
How to Use 8 Way Channel Expansion Relay Module 5V Power Supply Optocoupler Isolation Board IIC I2C Communication: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
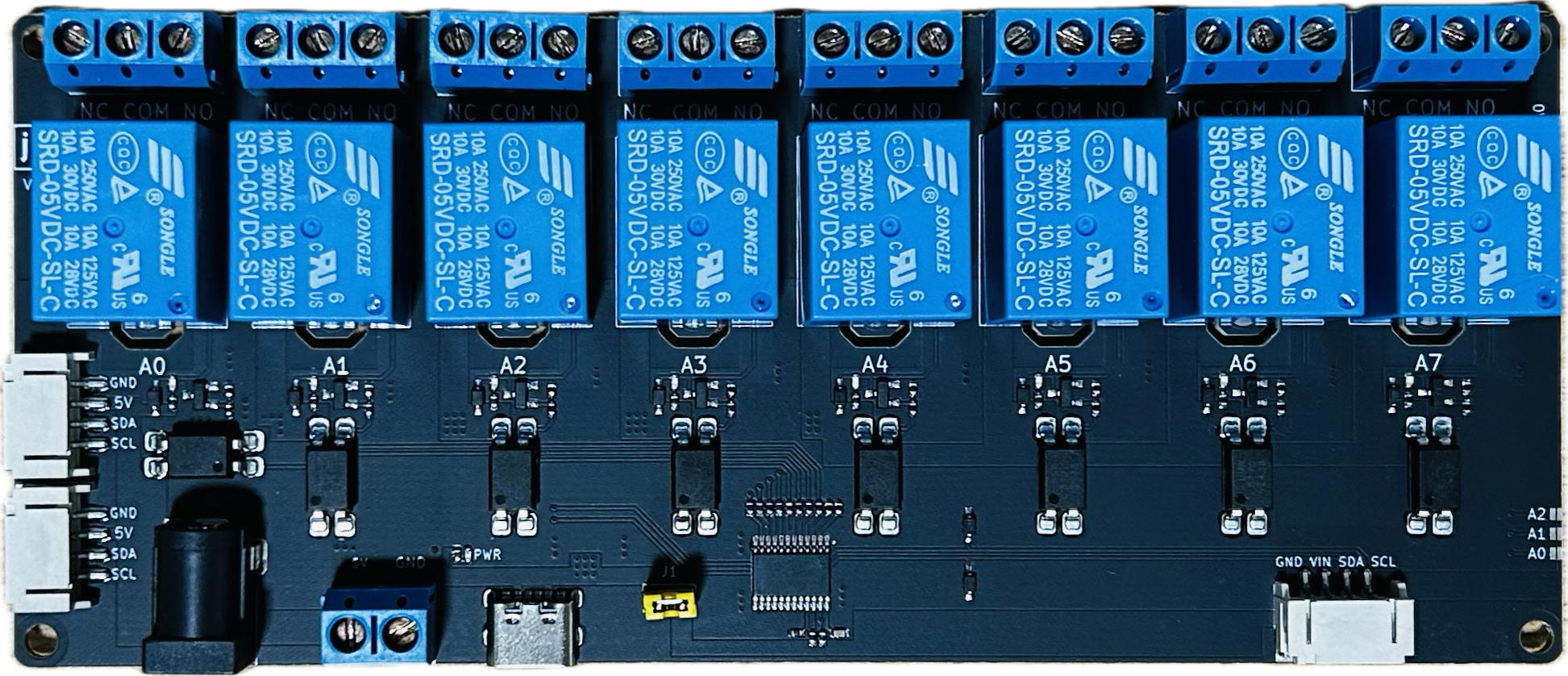
 Design with 8 Way Channel Expansion Relay Module 5V Power Supply Optocoupler Isolation Board IIC I2C Communication in Cirkit Designer
Design with 8 Way Channel Expansion Relay Module 5V Power Supply Optocoupler Isolation Board IIC I2C Communication in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 8 Way Channel Expansion Relay Module by Songle (Part ID: RELAY) is a versatile and reliable relay module designed for controlling high-power devices using low-power control signals. This module features 8 independent relays, each capable of switching AC or DC loads, and is equipped with optocoupler isolation for enhanced safety and noise immunity. It supports IIC/I2C communication, making it ideal for microcontroller-based projects, including Arduino and Raspberry Pi applications.
