
How to Use RS485: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with RS485 in Cirkit Designer
Design with RS485 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
RS485 is a standard for serial communication that enables reliable, long-distance data transmission. It supports multiple devices on a single bus, making it ideal for multi-point communication. RS485 is widely used in industrial applications due to its robustness, noise immunity, and ability to operate over extended distances. It is commonly employed in systems such as building automation, industrial control systems, and data acquisition networks.
Explore Projects Built with RS485
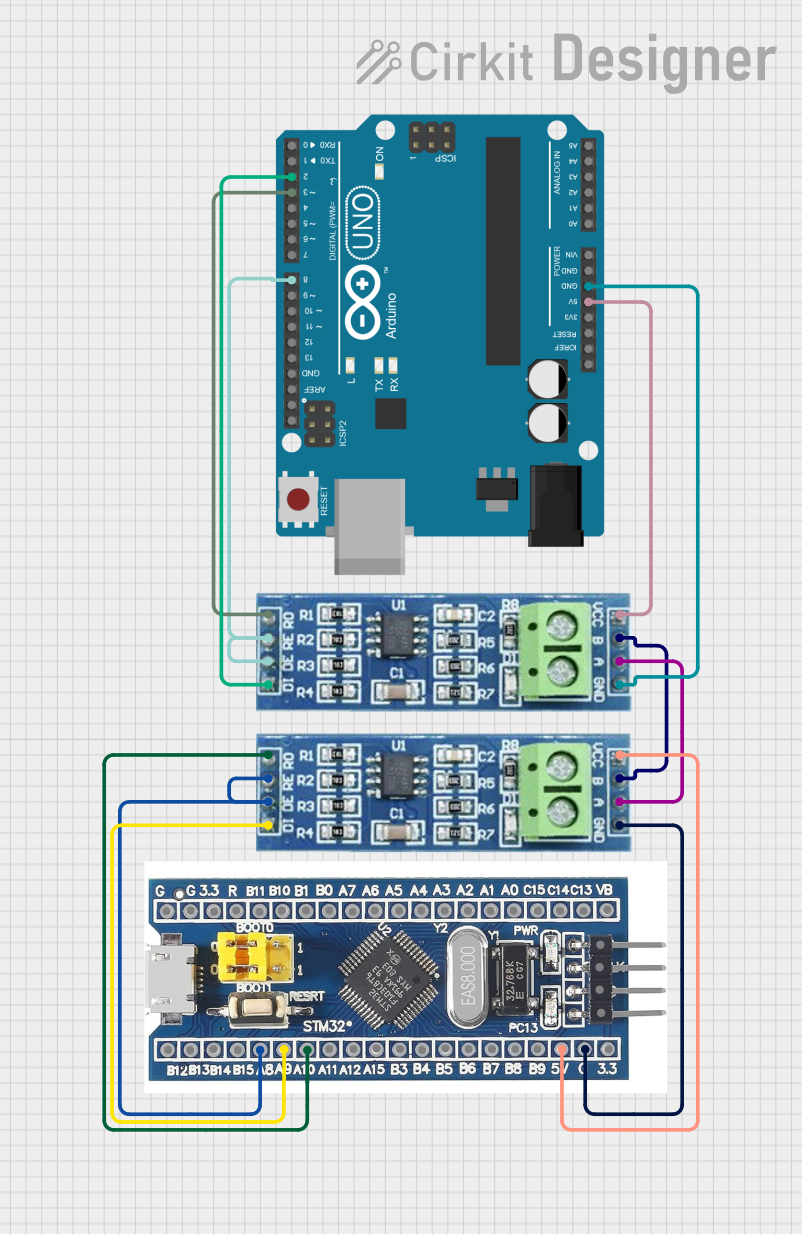
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer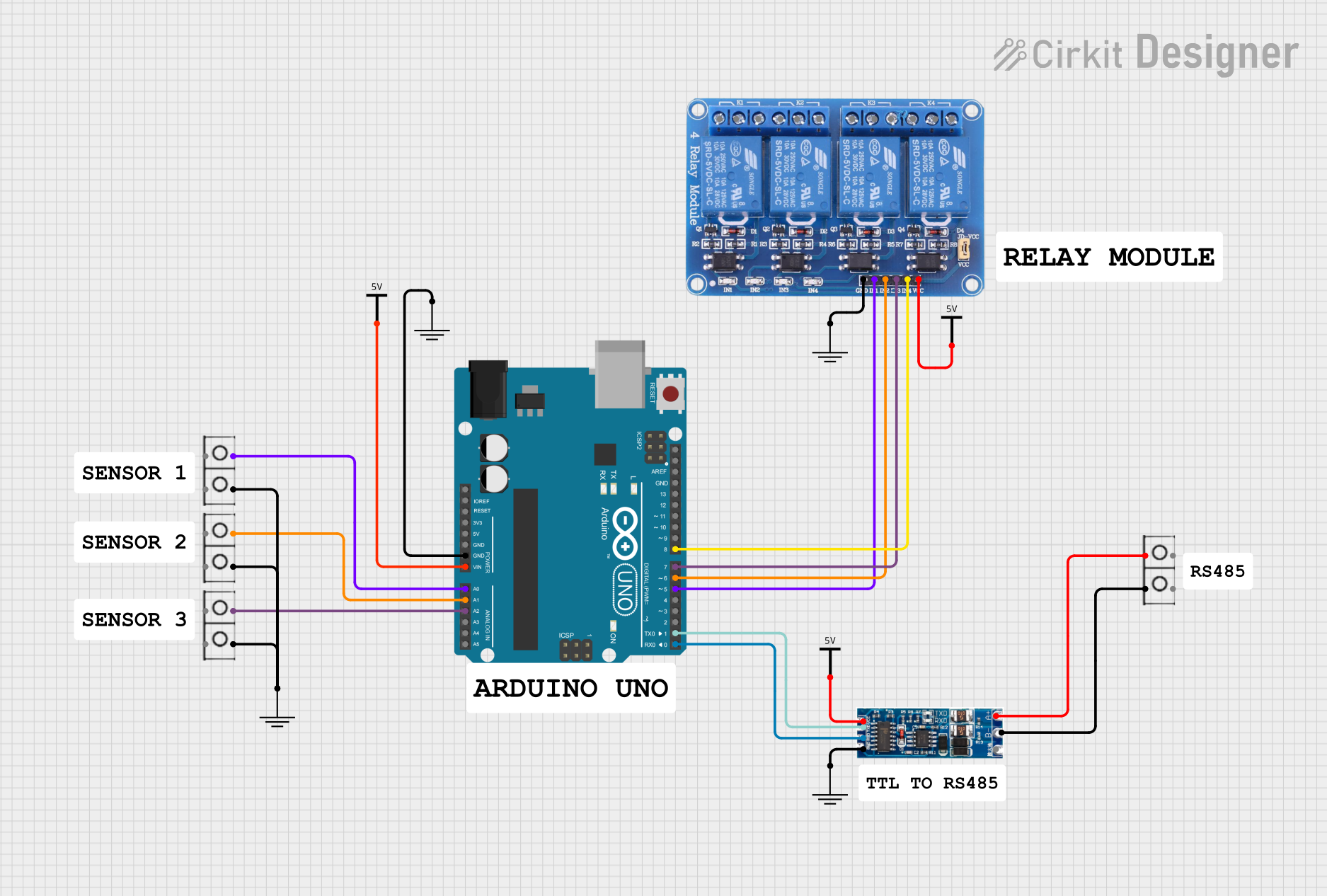
