
How to Use Mini NRF24L01: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
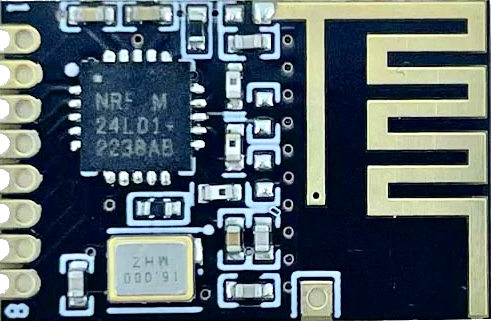
 Design with Mini NRF24L01 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Mini NRF24L01 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Mini NRF24L01, manufactured by Nordic Semiconductor (Part ID: NRF24L01+), is a compact 2.4GHz wireless transceiver module designed for short-range communication. It is widely used in wireless data transmission applications due to its low power consumption, high data rates, and reliable performance. The module is ideal for projects requiring wireless communication between devices, such as remote controls, IoT devices, and wireless sensors.
Explore Projects Built with Mini NRF24L01
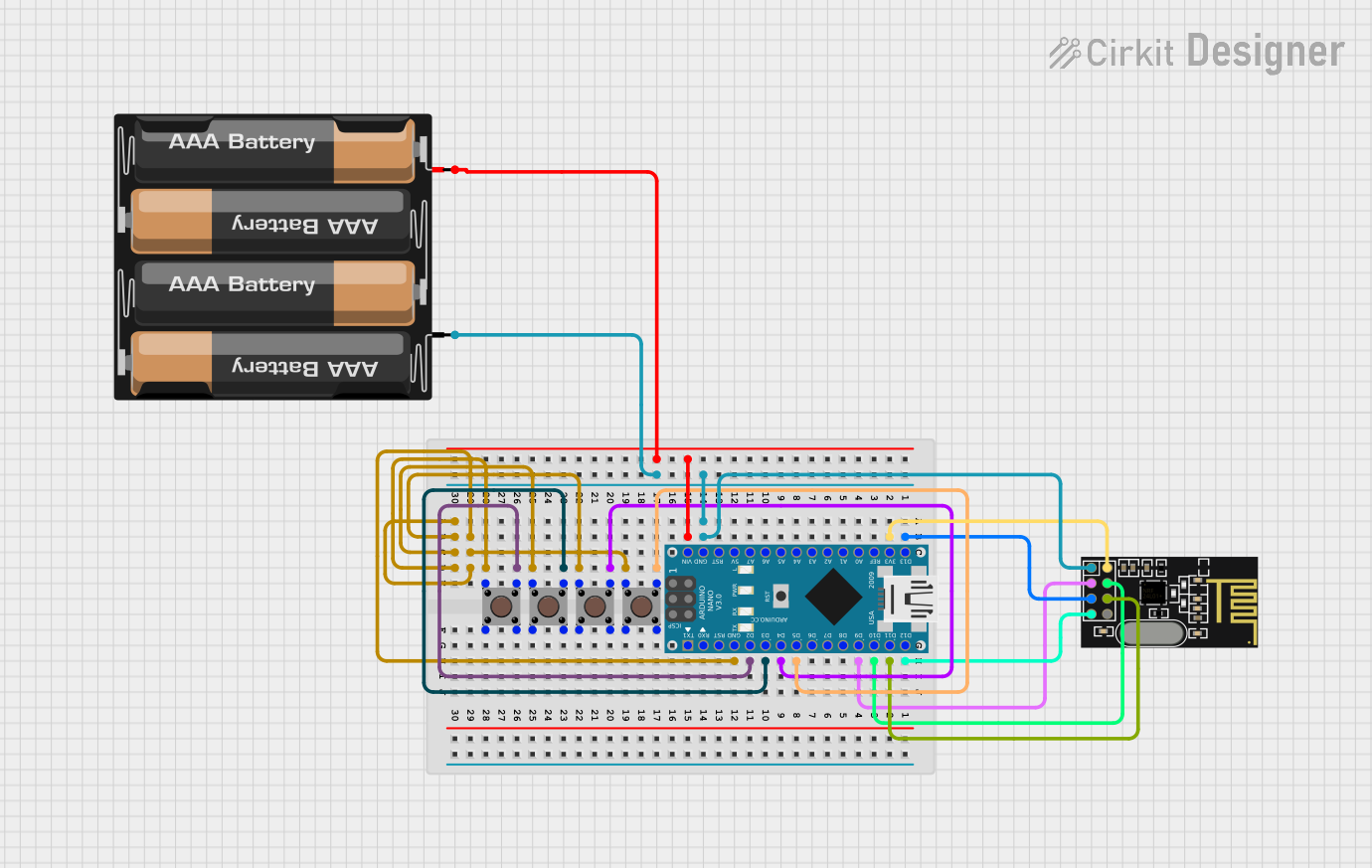
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer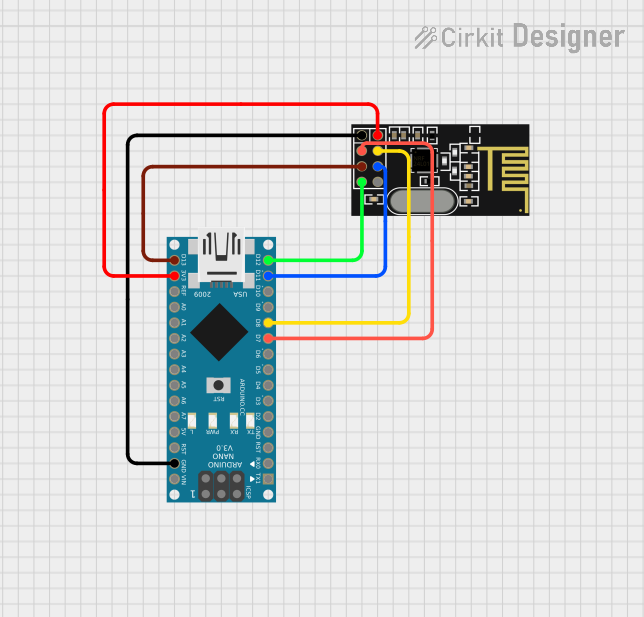
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer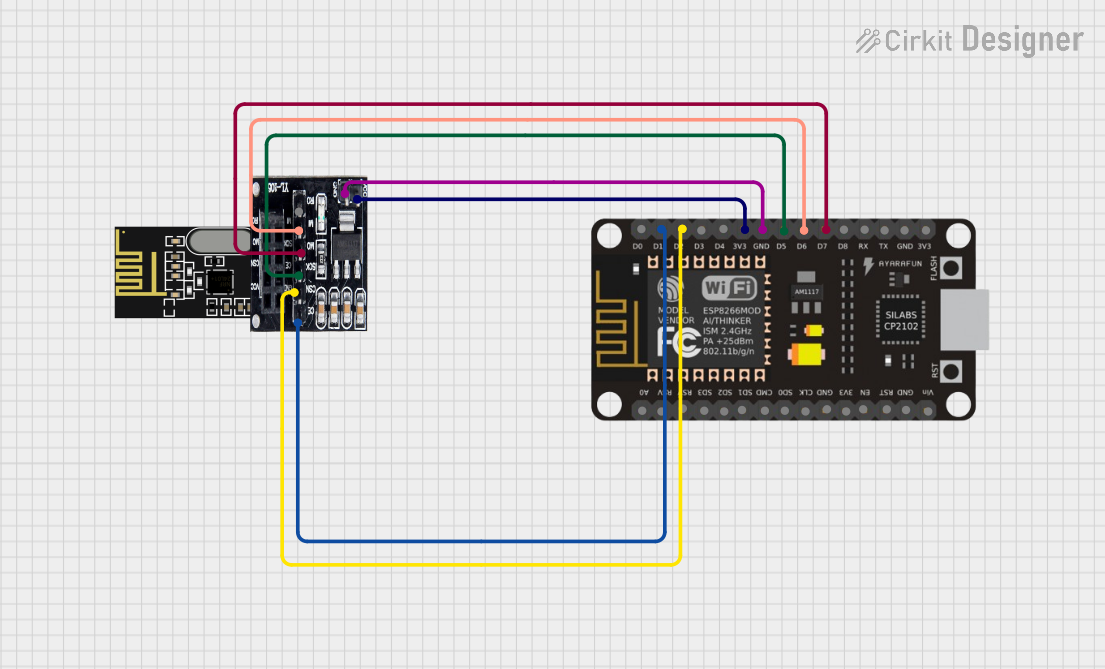