Explore Projects Built with 8 Way Channel Expansion Relay Module 5V Power Supply Optocoupler Isolation Board IIC I2C Communication

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer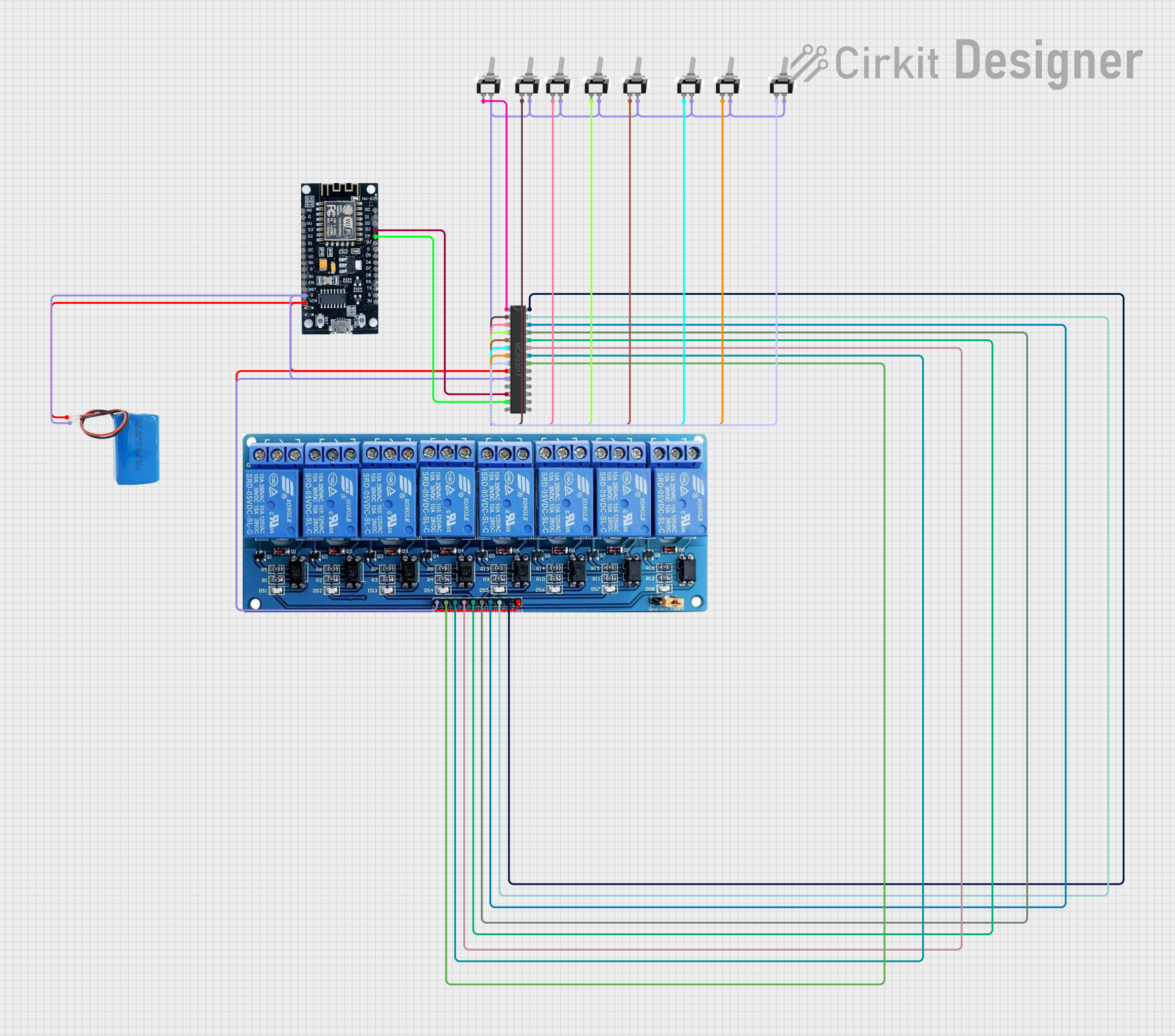
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer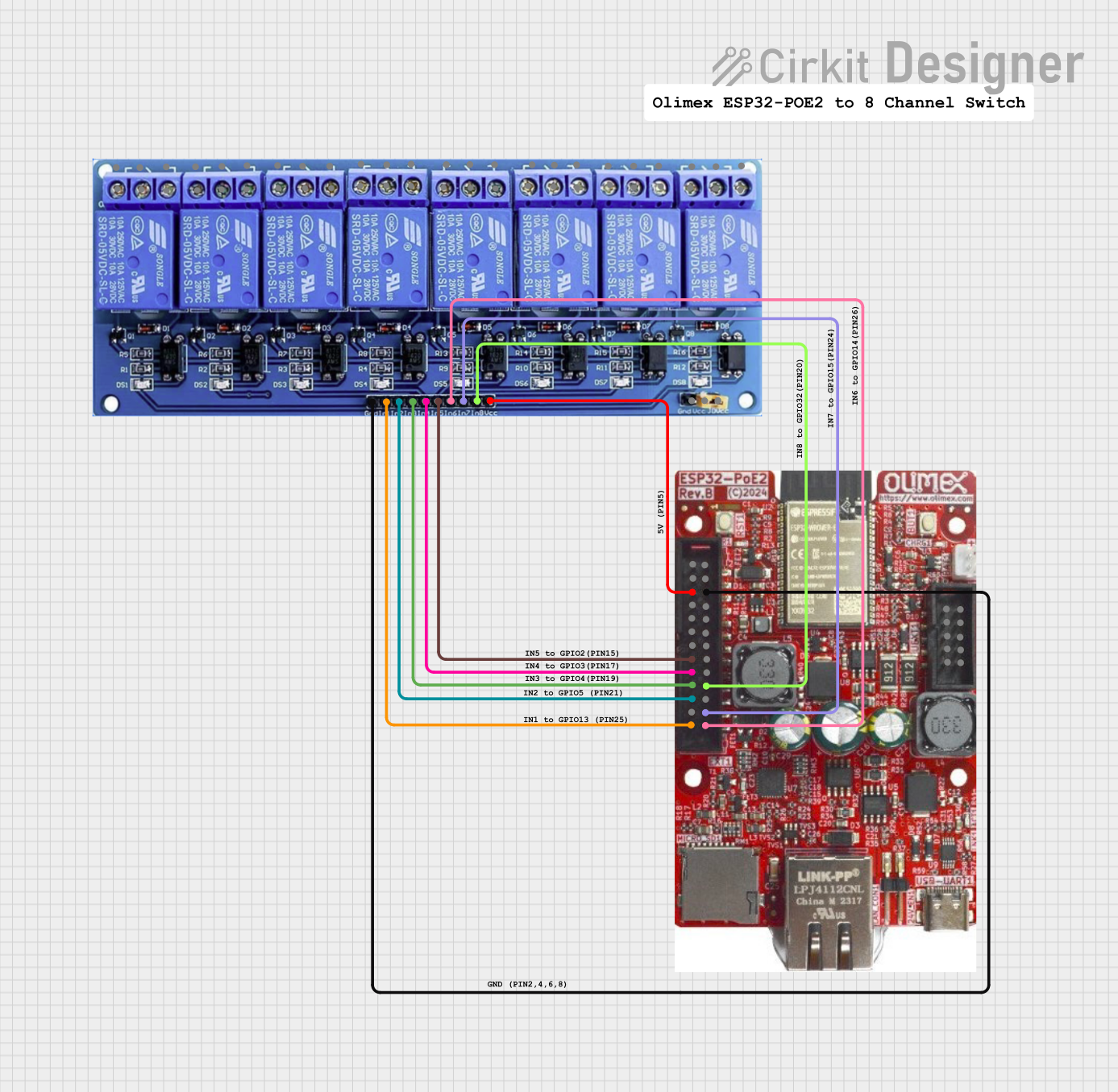
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 8 Way Channel Expansion Relay Module 5V Power Supply Optocoupler Isolation Board IIC I2C Communication

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Home automation systems (e.g., controlling lights, fans, or appliances)
- Industrial automation and control
- Robotics and motor control
- IoT (Internet of Things) projects
- Signal isolation and power switching in embedded systems
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 5V DC |
| Trigger Voltage (High) | 4.5V - 5V |
| Trigger Voltage (Low) | 0V - 0.5V |
| Relay Type | Songle SRD-05VDC-SL-C |
| Maximum Load (AC) | 250V AC @ 10A |
| Maximum Load (DC) | 30V DC @ 10A |
| Communication Protocol | IIC/I2C |
| Isolation | Optocoupler isolation for each relay |
| Dimensions | 138mm x 56mm x 18mm |
| Weight | ~120g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Power and Communication Pins
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | 5V DC power supply input |
| GND | Ground connection |
| SDA | I2C data line for communication |
| SCL | I2C clock line for communication |
Relay Control Pins
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| IN1-IN8 | Control signals for relays 1 through 8. A HIGH signal activates the relay. |
Relay Output Terminals
| Terminal Name | Description |
|---|---|
| COM | Common terminal for the relay |
| NO | Normally Open terminal. Connects to COM when the relay is activated. |
| NC | Normally Closed terminal. Connects to COM when the relay is deactivated. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power the Module: Connect the VCC pin to a 5V DC power source and the GND pin to ground.
