
How to Use IP2326 2S LX LSCV2: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with IP2326 2S LX LSCV2 in Cirkit Designer
Design with IP2326 2S LX LSCV2 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The IP2326 2S LX LSCV2 is a highly efficient lithium-ion battery protection integrated circuit (IC) designed for 2-cell (2S) battery packs. It provides overcharge, over-discharge, overcurrent, and short-circuit protection, ensuring the safety and longevity of lithium-ion batteries. This IC is commonly used in battery management systems (BMS) for portable electronics, power tools, and other rechargeable devices.
Explore Projects Built with IP2326 2S LX LSCV2
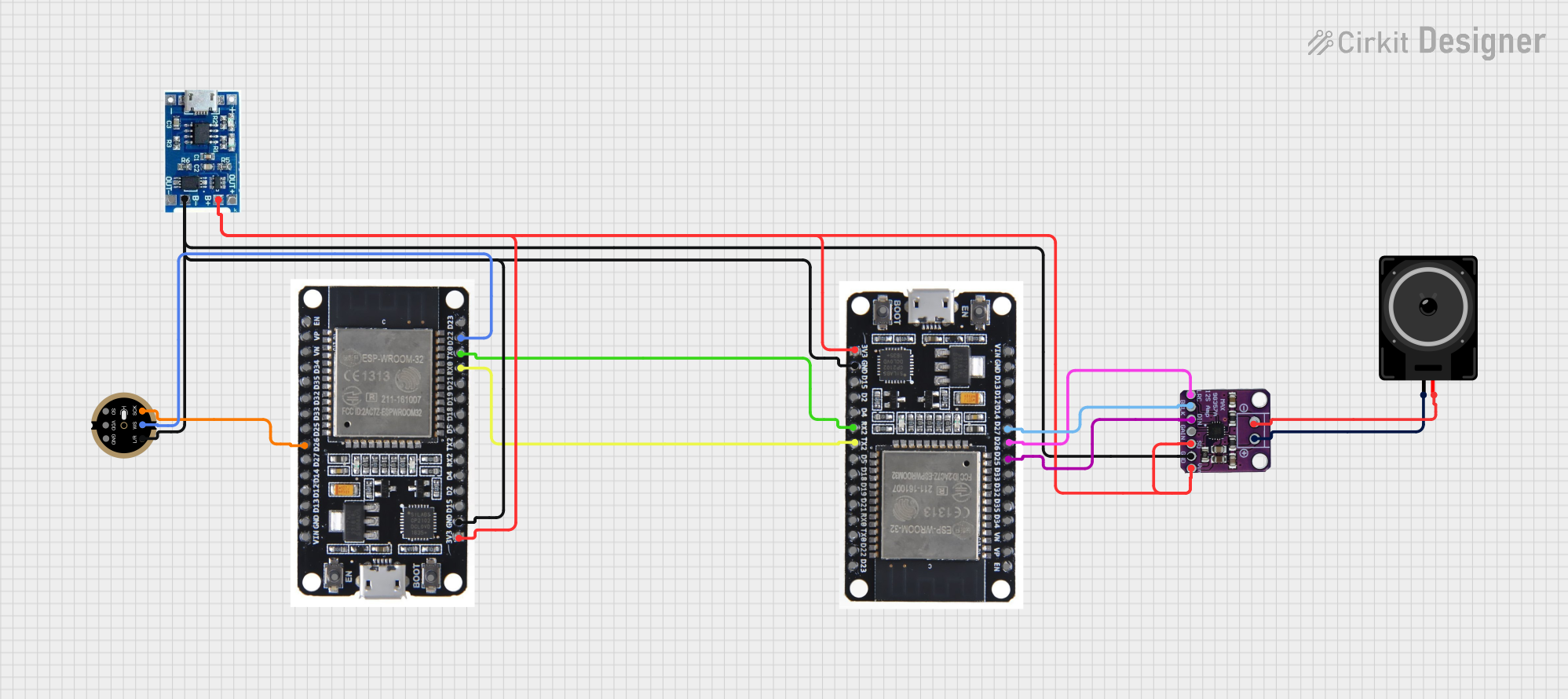
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer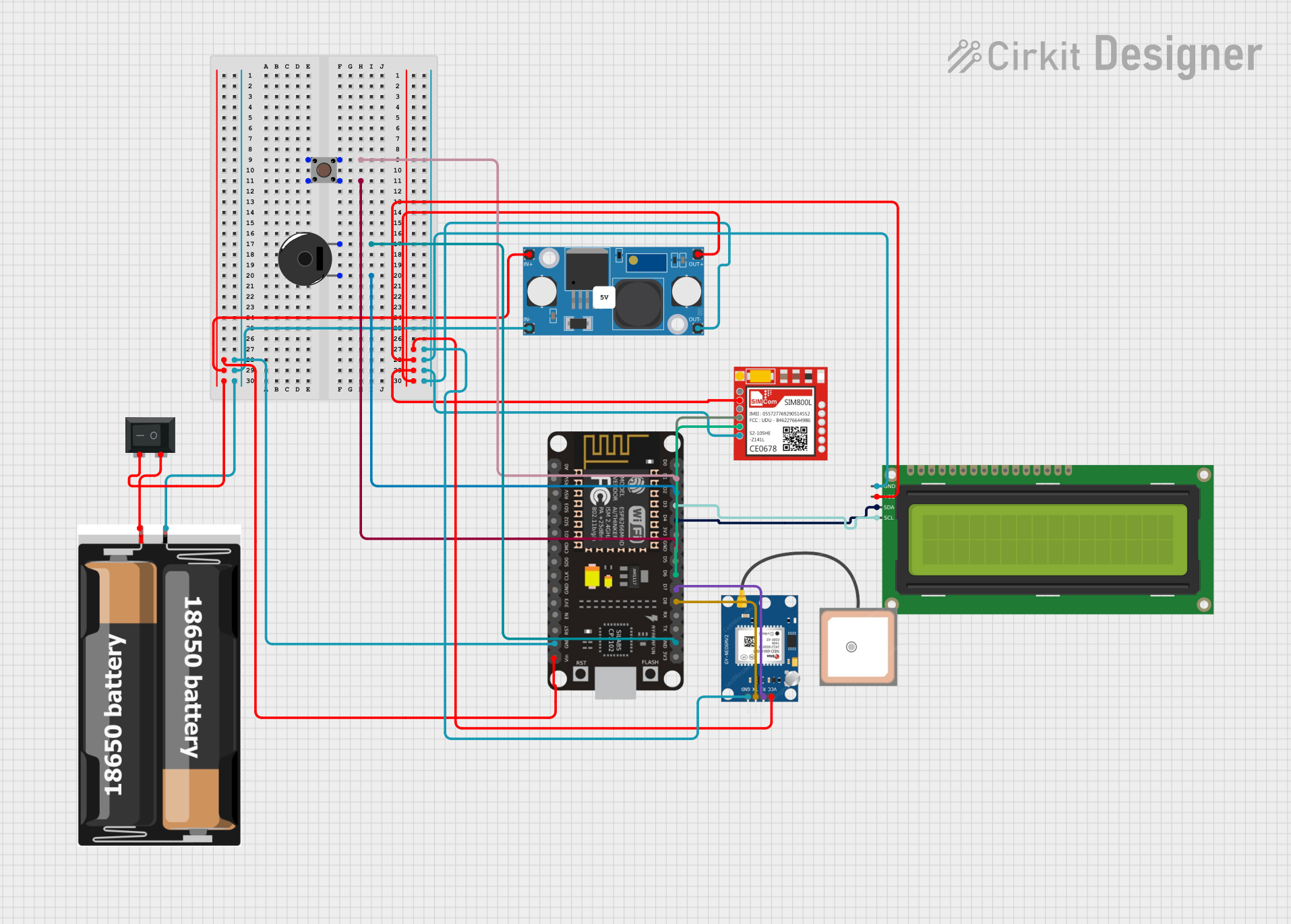
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with IP2326 2S LX LSCV2

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Lithium-ion battery packs for consumer electronics
- Power tools and cordless devices
- Electric bicycles and scooters
- Backup power systems and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS)
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Operating Voltage Range: 4.25V to 8.4V (2-cell configuration)
- Overcharge Detection Voltage: 4.25V ± 0.025V per cell
- Over-discharge Detection Voltage: 2.50V ± 0.08V per cell
- Overcurrent Protection: 3A to 6A (configurable via external components)
- Short-Circuit Protection: Triggered at high current spikes
- Quiescent Current: ≤ 10µA
- Operating Temperature Range: -40°C to +85°C
- Package Type: SOT-23-6
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The IP2326 2S LX LSCV2 comes in a 6-pin SOT-23 package. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VDD | Positive power supply input; connects to the positive terminal of the battery. |
