
How to Use ESP 32 CAM: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with ESP 32 CAM in Cirkit Designer
Design with ESP 32 CAM in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ESP32-CAM is a low-cost, low-power system on a chip (SoC) that integrates Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, along with a camera module for image and video capture. It is based on the ESP32 microcontroller and is widely used in IoT projects and applications requiring remote monitoring, such as home automation, security systems, and wireless video streaming. Its compact size and powerful features make it an excellent choice for developers and hobbyists alike.
Explore Projects Built with ESP 32 CAM
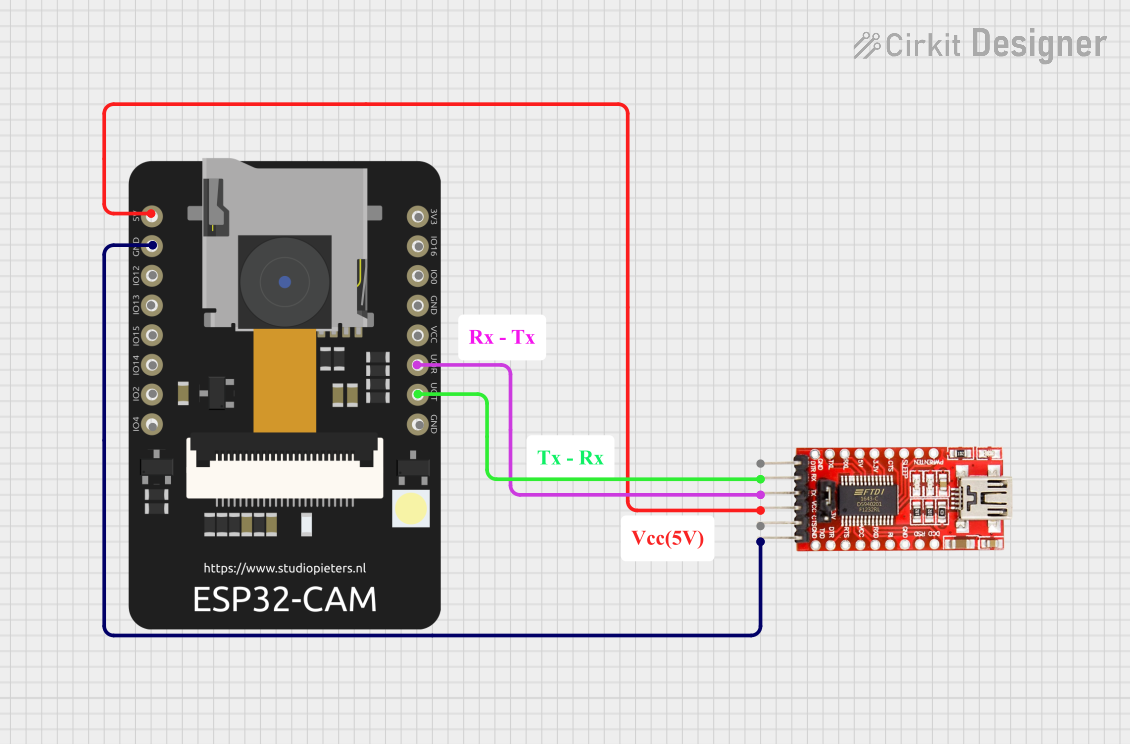
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer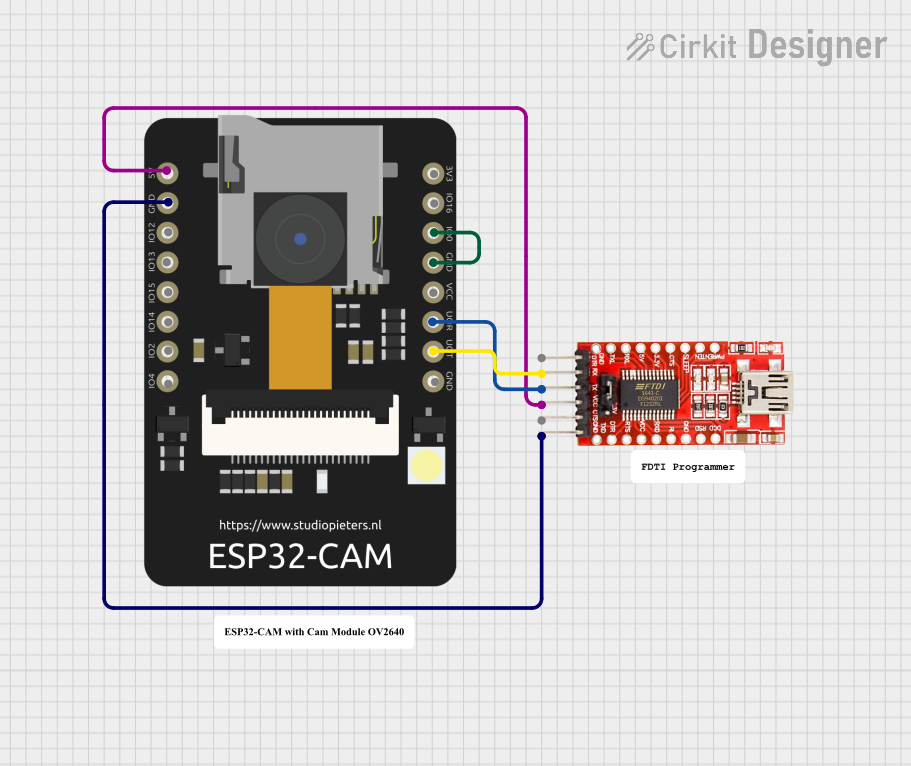
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer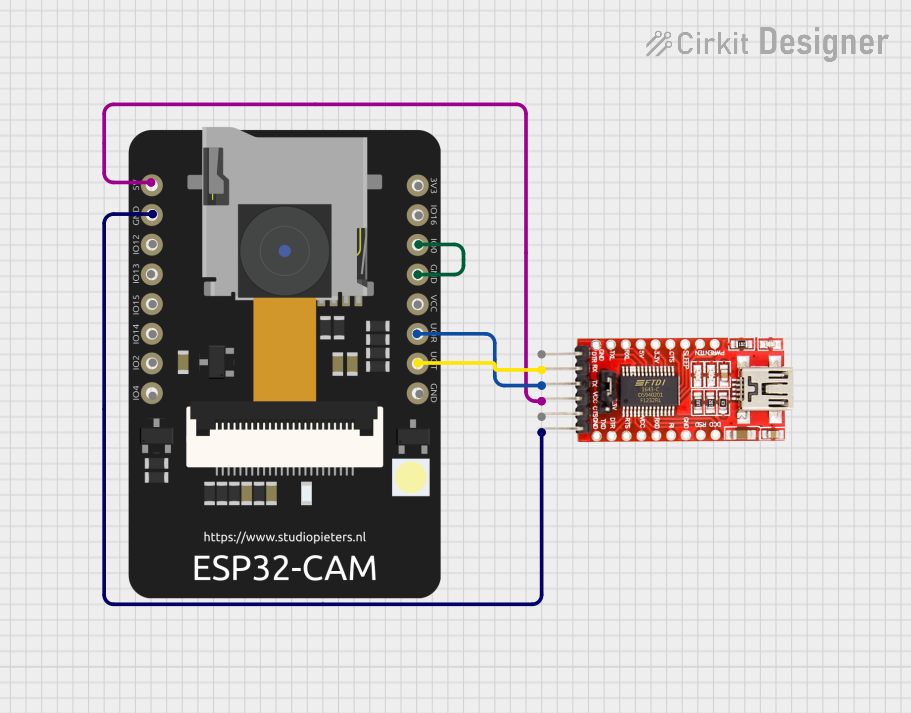
