
How to Use ICM-20948: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
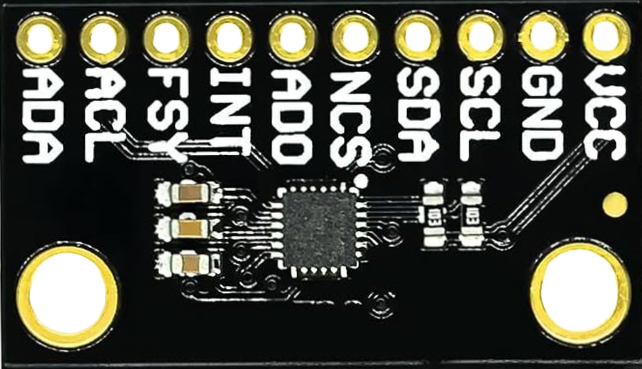
 Design with ICM-20948 in Cirkit Designer
Design with ICM-20948 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ICM-20948 is a highly integrated 9-axis motion tracking device that combines a 3-axis gyroscope, a 3-axis accelerometer, and a 3-axis magnetometer in a single compact package. This sensor is designed for applications requiring precise motion and orientation tracking, such as robotics, drones, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mobile devices. Its small size, low power consumption, and high performance make it an ideal choice for embedded systems and IoT applications.
Explore Projects Built with ICM-20948

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer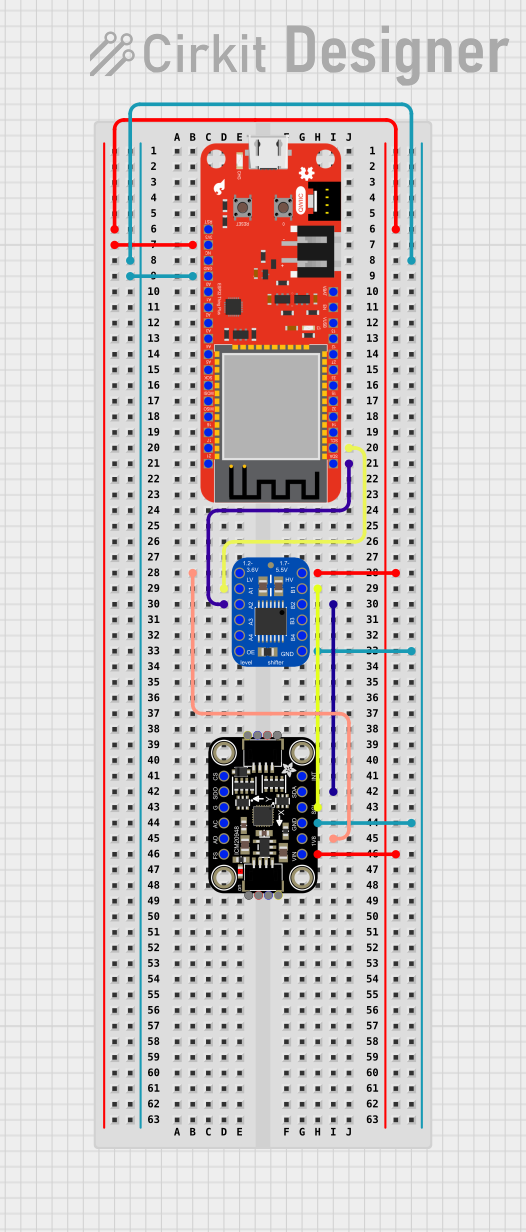
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ICM-20948

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Robotics for motion and orientation sensing
- Drones for stabilization and navigation
- Mobile devices for gesture recognition and gaming
- Wearable devices for fitness tracking
- Augmented and virtual reality systems
Technical Specifications
The ICM-20948 offers a wide range of features and capabilities. Below are its key technical specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Gyroscope Range | ±250, ±500, ±1000, ±2000 degrees per second |
| Accelerometer Range | ±2g, ±4g, ±8g, ±16g |
| Magnetometer Range | ±4900 µT |
| Gyroscope Resolution | 16-bit |
| Accelerometer Resolution | 16-bit |
| Magnetometer Resolution | 16-bit |
| Communication Interface | I²C (up to 400 kHz) and SPI (up to 7 MHz) |
| Operating Voltage | 1.71V to 3.6V |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Power Consumption | 2.5 mA (typical, in full operation mode) |
| Package Size | 3 mm x 3 mm x 1 mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ICM-20948 is typically available in a 24-pin QFN package. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VDD | Power supply input (1.71V to 3.6V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | SCL/SCLK | I²C clock line / SPI clock |
| 4 | SDA/SDI | I²C data line / SPI data input |
| 5 | AD0/SDO | I²C address select / SPI data output |
| 6 | INT | Interrupt output |
| 7 | FSYNC | Frame synchronization input/output |
| 8-24 | NC | No connection (reserved for future use) |
Usage Instructions
The ICM-20948 can be used in a variety of circuits and is compatible with microcontrollers such as the Arduino UNO. Below are the steps to use the ICM-20948 in a circuit:
Connecting the ICM-20948 to an Arduino UNO
- Power Supply: Connect the VDD pin of the ICM-20948 to the 3.3V pin of the Arduino UNO. Connect the GND pin to the Arduino's GND.
