
How to Use TWS-434 Transmitter: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with TWS-434 Transmitter in Cirkit Designer
Design with TWS-434 Transmitter in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TWS-434 is a low-power wireless transmitter module manufactured by WEN SHING. It operates in the 434 MHz frequency band and is designed for short-range communication. This module is widely used in applications such as remote controls, wireless sensor networks, home automation systems, and other embedded systems requiring wireless data transmission.
The TWS-434 is compact, cost-effective, and easy to integrate into various projects, making it a popular choice for hobbyists and professionals alike.
Explore Projects Built with TWS-434 Transmitter

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer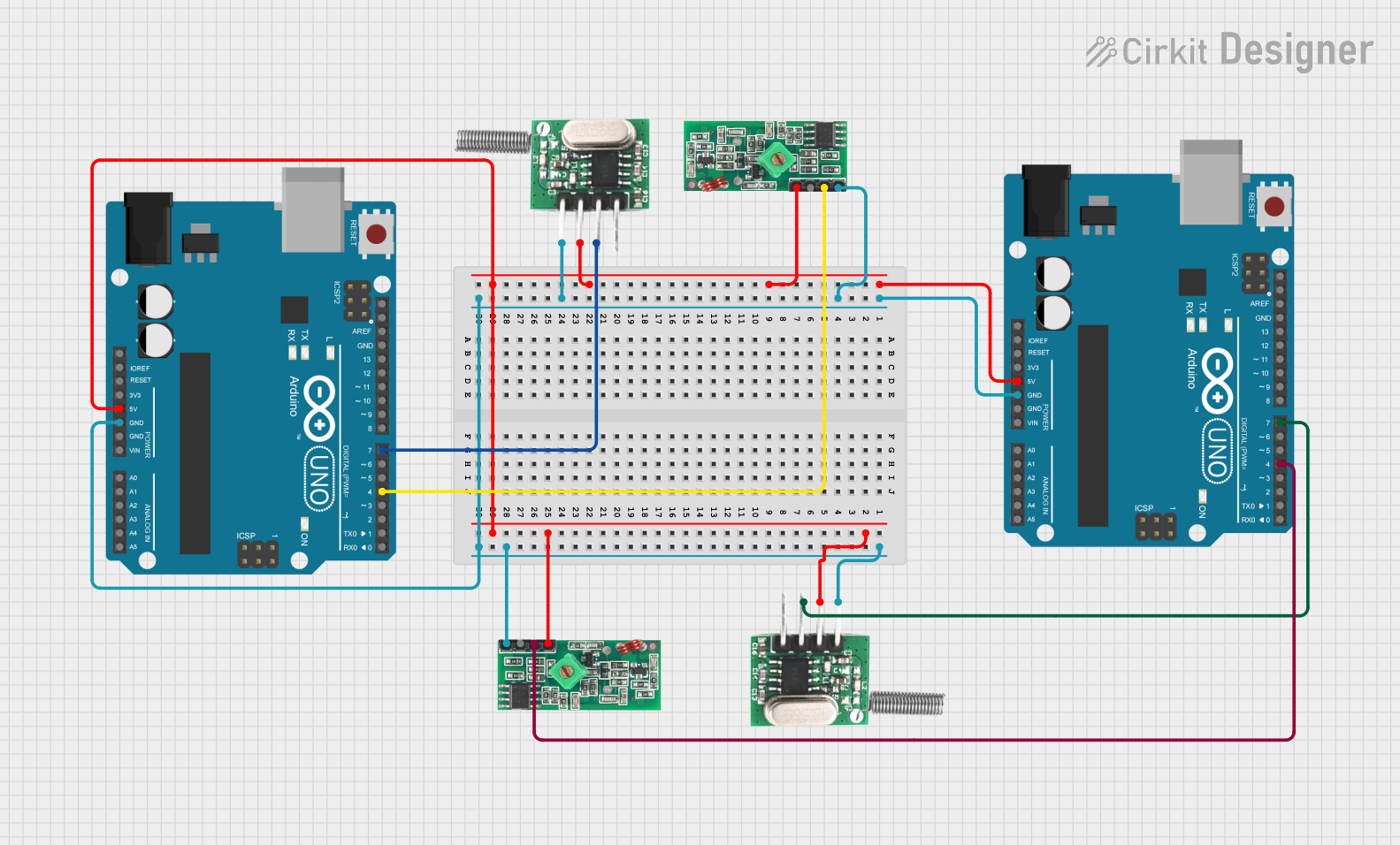
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer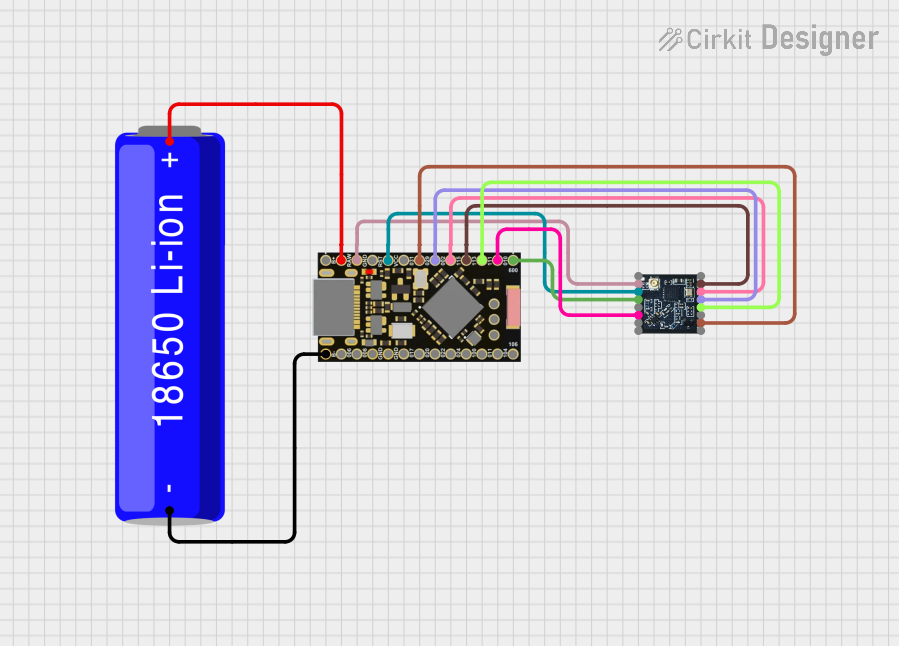
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer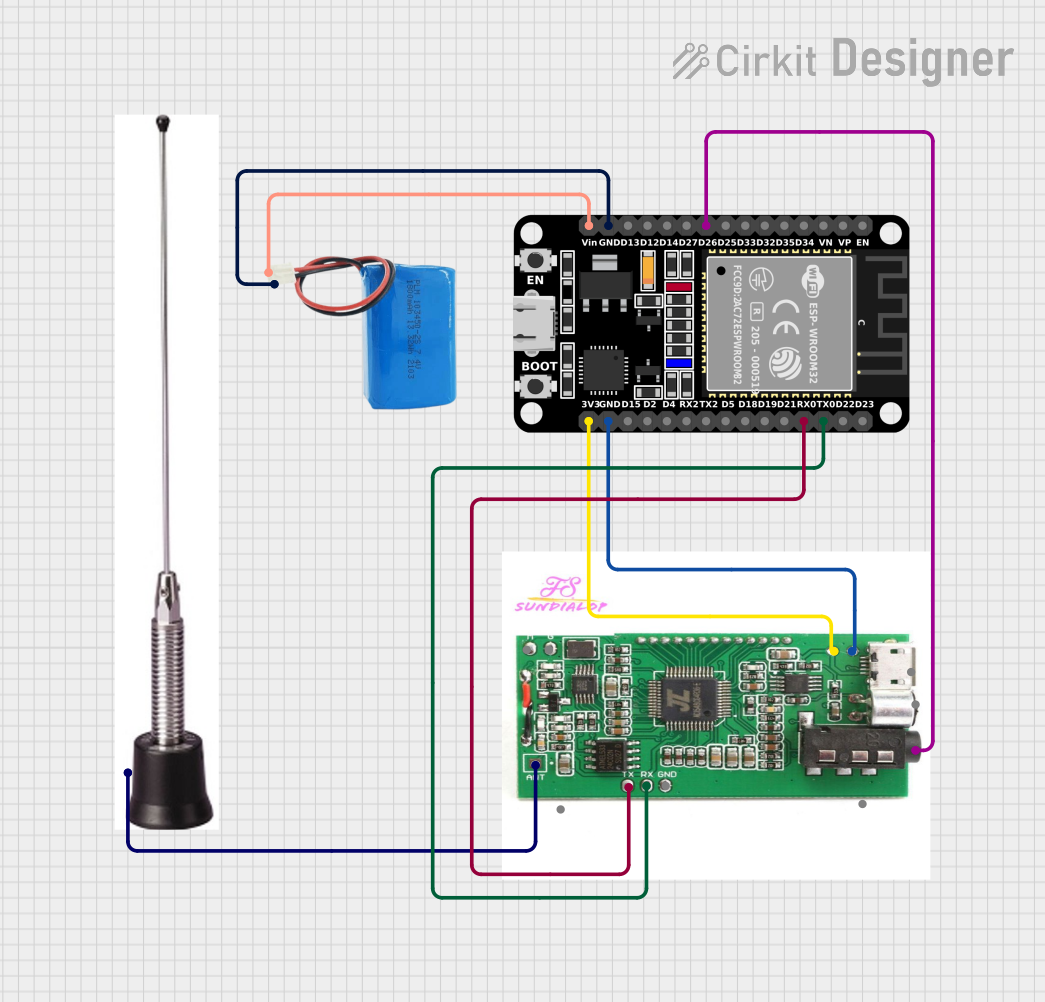
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TWS-434 Transmitter

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the TWS-434 transmitter module:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Frequency | 434 MHz |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 12V DC |
| Operating Current | 10 mA (typical) |
| Transmission Range | Up to 500 feet (line of sight) |
| Modulation Type | Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) |
| Data Rate | Up to 10 kbps |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to +70°C |
| Dimensions | 19mm x 19mm x 7mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The TWS-434 module has four pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (3.3V to 12V DC). |
| 2 | DATA | Data input pin. Connect this to the microcontroller or data source. |
| 3 | GND | Ground connection. |
| 4 | ANT | Antenna connection. Attach a 17 cm wire or a suitable 434 MHz antenna here. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the TWS-434 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a regulated power supply (3.3V to 12V DC). Ensure the power source is stable to avoid transmission issues.