| 2 | COUT | Overcharge detection output; controls the external MOSFET for charge protection. |
| 3 | DOUT | Over-discharge detection output; controls the external MOSFET for discharge protection. |
| 4 | VSS | Ground connection; connects to the negative terminal of the battery. |
| 5 | VM | Voltage monitoring input for the second cell in the 2S configuration. |
| 6 | V1 | Voltage monitoring input for the first cell in the 2S configuration. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the Battery Pack:
- Connect the positive terminal of the battery pack to the VDD pin.
- Connect the negative terminal of the battery pack to the VSS pin.
- Connect the midpoint between the two cells to the VM pin for voltage monitoring.
External MOSFETs:
- Use N-channel MOSFETs for charge and discharge control.
- Connect the gates of the MOSFETs to the COUT and DOUT pins, respectively.
Load and Charger Connections:
- Connect the load to the discharge MOSFET's drain.
- Connect the charger to the charge MOSFET's drain.
Resistors and Capacitors:
- Add appropriate resistors and capacitors as specified in the datasheet to stabilize the circuit and configure overcurrent protection.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the battery pack is properly balanced before connecting to the IC.
- Use low-resistance MOSFETs to minimize power loss and heat generation.
- Avoid exceeding the IC's voltage and current ratings to prevent damage.
- Place decoupling capacitors close to the IC to reduce noise and improve stability.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