- I²C Communication:
- Connect the SCL pin of the ICM-20948 to the A5 pin of the Arduino UNO.
- Connect the SDA pin of the ICM-20948 to the A4 pin of the Arduino UNO.
- Address Selection: Connect the AD0 pin to GND for the default I²C address (0x68). Connect it to VDD for the alternate address (0x69).
- Interrupt Pin (Optional): Connect the INT pin to a digital input pin on the Arduino if you want to use interrupts.
Sample Arduino Code
Below is an example Arduino sketch to read data from the ICM-20948 using the I²C interface:
#include <Wire.h>
// ICM-20948 I2C address (default is 0x68 if AD0 is connected to GND)
#define ICM20948_ADDRESS 0x68
// Register addresses
#define WHO_AM_I 0x00
#define ACCEL_XOUT_H 0x2D
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I2C communication
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
// Check if the ICM-20948 is connected
Wire.beginTransmission(ICM20948_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(WHO_AM_I); // Request the WHO_AM_I register
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(ICM20948_ADDRESS, 1);
if (Wire.available()) {
byte whoAmI = Wire.read();
if (whoAmI == 0xEA) { // Expected WHO_AM_I response for ICM-20948
Serial.println("ICM-20948 detected!");
} else {
Serial.println("ICM-20948 not detected. Check connections.");
}
}
}
void loop() {
// Read accelerometer data
Wire.beginTransmission(ICM20948_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(ACCEL_XOUT_H); // Request accelerometer X-axis high byte
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(ICM20948_ADDRESS, 6); // Request 6 bytes (X, Y, Z)
if (Wire.available() == 6) {
int16_t accelX = (Wire.read() << 8) | Wire.read();
int16_t accelY = (Wire.read() << 8) | Wire.read();
int16_t accelZ = (Wire.read() << 8) | Wire.read();
Serial.print("Accel X: ");
Serial.print(accelX);
Serial.print(" Y: ");
Serial.print(accelY);
Serial.print(" Z: ");
Serial.println(accelZ);
}
delay(500); // Wait 500ms before the next reading
}
Important Considerations
- Ensure the ICM-20948 is powered with a voltage within its operating range (1.71V to 3.6V).
- Use appropriate pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ) on the I²C lines (SCL and SDA) if they are not already present on your breakout board.
- Avoid excessive noise on the power supply and communication lines to ensure accurate readings.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
ICM-20948 Not Detected
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or I²C address mismatch.
- Solution: Verify the connections and ensure the AD0 pin is set correctly for the desired I²C address.
Inaccurate Sensor Readings
- Cause: Calibration not performed or excessive noise in the environment.
- Solution: Perform sensor calibration and ensure the sensor is mounted securely to minimize vibrations.
No Data from the Sensor
- Cause: Incorrect register address or communication failure.
- Solution: Double-check the register addresses in your code and ensure proper pull-up resistors are used on the I²C lines.
FAQs
Q: Can the ICM-20948 be used with SPI instead of I²C?
A: Yes, the ICM-20948 supports both I²C and SPI communication. For SPI, connect the SCL/SCLK, SDA/SDI, and AD0/SDO pins to the appropriate SPI pins on your microcontroller.
Q: How do I calibrate the ICM-20948?
A: Calibration involves collecting raw data from the gyroscope, accelerometer, and magnetometer, and applying offsets to account for biases. Many libraries provide built-in calibration functions.
Q: What is the maximum sampling rate of the ICM-20948?
A: The ICM-20948 supports a maximum sampling rate of 1125 Hz for the gyroscope and accelerometer.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the ICM-20948 into your projects for precise motion and orientation tracking.