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer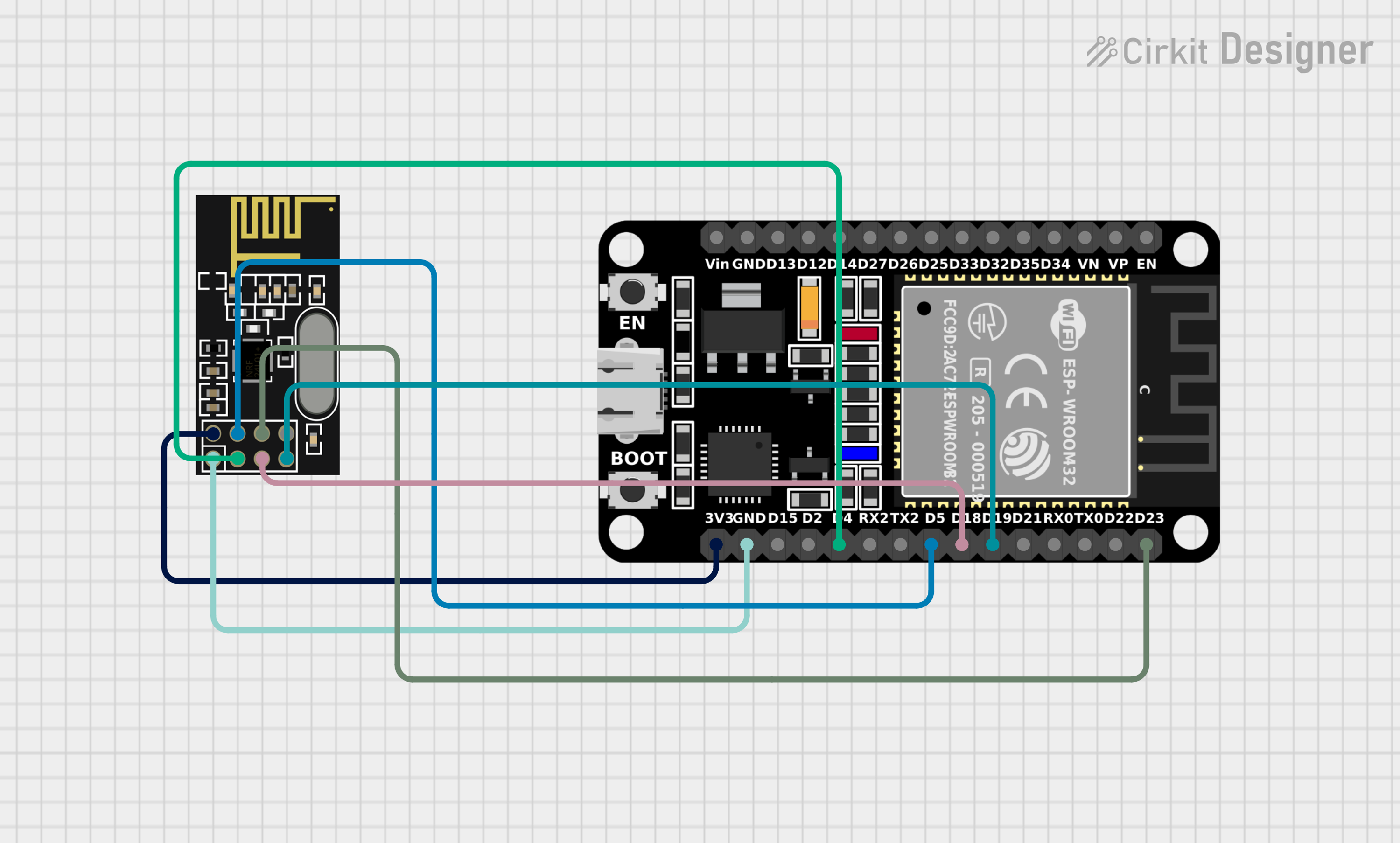
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Mini NRF24L01

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Wireless sensor networks
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices
- Remote controls for drones, robots, and other electronics
- Home automation systems
- Wireless data logging and monitoring
Technical Specifications
The Mini NRF24L01 module is built around the NRF24L01+ transceiver IC and offers the following key specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Frequency | 2.4GHz ISM band |
| Data Rate | 250kbps, 1Mbps, 2Mbps |
| Operating Voltage | 1.9V to 3.6V |
| Power Consumption | 11.3mA (transmit at 0dBm), 13.5mA (receive) |
| Sleep Mode Current | 900nA |
| Communication Protocol | SPI |
| Maximum Output Power | 0dBm |
| Sensitivity | -94dBm at 250kbps |
| Range (Line of Sight) | Up to 100 meters (with proper antenna) |
| Number of Channels | 125 |
| Address Width | 3 to 5 bytes |
| Payload Size | 1 to 32 bytes |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Mini NRF24L01 module has 8 pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground connection |
| 2 | VCC | Power supply (1.9V to 3.6V) |
| 3 | CE | Chip Enable: Activates the module for transmission or reception |
| 4 | CSN | Chip Select Not: SPI chip select (active low) |
| 5 | SCK | Serial Clock: SPI clock input |
| 6 | MOSI | Master Out Slave In: SPI data input |
| 7 | MISO | Master In Slave Out: SPI data output |
| 8 | IRQ | Interrupt Request: Indicates data received or transmission complete (optional) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Mini NRF24L01 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V power source. Do not exceed 3.6V, as this may damage the module. Connect the GND pin to the ground of your circuit.