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer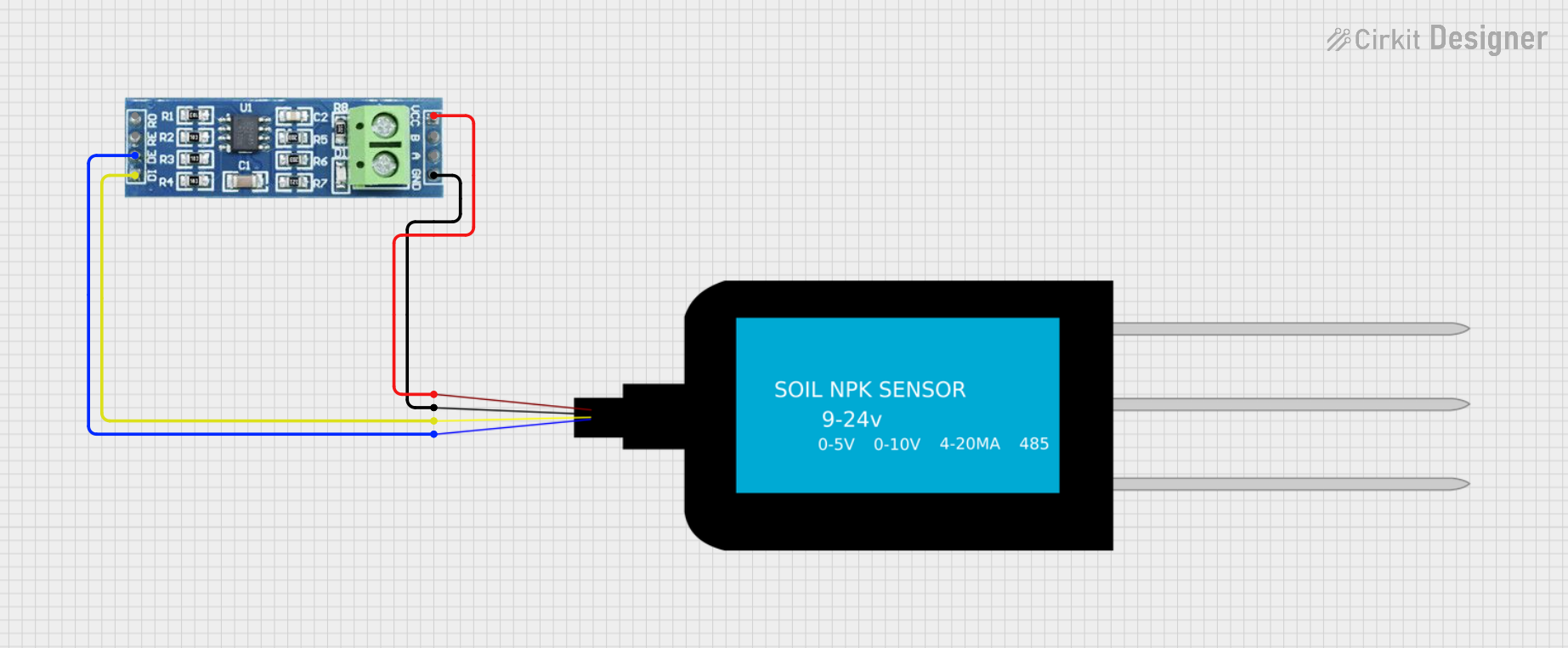
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer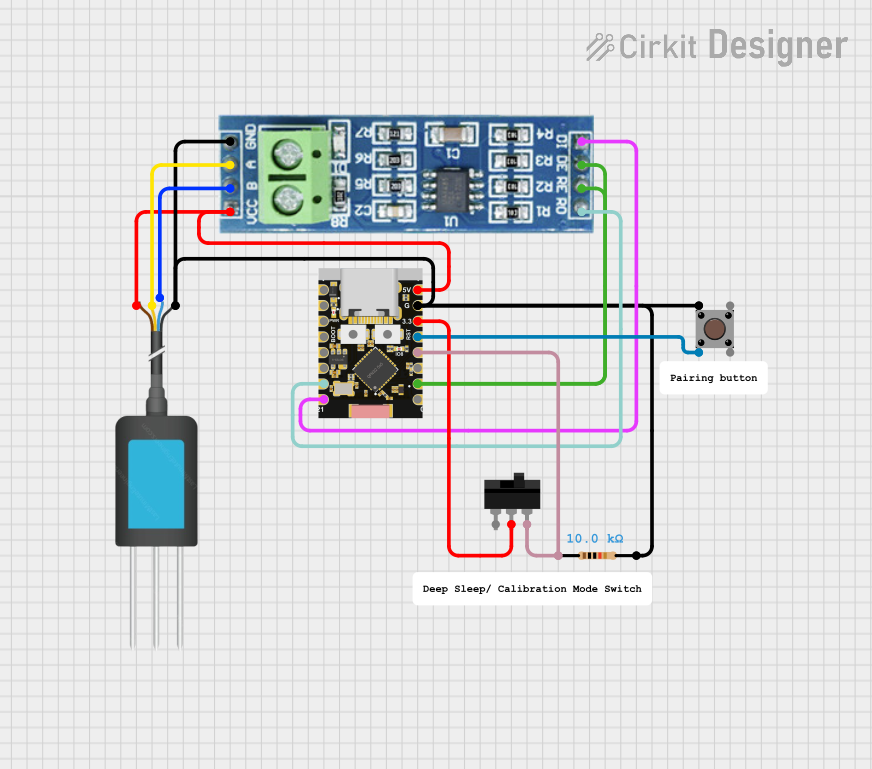
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with RS485

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
- Communication Standard: RS485 (TIA/EIA-485)
- Maximum Data Rate: Up to 10 Mbps (short distances)
- Maximum Cable Length: Up to 1200 meters (at lower data rates, typically 100 kbps)
- Number of Devices: Supports up to 32 drivers and 32 receivers on a single bus
- Voltage Levels: Differential signaling with typical voltage levels of ±1.5V to ±5V
- Termination: Requires termination resistors at both ends of the bus to prevent signal reflections
- Connector Type: Typically uses screw terminals or DB9 connectors
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The RS485 transceiver typically has the following pin configuration:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| A (D+) | Non-inverting differential signal line (positive data line) |
| B (D-) | Inverting differential signal line (negative data line) |
| GND | Ground reference for the communication bus |
| VCC | Power supply for the transceiver (commonly 3.3V or 5V) |
| DE | Driver Enable: Activates the driver for transmitting data |
| RE | Receiver Enable: Activates the receiver for receiving data |
| DI | Data Input: Input data to be transmitted (connected to the microcontroller) |
| RO | Receiver Output: Output data received from the bus (connected to the microcontroller) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use RS485 in a Circuit
Connect the RS485 Transceiver:
- Connect the A (D+) and B (D-) pins to the RS485 bus.
