
How to Use Gobilda 12VDC Motor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Gobilda 12VDC Motor in Cirkit Designer
Design with Gobilda 12VDC Motor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Gobilda 12VDC Motor is a compact and efficient direct current motor designed for robotics and automation applications. It provides reliable torque and speed control, making it an ideal choice for projects requiring precise motion and power delivery. This motor is widely used in robotic arms, mobile robots, conveyor systems, and other automated mechanisms due to its robust design and consistent performance.
Explore Projects Built with Gobilda 12VDC Motor
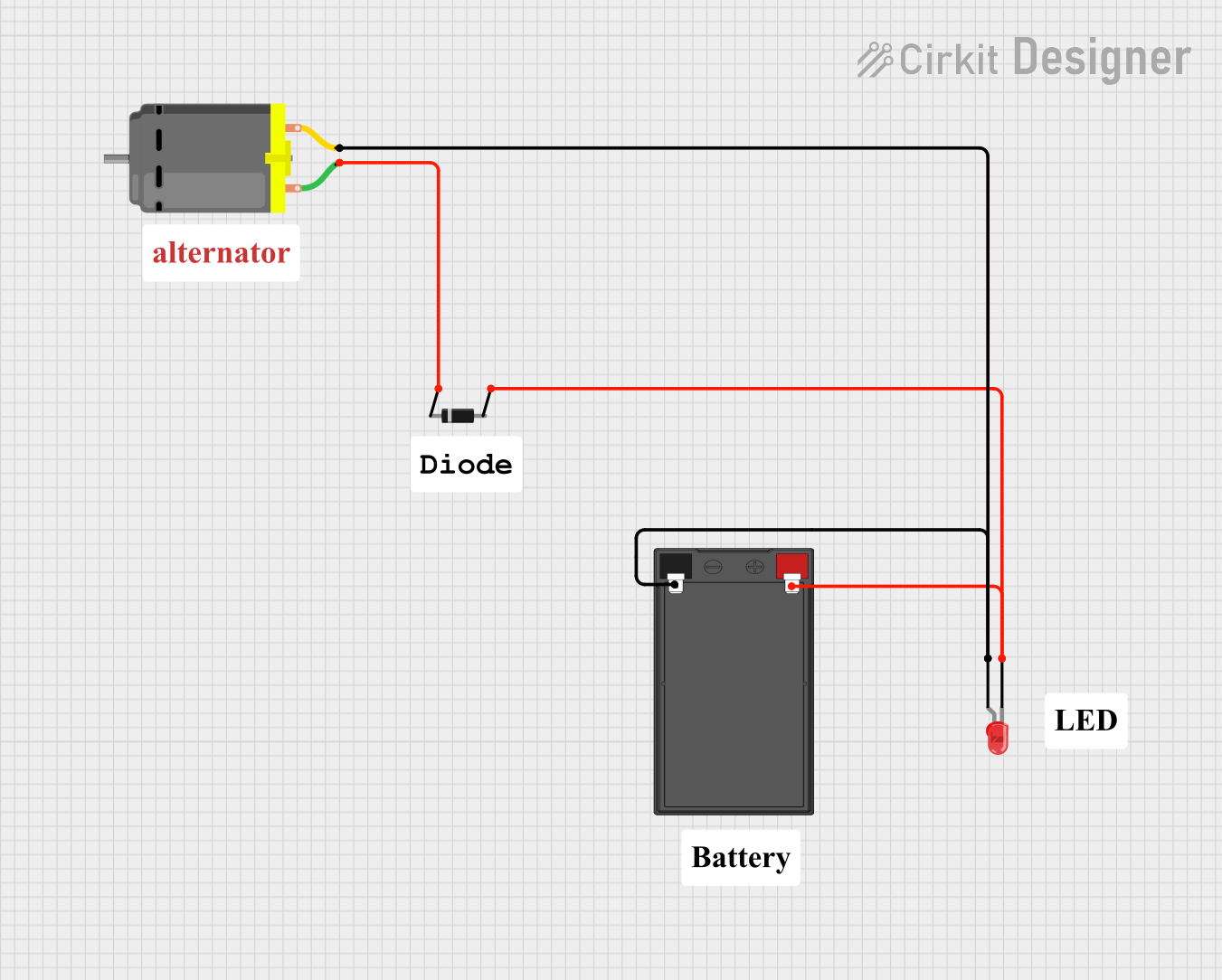
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer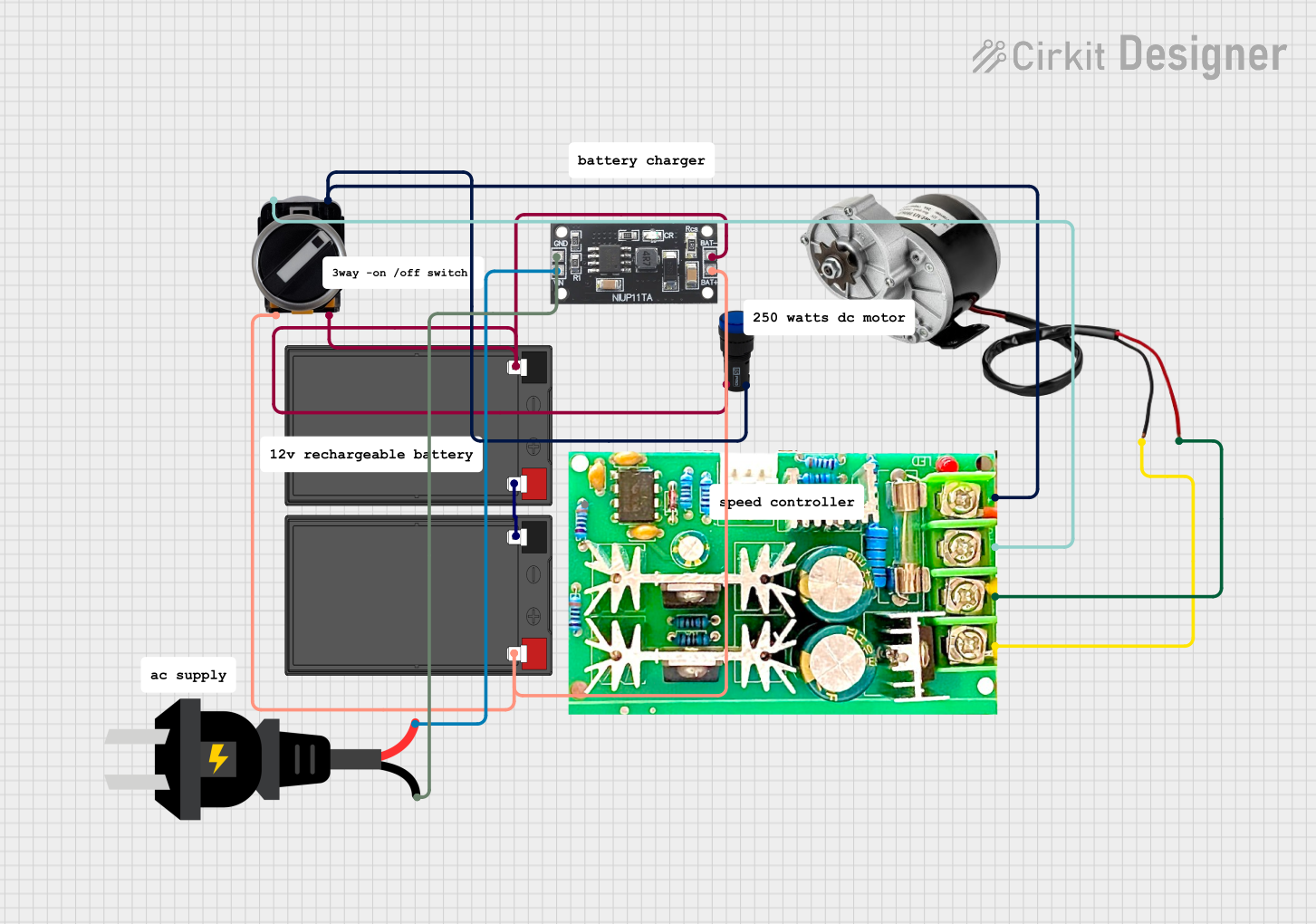
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer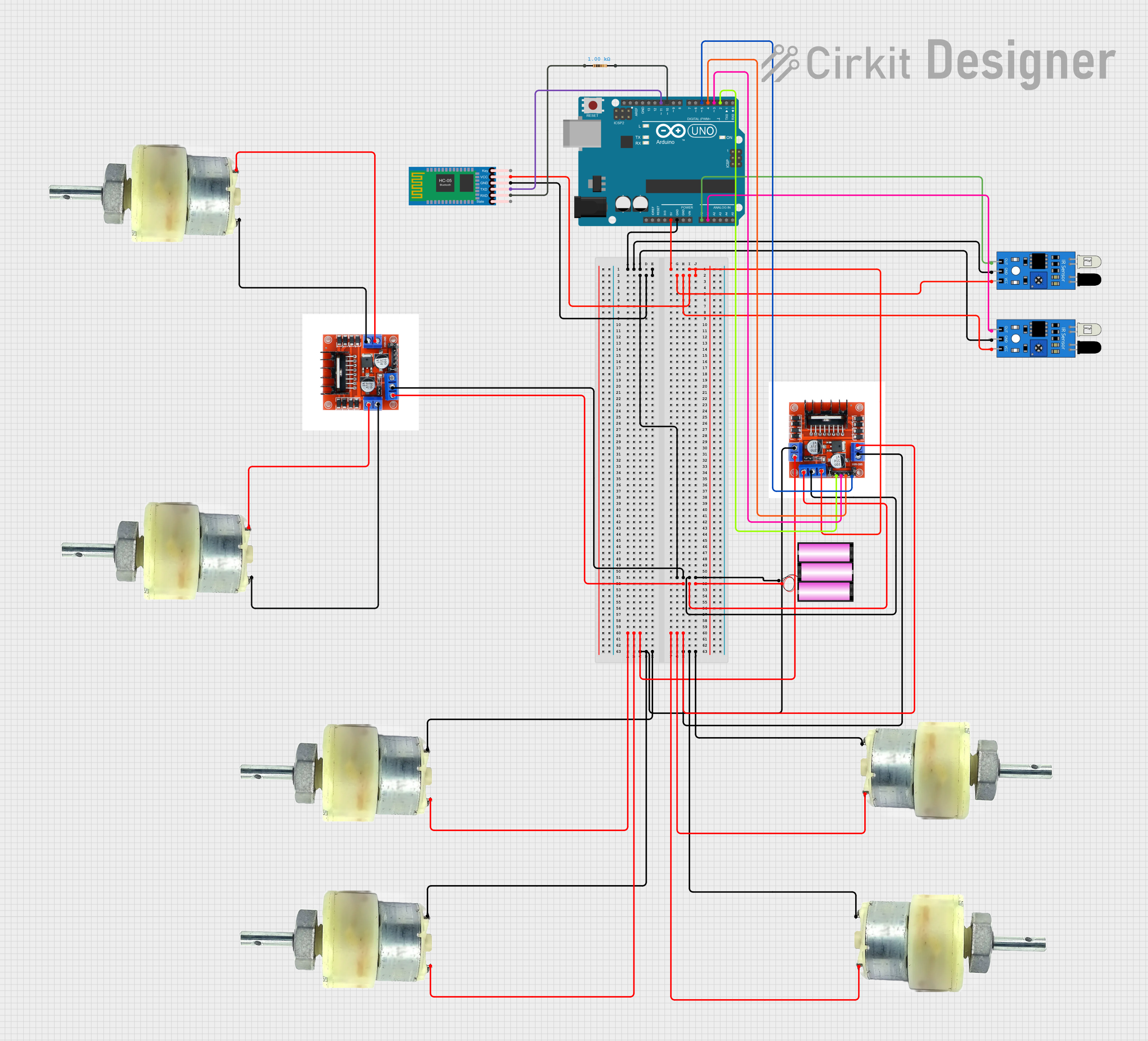
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer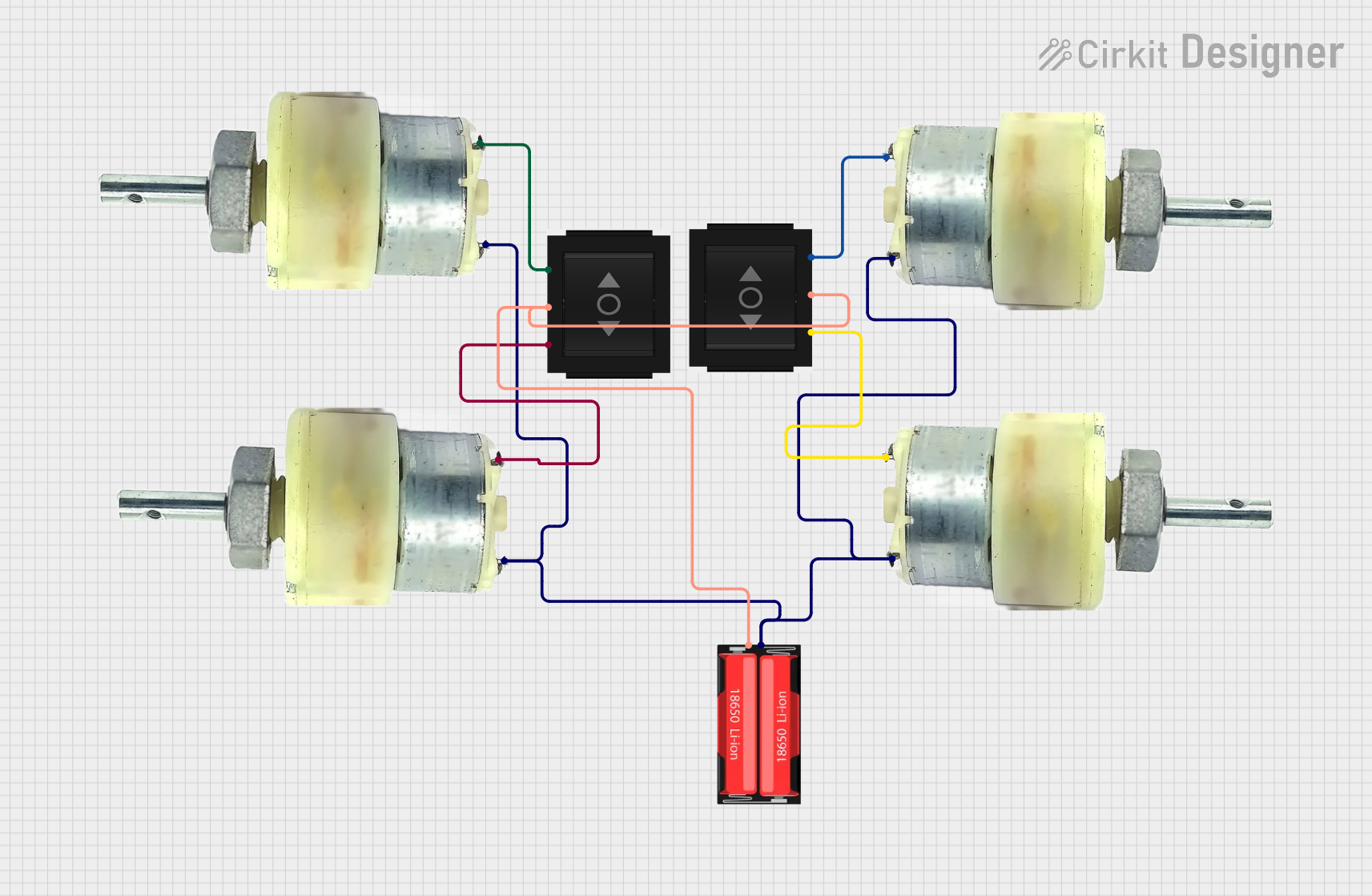
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Gobilda 12VDC Motor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the Gobilda 12VDC Motor:
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 12V DC |
| No-Load Speed | 312 RPM |
| Stall Torque | 11.3 kg·cm |
| Stall Current | 5.5A |
| Gearbox Ratio | 19.2:1 |
| Shaft Diameter | 8mm (D-shaft) |
| Motor Weight | 365g |
| Operating Temperature | -10°C to 50°C |
| Motor Type | Brushed DC Motor |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Gobilda 12VDC Motor typically has two terminals for electrical connections:
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| + | Positive terminal for power input (12V DC) |
| - | Negative terminal for power input (Ground) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Gobilda 12VDC Motor in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the motor to a 12V DC power source. Ensure the power supply can provide sufficient current (at least 5.5A for stall conditions).
