
How to Use Buck Converter 6v-60v to 1.5v-30v: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Buck Converter 6v-60v to 1.5v-30v in Cirkit Designer
Design with Buck Converter 6v-60v to 1.5v-30v in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A buck converter is a DC-DC power converter that steps down voltage from a higher input voltage range (6V-60V) to a lower output voltage range (1.5V-30V). It is commonly used in power supply circuits to efficiently reduce voltage levels. This component is essential in applications where a stable and lower voltage is required from a higher voltage source, such as in battery-powered devices, automotive electronics, and various embedded systems.
Explore Projects Built with Buck Converter 6v-60v to 1.5v-30v

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Buck Converter 6v-60v to 1.5v-30v

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 6V - 60V |
| Output Voltage Range | 1.5V - 30V |
| Output Current | Up to 5A (depending on input voltage and cooling) |
| Efficiency | Up to 95% |
| Switching Frequency | 150kHz |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | 60mm x 21mm x 14mm |
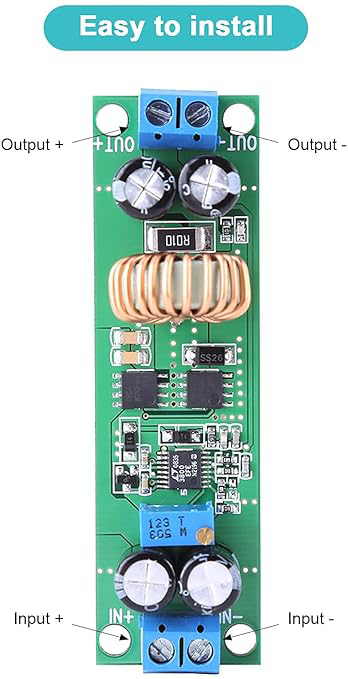
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VIN | Input Voltage (6V - 60V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground |
| 3 | VOUT | Output Voltage (1.5V - 30V) |
| 4 | ADJ | Output Voltage Adjustment (via potentiometer) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the Input Voltage:
- Connect the positive terminal of your power source to the
VINpin. - Connect the negative terminal of your power source to the
GNDpin.
- Connect the positive terminal of your power source to the
Connect the Output Voltage:
- Connect the
VOUTpin to the load where the stepped-down voltage is required. - Ensure the
GNDpin is also connected to the ground of the load.
- Connect the
Adjust the Output Voltage:
- Use the potentiometer connected to the
ADJpin to adjust the output voltage. - Measure the output voltage with a multimeter while adjusting to achieve the desired voltage level.
- Use the potentiometer connected to the
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Heat Dissipation: Ensure adequate cooling for the buck converter, especially when operating at higher currents. Use heat sinks or active cooling if necessary.
- Input Voltage Range: Do not exceed the specified input voltage range (6V-60V) to avoid damaging the converter.
- Output Current: Be mindful of the maximum output current (up to 5A). Exceeding this limit can cause overheating and potential failure.
- Polarity: Double-check the polarity of the connections to prevent damage to the converter and connected devices.
Example Circuit with Arduino UNO
To use the buck converter with an Arduino UNO, you can power the Arduino with a stable 5V output from the converter.
// Example code to blink an LED connected to pin 13 of Arduino UNO
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
No Output Voltage:
- Solution: Check the input voltage connections and ensure they are within the specified range. Verify that the ground connections are secure.
Overheating:
- Solution: Ensure proper cooling and ventilation. Use heat sinks or active cooling methods if necessary. Check if the output current exceeds the specified limit.
Unstable Output Voltage:
- Solution: Verify the input voltage stability. Adjust the potentiometer carefully and ensure it is not loose. Check for any loose connections in the circuit.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use the buck converter to power my Arduino UNO directly?
- A1: Yes, you can set the output voltage of the buck converter to 5V and connect it to the 5V pin of the Arduino UNO.
Q2: What happens if I exceed the input voltage range?
- A2: Exceeding the input voltage range can damage the buck converter and connected devices. Always ensure the input voltage is within the specified range (6V-60V).
Q3: How do I know if the buck converter is overheating?
- A3: If the converter becomes too hot to touch or if you notice a significant drop in efficiency, it may be overheating. Ensure proper cooling and check the output current.
By following this documentation, users can effectively utilize the buck converter in their projects, ensuring efficient and stable voltage regulation.