- Attach termination resistors (typically 120 ohms) at both ends of the bus to reduce signal reflections.
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of the system.
- Provide power to the VCC pin (3.3V or 5V, depending on the transceiver).
Enable Communication:
- Use the DE (Driver Enable) pin to control when the transceiver sends data. Set DE high to enable transmission.
- Use the RE (Receiver Enable) pin to control when the transceiver receives data. Set RE low to enable reception.
Connect to a Microcontroller:
- Connect the DI pin to the microcontroller's TX (transmit) pin.
- Connect the RO pin to the microcontroller's RX (receive) pin.
Write Code for Communication:
- Use a UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter) interface on the microcontroller to send and receive data over RS485.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use RS485 with an Arduino UNO:
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define RS485 pins
#define DE_PIN 2 // Driver Enable pin
#define RE_PIN 3 // Receiver Enable pin
#define TX_PIN 4 // TX pin for RS485
#define RX_PIN 5 // RX pin for RS485
// Create a SoftwareSerial object for RS485 communication
SoftwareSerial RS485Serial(RX_PIN, TX_PIN);
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication
Serial.begin(9600); // For debugging via Serial Monitor
RS485Serial.begin(9600); // RS485 communication baud rate
// Set DE and RE pins as outputs
pinMode(DE_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RE_PIN, OUTPUT);
// Set RS485 to receive mode initially
digitalWrite(DE_PIN, LOW); // Disable driver
digitalWrite(RE_PIN, LOW); // Enable receiver
}
void loop() {
// Example: Send data over RS485
digitalWrite(DE_PIN, HIGH); // Enable driver
digitalWrite(RE_PIN, HIGH); // Disable receiver
RS485Serial.println("Hello, RS485!"); // Send data
delay(100); // Short delay to ensure data is sent
digitalWrite(DE_PIN, LOW); // Disable driver
digitalWrite(RE_PIN, LOW); // Enable receiver
// Example: Receive data over RS485
if (RS485Serial.available()) {
String receivedData = RS485Serial.readString();
Serial.println("Received: " + receivedData); // Print received data
}
delay(1000); // Wait before next iteration
}
Important Considerations
- Termination Resistors: Always use termination resistors at both ends of the RS485 bus to prevent signal reflections and ensure reliable communication.
- Biasing Resistors: Use pull-up and pull-down resistors on the A and B lines to maintain a known idle state when no devices are transmitting.
- Grounding: Ensure all devices on the RS485 bus share a common ground to avoid communication errors.
- Bus Length and Data Rate: The maximum cable length decreases as the data rate increases. Choose appropriate settings based on your application.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Communication Between Devices:
- Verify the wiring of the A (D+) and B (D-) lines. Ensure they are not swapped.
- Check that the DE and RE pins are correctly controlled for transmission and reception.
Data Corruption or Noise:
- Ensure termination resistors are installed at both ends of the RS485 bus.
- Use shielded twisted-pair cables to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Devices Not Responding:
- Confirm that all devices share a common ground.
- Check the power supply voltage and ensure it matches the transceiver's requirements.
Communication Fails Over Long Distances:
- Reduce the data rate to improve signal integrity over long distances.
- Use repeaters if the cable length exceeds 1200 meters.
FAQs
Q: Can RS485 support full-duplex communication?
A: RS485 is inherently half-duplex, but full-duplex communication can be achieved by using two separate RS485 transceivers.Q: How many devices can I connect to an RS485 bus?
A: RS485 supports up to 32 drivers and 32 receivers. However, modern transceivers may allow more devices.Q: Do I need special software to use RS485?
A: No, RS485 uses standard UART communication, which is supported by most microcontrollers.Q: Can I use RS485 for wireless communication?
A: RS485 is a wired communication standard. For wireless communication, consider using protocols like Zigbee or LoRa.