
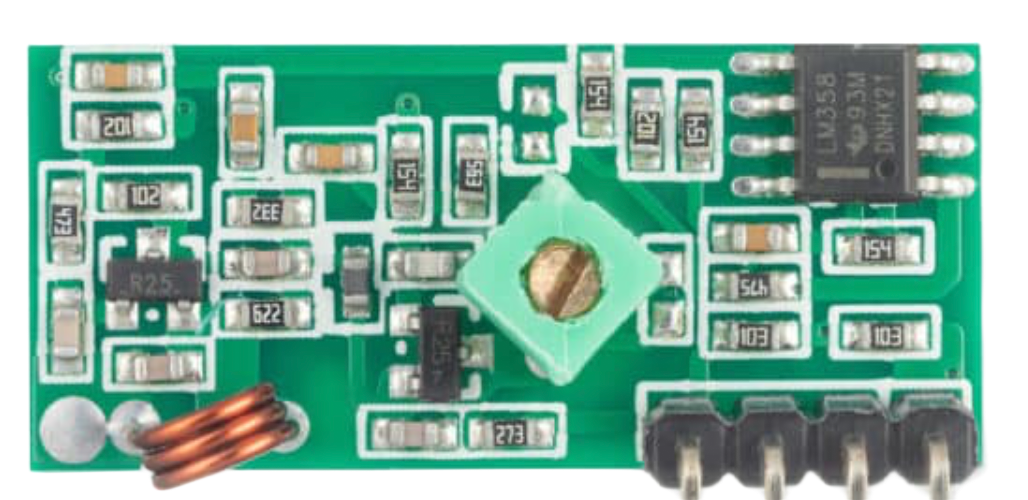
How to Use Receiver Module : Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Receiver Module in Cirkit Designer
Design with Receiver Module in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Receiver Module is a device designed to receive signals, typically in wireless communication systems, and convert them into usable data or audio. It plays a critical role in enabling communication between devices by capturing transmitted signals and processing them for further use. Receiver Modules are widely used in applications such as remote controls, wireless data transmission, audio systems, and IoT devices.
Common applications and use cases:
- Wireless remote controls (e.g., TV remotes, garage door openers)
- IoT devices for data communication
- Wireless audio systems
- RF-based communication systems
- Robotics and automation systems
Explore Projects Built with Receiver Module
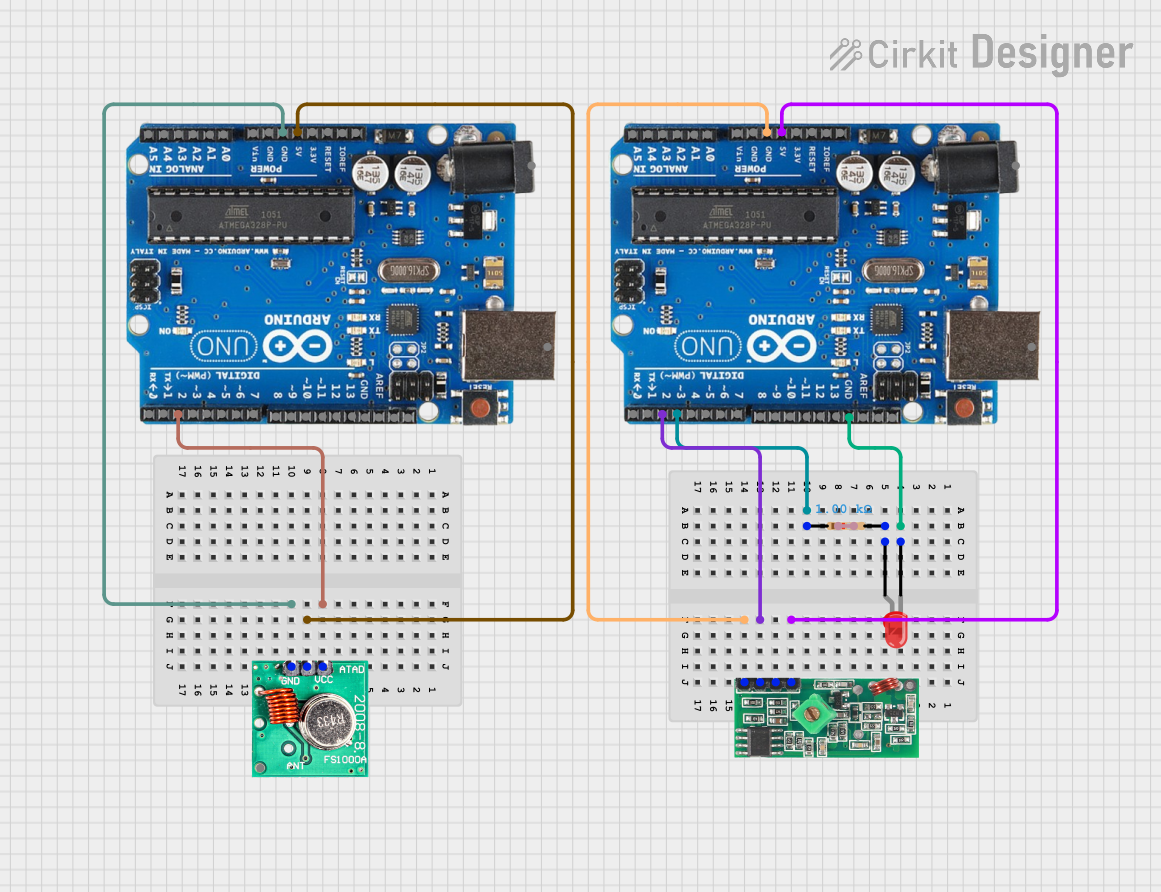
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer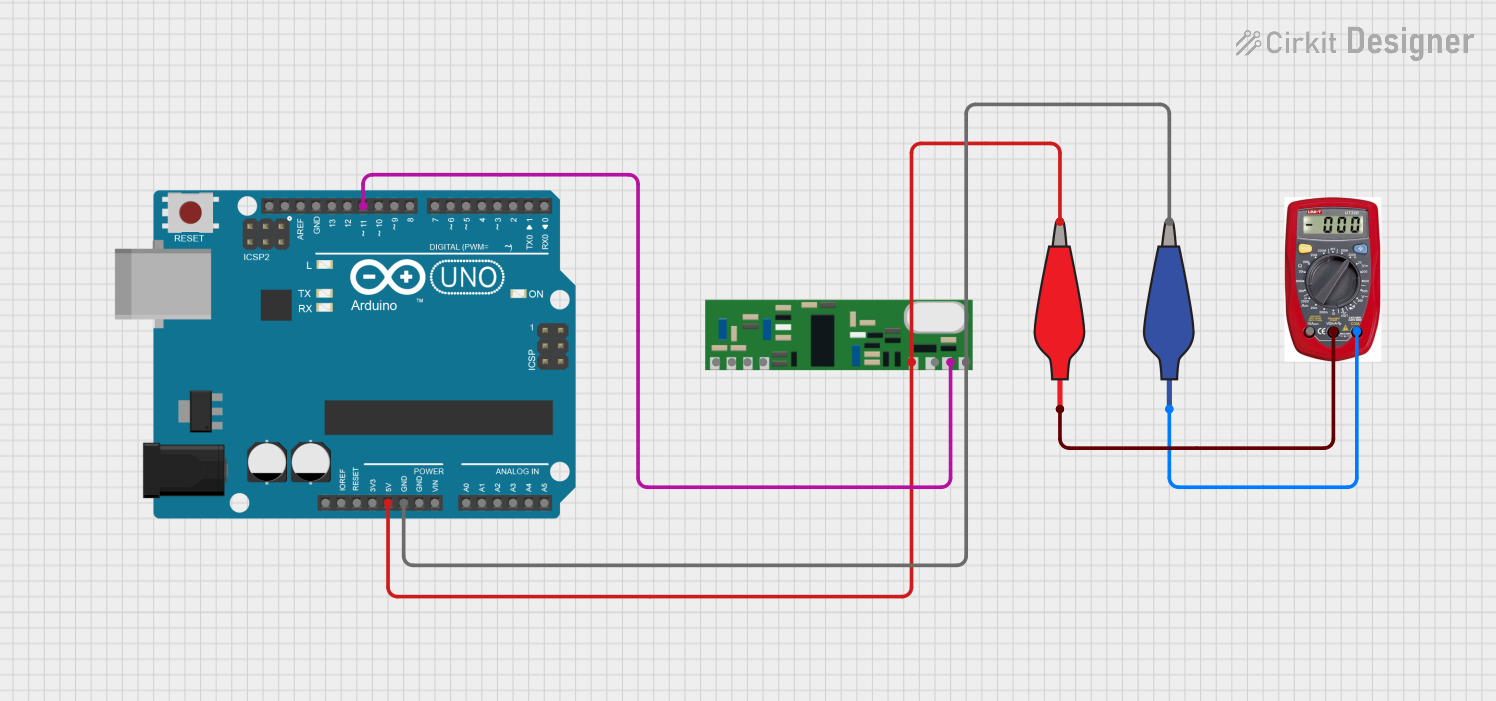
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer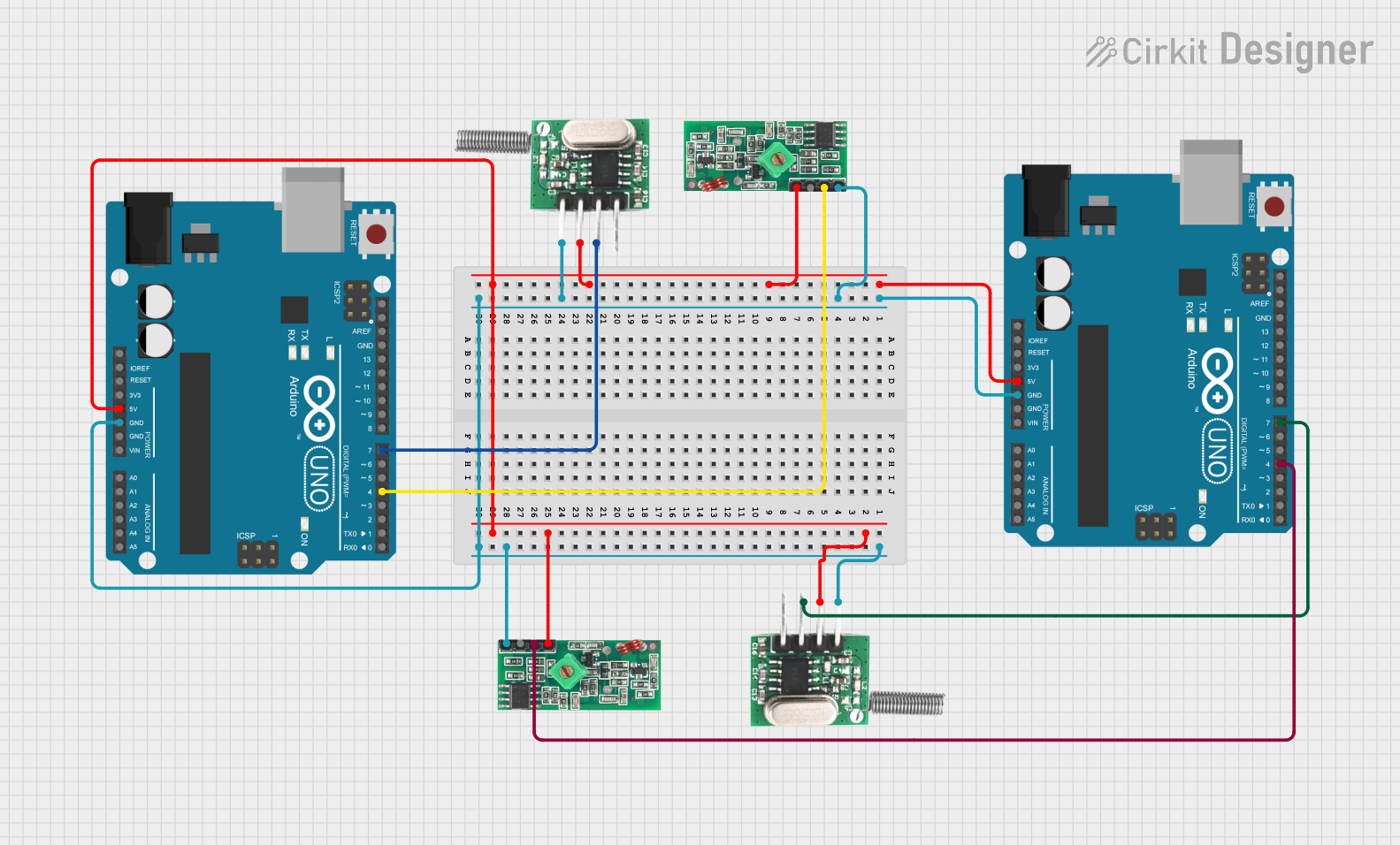
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Receiver Module