- Data Input: Connect the DATA pin to the output of a microcontroller, encoder, or other data source. The module transmits the data it receives on this pin.
- Ground Connection: Connect the GND pin to the ground of your circuit.
- Antenna: Attach a 17 cm wire or a pre-made 434 MHz antenna to the ANT pin for optimal transmission range.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Antenna Placement: Ensure the antenna is placed away from metal objects or other components that may interfere with the signal.
- Power Supply Noise: Use a decoupling capacitor (e.g., 0.1 µF) near the VCC pin to filter out noise from the power supply.
- Data Encoding: For reliable communication, use an encoder (e.g., HT12E) to encode the data before transmitting it.
- Line of Sight: The module performs best in line-of-sight conditions. Obstacles like walls or furniture may reduce the transmission range.
Example: Connecting TWS-434 to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the TWS-434 with an Arduino UNO to transmit data:
Circuit Connections
- Connect the VCC pin of the TWS-434 to the 5V pin on the Arduino.
- Connect the GND pin of the TWS-434 to the GND pin on the Arduino.
- Connect the DATA pin of the TWS-434 to digital pin 12 on the Arduino.
- Attach a 17 cm wire to the ANT pin of the TWS-434.
Arduino Code
// TWS-434 Transmitter Example Code
// This code sends a simple HIGH/LOW signal to the TWS-434 module.
#define DATA_PIN 12 // Define the pin connected to the DATA pin of TWS-434
void setup() {
pinMode(DATA_PIN, OUTPUT); // Set the DATA pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(DATA_PIN, HIGH); // Send a HIGH signal
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(DATA_PIN, LOW); // Send a LOW signal
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Notes:
- The above code sends a simple HIGH/LOW signal. For more complex data transmission, consider using an encoder/decoder pair (e.g., HT12E/HT12D).
- Ensure the receiver module (e.g., RWS-434) is properly configured to receive the transmitted signal.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Signal Transmission
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or power supply issues.
- Solution: Double-check all connections and ensure the power supply voltage is within the specified range (3.3V to 12V).
Short Transmission Range
- Cause: Poor antenna placement or interference.
- Solution: Use a 17 cm wire as the antenna and ensure it is placed away from obstructions or interference sources.
Data Corruption
- Cause: Noise or lack of data encoding.
- Solution: Use an encoder (e.g., HT12E) to encode the data before transmission.
Interference with Other Devices
- Cause: Operating in a crowded frequency band.
- Solution: Ensure the module is used in an environment with minimal interference. Avoid using multiple transmitters on the same frequency.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use the TWS-434 with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A1: Yes, the TWS-434 can operate with a 3.3V power supply. Ensure the data signal from the microcontroller is also 3.3V compatible.
Q2: What is the maximum data rate supported by the TWS-434?
A2: The TWS-434 supports a maximum data rate of 10 kbps.
Q3: Can I use the TWS-434 without an antenna?
A3: While the module may work without an antenna, the transmission range will be significantly reduced. It is recommended to use a 17 cm wire or a suitable 434 MHz antenna.
Q4: Is the TWS-434 compatible with the RWS-434 receiver module?
A4: Yes, the TWS-434 is designed to work seamlessly with the RWS-434 receiver module for wireless communication.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the TWS-434 transmitter module into your projects and troubleshoot common issues.