- SPI Communication: Connect the CE, CSN, SCK, MOSI, and MISO pins to the corresponding SPI pins on your microcontroller.
- Antenna Placement: Ensure the module's onboard antenna is not obstructed by metal objects or other components to maximize range and signal quality.
- Interrupt Pin (Optional): Connect the IRQ pin to a GPIO pin on your microcontroller if you want to use interrupt-driven communication.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Use a 10µF capacitor across the VCC and GND pins to stabilize the power supply and reduce noise.
- Keep the module away from high-frequency noise sources to avoid interference.
- For longer range, consider using an external antenna or a power amplifier version of the module.
- Ensure proper SPI configuration on your microcontroller (Mode 0, MSB first).
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect the Mini NRF24L01 to an Arduino UNO and send data wirelessly.
Wiring Diagram
| NRF24L01 Pin | Arduino UNO Pin |
|---|---|
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3.3V |
| CE | Pin 9 |
| CSN | Pin 10 |
| SCK | Pin 13 |
| MOSI | Pin 11 |
| MISO | Pin 12 |
| IRQ (Optional) | Not connected |
Arduino Code Example
#include <SPI.h>
#include <nRF24L01.h>
#include <RF24.h>
// Define CE and CSN pins
#define CE_PIN 9
#define CSN_PIN 10
// Create an RF24 object
RF24 radio(CE_PIN, CSN_PIN);
// Define the address for communication
const byte address[6] = "00001";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
radio.begin(); // Initialize the NRF24L01 module
radio.openWritingPipe(address); // Set the address for transmission
radio.setPALevel(RF24_PA_LOW); // Set power level to low
radio.stopListening(); // Set the module to transmit mode
}
void loop() {
const char text[] = "Hello, World!"; // Data to send
bool success = radio.write(&text, sizeof(text)); // Send data
if (success) {
Serial.println("Data sent successfully!");
} else {
Serial.println("Data transmission failed.");
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before sending again
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Module Not Responding
- Ensure the VCC pin is connected to a 3.3V power source. Do not use 5V.
- Check all SPI connections for proper wiring.
- Add a 10µF capacitor across VCC and GND to stabilize the power supply.
Poor Range or Signal Quality
- Ensure the module's antenna is unobstructed and positioned away from metal objects.
- Use a power amplifier version of the module for extended range.
- Reduce the data rate to 250kbps for better sensitivity.
Data Transmission Fails
- Verify that the CE and CSN pins are correctly connected to the microcontroller.
- Ensure both transmitter and receiver modules are using the same address and data rate.
- Check for interference from other 2.4GHz devices (e.g., Wi-Fi routers).
FAQs
Q: Can I power the Mini NRF24L01 with 5V?
A: No, the module operates at 1.9V to 3.6V. Use a 3.3V regulator if your system provides only 5V.
Q: What is the maximum range of the Mini NRF24L01?
A: The range is up to 100 meters in line-of-sight conditions. Obstacles and interference may reduce the range.
Q: Can I use multiple NRF24L01 modules in the same network?
A: Yes, the module supports up to 6 simultaneous data pipes, allowing communication with multiple devices.
Q: How do I debug communication issues?
A: Use the radio.printDetails() function from the RF24 library to check the module's configuration and status.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the Mini NRF24L01 module into your projects and troubleshoot common issues.