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer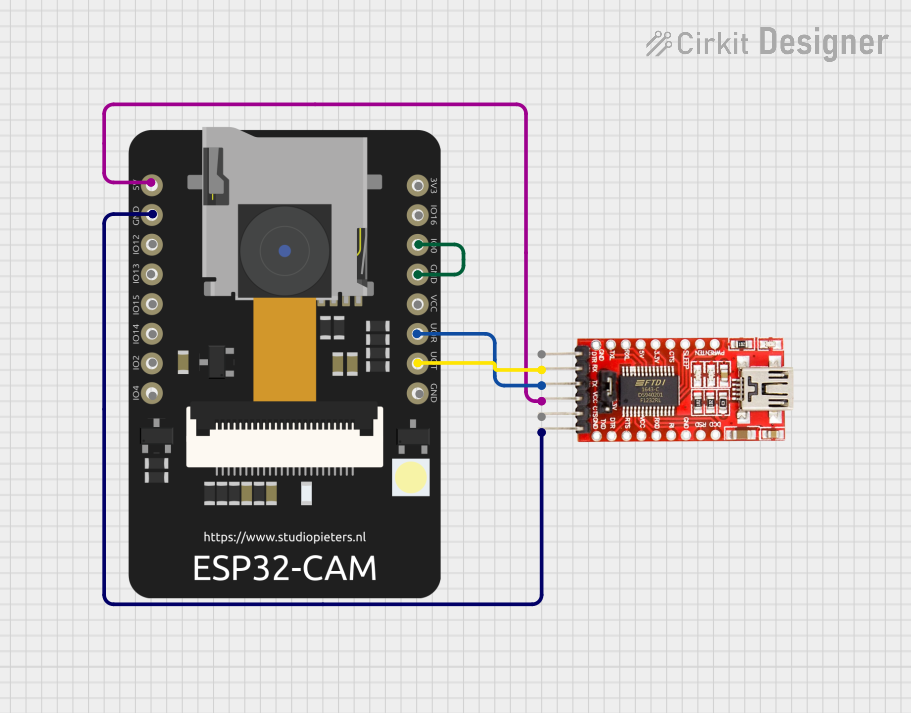
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ESP 32 CAM

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Wireless video surveillance and monitoring
- Smart home automation systems
- IoT devices with image or video processing
- Face recognition and object detection
- Remote-controlled robots with live video feed
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Microcontroller | ESP32-D0WDQ6 |
| Wireless Connectivity | Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n, Bluetooth 4.2 |
| Camera Module | OV2640 (2MP) |
| Flash Memory | 4 MB (PSRAM) |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V |
| Input Voltage Range | 5V (via micro-USB or external source) |
| GPIO Pins | 9 (configurable for various functions) |
| Power Consumption | ~160 mA (active), ~10 µA (deep sleep) |
| Dimensions | 27mm x 40.5mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ESP32-CAM has a total of 16 pins. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Name | Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GND | 1 | Ground |
| 3.3V | 2 | 3.3V Power Supply |
| IO0 | 3 | GPIO0, used for boot mode selection |
| IO1 | 4 | GPIO1, UART TX |
| IO2 | 5 | GPIO2, General-purpose I/O |
| IO3 | 6 | GPIO3, UART RX |
| IO4 | 7 | GPIO4, General-purpose I/O |
| IO12 | 8 | GPIO12, General-purpose I/O |
| IO13 | 9 | GPIO13, General-purpose I/O |
| IO14 | 10 | GPIO14, General-purpose I/O |
| IO15 | 11 | GPIO15, General-purpose I/O |
| IO16 | 12 | GPIO16, General-purpose I/O |
| IO17 | 13 | GPIO17, General-purpose I/O |
| RESET | 14 | Reset Pin |
| TXD0 | 15 | UART0 Transmit |
| RXD0 | 16 | UART0 Receive |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the ESP32-CAM in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Provide a stable 5V power supply to the ESP32-CAM via the micro-USB port or the 5V pin. Ensure the current supply is sufficient (at least 500mA).