- Connect the I2C Lines: Connect the SDA and SCL pins to the corresponding I2C pins on your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO: A4 for SDA, A5 for SCL).
- Control the Relays: Use the I2C protocol to send commands to the module, activating or deactivating the desired relays.
- Connect the Load: Wire the load to the relay terminals (COM, NO, NC) as per your application requirements.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure the module is powered with a stable 5V DC supply. Avoid exceeding the voltage rating.
- Isolation: The optocoupler isolation protects your microcontroller from high-voltage spikes. Ensure proper grounding for safety.
- Load Ratings: Do not exceed the maximum load ratings of 250V AC @ 10A or 30V DC @ 10A to prevent damage.
- I2C Address: The module's default I2C address is typically 0x20. Check the datasheet or documentation for address configuration if needed.
- Decoupling Capacitors: Use decoupling capacitors near the power supply pins to reduce noise and improve stability.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
#include <Wire.h> // Include the Wire library for I2C communication
#define RELAY_I2C_ADDRESS 0x20 // Default I2C address of the relay module
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I2C communication
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
// Turn off all relays at startup
Wire.beginTransmission(RELAY_I2C_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x00); // Send command to turn off all relays
Wire.endTransmission();
Serial.println("Relay module initialized. All relays are OFF.");
}
void loop() {
// Example: Turn on relay 1
Wire.beginTransmission(RELAY_I2C_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x01); // Send command to turn on relay 1
Wire.endTransmission();
Serial.println("Relay 1 is ON.");
delay(2000); // Wait for 2 seconds
// Example: Turn off relay 1
Wire.beginTransmission(RELAY_I2C_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x00); // Send command to turn off relay 1
Wire.endTransmission();
Serial.println("Relay 1 is OFF.");
delay(2000); // Wait for 2 seconds
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Relays Not Activating:
- Ensure the module is powered with a stable 5V DC supply.
- Verify the I2C connections (SDA, SCL) and ensure they are correctly wired.
- Check the I2C address of the module and update your code if necessary.
High-Voltage Spikes:
- Use snubber circuits or flyback diodes across inductive loads to suppress voltage spikes.
Noise or Unstable Operation:
- Add decoupling capacitors near the power supply pins.
- Ensure proper grounding and avoid long, unshielded wires for I2C communication.
I2C Communication Errors:
- Check the pull-up resistors on the SDA and SCL lines. Use 4.7kΩ or 10kΩ resistors if needed.
- Verify that no other devices on the I2C bus are using the same address.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use this module with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A1: Yes, but you will need a logic level shifter to safely interface the 3.3V signals with the 5V module.
Q2: How do I change the I2C address of the module?
A2: Refer to the module's datasheet or documentation for instructions on configuring the address using jumpers or solder pads.
Q3: Can I control multiple modules on the same I2C bus?
A3: Yes, as long as each module has a unique I2C address. Configure the addresses accordingly.
Q4: What happens if I exceed the load ratings?
A4: Exceeding the load ratings can damage the relays and pose safety risks. Always stay within the specified limits.