- Motor Driver: Use a motor driver or H-bridge circuit to control the motor's speed and direction. Directly connecting the motor to a microcontroller is not recommended due to high current requirements.
- Polarity: Reversing the polarity of the power supply will reverse the motor's rotation direction.
- Mounting: Secure the motor using compatible mounting brackets to prevent vibration or misalignment during operation.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Current Limiting: Use a motor driver with current limiting features to protect the motor from damage during stall conditions.
- Heat Dissipation: Avoid prolonged operation at stall torque to prevent overheating. Ensure proper ventilation around the motor.
- Load Matching: Select a gearbox ratio and load that match the motor's torque and speed characteristics for optimal performance.
- Power Supply: Use a regulated 12V DC power supply to ensure stable operation.
Example: Controlling the Motor with an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control the Gobilda 12VDC Motor using an Arduino UNO and an L298N motor driver:
// Include necessary libraries
// No external libraries are required for basic motor control
// Define motor driver pins
const int ENA = 9; // PWM pin for speed control
const int IN1 = 8; // Direction control pin 1
const int IN2 = 7; // Direction control pin 2
void setup() {
// Set motor driver pins as outputs
pinMode(ENA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN2, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Rotate motor in forward direction
digitalWrite(IN1, HIGH); // Set IN1 high
digitalWrite(IN2, LOW); // Set IN2 low
analogWrite(ENA, 128); // Set speed to 50% (PWM value: 0-255)
delay(3000); // Run motor for 3 seconds
// Stop the motor
analogWrite(ENA, 0); // Set speed to 0
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
// Rotate motor in reverse direction
digitalWrite(IN1, LOW); // Set IN1 low
digitalWrite(IN2, HIGH); // Set IN2 high
analogWrite(ENA, 128); // Set speed to 50% (PWM value: 0-255)
delay(3000); // Run motor for 3 seconds
// Stop the motor
analogWrite(ENA, 0); // Set speed to 0
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Notes:
- Ensure the L298N motor driver is connected to a 12V DC power supply.
- The ENA pin controls the motor speed using PWM, while IN1 and IN2 control the direction.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Does Not Spin
- Cause: Insufficient power supply or loose connections.
- Solution: Verify that the power supply provides 12V DC and sufficient current. Check all connections.
Motor Overheats
- Cause: Prolonged operation at stall torque or excessive load.
- Solution: Reduce the load or use a current-limiting motor driver. Allow the motor to cool down before resuming operation.
Motor Vibrates or Makes Noise
- Cause: Misalignment or loose mounting.
- Solution: Secure the motor using proper mounting brackets and ensure alignment with the load.
Motor Spins in the Wrong Direction
- Cause: Incorrect polarity or wiring.
- Solution: Reverse the connections to the motor terminals or adjust the control signals.
FAQs
Q: Can I power the motor with a voltage higher than 12V?
A: No, exceeding 12V may damage the motor. Always use a regulated 12V DC power supply.Q: Is the motor compatible with PWM speed control?
A: Yes, the motor supports PWM-based speed control when used with a compatible motor driver.Q: Can the motor be used for continuous operation?
A: Yes, but ensure proper ventilation and avoid operating at stall torque for extended periods.Q: What is the maximum load the motor can handle?
A: The motor can handle loads up to its stall torque of 11.3 kg·cm, but operating near stall conditions should be avoided to prevent overheating.