- Boot Mode: To upload code, connect GPIO0 to GND and reset the board. After uploading, disconnect GPIO0 from GND and reset the board again to run the program.
- Camera Module: The OV2640 camera module is pre-attached. Ensure it is securely connected to the board before powering it on.
- Connections: Use the GPIO pins for interfacing with external components like sensors, LEDs, or relays. Note that some GPIO pins are reserved for the camera and cannot be used for other purposes.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: The ESP32-CAM operates at 3.3V logic levels. Avoid connecting 5V signals directly to its GPIO pins.
- Heat Management: The ESP32-CAM can get warm during operation. Ensure proper ventilation or use a heatsink if necessary.
- Antenna: The onboard PCB antenna provides decent Wi-Fi range. For better performance, use an external antenna (via the IPEX connector).
- Programming: Use a USB-to-TTL converter (e.g., FTDI module) to upload code, as the ESP32-CAM does not have a built-in USB interface.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the ESP32-CAM with the Arduino IDE to capture and stream video:
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <esp_camera.h>
// Replace with your Wi-Fi credentials
const char* ssid = "Your_SSID";
const char* password = "Your_PASSWORD";
// Camera configuration
#define PWDN_GPIO_NUM -1
#define RESET_GPIO_NUM -1
#define XCLK_GPIO_NUM 0
#define SIOD_GPIO_NUM 26
#define SIOC_GPIO_NUM 27
#define Y9_GPIO_NUM 35
#define Y8_GPIO_NUM 34
#define Y7_GPIO_NUM 39
#define Y6_GPIO_NUM 36
#define Y5_GPIO_NUM 21
#define Y4_GPIO_NUM 19
#define Y3_GPIO_NUM 18
#define Y2_GPIO_NUM 5
#define VSYNC_GPIO_NUM 25
#define HREF_GPIO_NUM 23
#define PCLK_GPIO_NUM 22
void startCameraServer();
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
// Wait for Wi-Fi connection
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
// Initialize the camera
camera_config_t config;
config.ledc_channel = LEDC_CHANNEL_0;
config.ledc_timer = LEDC_TIMER_0;
config.pin_d0 = Y2_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d1 = Y3_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d2 = Y4_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d3 = Y5_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d4 = Y6_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d5 = Y7_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d6 = Y8_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d7 = Y9_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_xclk = XCLK_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_pclk = PCLK_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_vsync = VSYNC_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_href = HREF_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_sscb_sda = SIOD_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_sscb_scl = SIOC_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_pwdn = PWDN_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_reset = RESET_GPIO_NUM;
config.xclk_freq_hz = 20000000;
config.pixel_format = PIXFORMAT_JPEG;
if (!esp_camera_init(&config)) {
Serial.println("Camera initialized successfully");
} else {
Serial.println("Camera initialization failed");
return;
}
startCameraServer();
Serial.println("Camera server started");
}
void loop() {
// Main loop does nothing; camera server handles requests
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Wi-Fi Connection Fails:
- Ensure the SSID and password are correct.
- Check if the Wi-Fi signal strength is sufficient.
Camera Initialization Fails:
- Verify that the camera module is securely connected.
- Ensure the correct camera configuration is used in the code.
Board Overheats:
- Avoid prolonged operation at high power levels.
- Use a heatsink or ensure proper ventilation.
Code Upload Fails:
- Ensure GPIO0 is connected to GND during code upload.
- Check the USB-to-TTL converter connections.
Tips for Troubleshooting
- Use the Serial Monitor to debug issues and view error messages.
- Double-check all connections and power supply levels.
- Update the ESP32 board package in the Arduino IDE to the latest version.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the ESP32-CAM for your IoT and video streaming projects.