SDO | Serial Data Output for SPI or I2C address selection. |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the BME BMP280 to an Arduino UNO
The BME BMP280 can be easily connected to an Arduino UNO using the I2C interface. Below is the wiring guide:
| BME BMP280 Pin | Arduino UNO Pin |
|---|---|
| VCC | 3.3V |
| GND | GND |
| SCL | A5 (SCL) |
| SDA | A4 (SDA) |
| CSB | Pull high (3.3V) |
| SDO | Leave unconnected or connect to GND for default I2C address (0x76). |
Sample Arduino Code
The following code demonstrates how to read temperature and pressure data from the BME BMP280 using the Adafruit BMP280 library.
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#include <Adafruit_BMP280.h>
// Create an instance of the BMP280 sensor
Adafruit_BMP280 bmp;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
// Initialize the BMP280 sensor
if (!bmp.begin(0x76)) {
// Check if the sensor is connected at I2C address 0x76
Serial.println("Could not find a valid BMP280 sensor, check wiring!");
while (1); // Halt the program if the sensor is not detected
}
// Configure the sensor settings
bmp.setSampling(Adafruit_BMP280::MODE_NORMAL, // Normal mode
Adafruit_BMP280::SAMPLING_X2, // Temperature oversampling x2
Adafruit_BMP280::SAMPLING_X16, // Pressure oversampling x16
Adafruit_BMP280::FILTER_X16, // Filter coefficient x16
Adafruit_BMP280::STANDBY_MS_500); // Standby time 500ms
}
void loop() {
// Read temperature and pressure data
float temperature = bmp.readTemperature();
float pressure = bmp.readPressure();
// Print the data to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Temperature = ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println(" *C");
Serial.print("Pressure = ");
Serial.print(pressure / 100.0); // Convert pressure from Pa to hPa
Serial.println(" hPa");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Important Considerations
- Ensure the sensor operates at 3.3V. Connecting it to 5V may damage the sensor.
- Use pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ) on the SDA and SCL lines if they are not already included on the breakout board.
- The default I2C address is 0x76. If the SDO pin is connected to VCC, the address changes to 0x77.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Sensor not detected:
- Ensure the wiring is correct and matches the pinout table.
- Verify that the I2C address (default 0x76) matches the address in your code.
- Check for loose connections or damaged wires.
Incorrect readings:
- Ensure the sensor is not exposed to extreme environmental conditions beyond its operating range.
- Verify that the sensor is properly calibrated using the library's configuration functions.
Arduino hangs or crashes:
- Ensure the sensor is powered with 3.3V and not 5V.
- Check for proper pull-up resistors on the I2C lines.
FAQs
Q: Can the BME BMP280 measure humidity?
A: No, the BMP280 measures only temperature and pressure. For humidity measurements, use the BME280 sensor.
Q: Can I use the BMP280 with a 5V microcontroller?
A: Yes, but you must use a logic level shifter to convert the 5V signals to 3.3V for the sensor.
Q: How do I switch between I2C and SPI modes?
A: For I2C mode, pull the CSB pin high. For SPI mode, pull the CSB pin low and connect the SDO pin to the SPI MISO line.
By following this documentation, you can successfully integrate the BME BMP280 into your projects for accurate temperature and pressure measurements.