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of a typical Receiver Module:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Operating Frequency | 315 MHz / 433 MHz (varies by model) |
| Sensitivity | -105 dBm (typical) |
| Data Rate | Up to 10 kbps |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to +70°C |
| Dimensions | Varies by model (e.g., 30mm x 14mm) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Receiver Module typically has 4 pins. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply pin. Connect to 3.3V or 5V depending on the module specifications. |
| 2 | GND | Ground pin. Connect to the ground of the circuit. |
| 3 | DATA | Data output pin. Outputs the received signal for further processing. |
| 4 | ANT | Antenna pin. Connect to an external antenna for better signal reception. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Receiver Module in a Circuit
- Power the Module: Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5V power source and theGNDpin to the ground of your circuit. - Connect the Data Pin: The
DATApin outputs the received signal. Connect this pin to a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino) or a decoder IC for further processing. - Attach an Antenna: For optimal performance, connect an external antenna to the
ANTpin. The antenna length should match the operating frequency (e.g., ~17 cm for 433 MHz). - Decode the Signal: Use a microcontroller or a dedicated decoder IC to interpret the received signal.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure a stable power supply to avoid noise and signal distortion.
- Antenna Placement: Place the antenna away from metal objects and other sources of interference for better reception.
- Signal Decoding: Use a compatible encoder/decoder pair (e.g., HT12D/HT12E) for reliable communication.
- Frequency Matching: Ensure the transmitter and receiver modules operate at the same frequency (e.g., 433 MHz).
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the Receiver Module with an Arduino UNO to receive data:
// Example code to read data from a 433 MHz Receiver Module
// Connect the DATA pin of the Receiver Module to Arduino pin 2
#define RECEIVER_PIN 2 // Pin connected to the DATA pin of the Receiver Module
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
pinMode(RECEIVER_PIN, INPUT); // Set the receiver pin as input
}
void loop() {
int receivedSignal = digitalRead(RECEIVER_PIN); // Read the signal from the receiver
Serial.println(receivedSignal); // Print the received signal to the Serial Monitor
delay(100); // Add a small delay to avoid flooding the Serial Monitor
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Signal Received:
- Solution: Check the power supply and ensure the module is powered correctly. Verify that the transmitter and receiver are operating at the same frequency.
Interference or Noise:
- Solution: Use a properly tuned antenna and place it away from sources of interference such as motors or other RF devices.
Unstable Output:
- Solution: Ensure a stable power supply and use decoupling capacitors near the module to filter noise.
Short Range:
- Solution: Use a longer antenna or a higher-gain antenna. Ensure there are no obstructions between the transmitter and receiver.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use the Receiver Module without an antenna?
A1: While it is possible, the range and signal quality will be significantly reduced. It is recommended to use a properly tuned antenna.
Q2: What is the maximum range of the Receiver Module?
A2: The range depends on factors such as the antenna, power supply, and environmental conditions. Typically, it ranges from 50 to 100 meters in open space.
Q3: Can I use multiple Receiver Modules in the same area?
A3: Yes, but ensure that each module is paired with a unique transmitter to avoid interference.
Q4: How do I decode the received signal?
A4: Use a microcontroller or a dedicated decoder IC (e.g., HT12D) to process the signal and extract the transmitted data.