The IP2326 2S LX LSCV2 does not directly interface with microcontrollers like the Arduino UNO. However, you can monitor the battery pack's voltage using the Arduino's analog input pins. Below is an example code snippet to monitor the voltage of a 2S battery pack:
// Define analog input pins for voltage monitoring
const int cell1Pin = A0; // Connect to the midpoint (VM pin)
const int cell2Pin = A1; // Connect to the positive terminal (VDD pin)
// Define voltage divider resistors (adjust based on your circuit)
const float R1 = 10000.0; // Resistor connected to the battery
const float R2 = 10000.0; // Resistor connected to ground
// ADC reference voltage
const float VREF = 5.0; // Arduino UNO's default reference voltage
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
// Read analog values
int cell1ADC = analogRead(cell1Pin);
int cell2ADC = analogRead(cell2Pin);
// Convert ADC values to voltages
float cell1Voltage = (cell1ADC * VREF / 1023.0) * ((R1 + R2) / R2);
float cell2Voltage = (cell2ADC * VREF / 1023.0) * ((R1 + R2) / R2);
// Calculate total battery voltage
float totalVoltage = cell1Voltage + cell2Voltage;
// Print voltages to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Cell 1 Voltage: ");
Serial.print(cell1Voltage);
Serial.println(" V");
Serial.print("Cell 2 Voltage: ");
Serial.print(cell2Voltage);
Serial.println(" V");
Serial.print("Total Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(totalVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
The IC does not trigger overcharge or over-discharge protection.
- Solution: Verify that the battery voltage levels are within the IC's detection thresholds. Check the connections to the VM and V1 pins.
Excessive heat generation in the MOSFETs.
- Solution: Use MOSFETs with lower Rds(on) values to reduce power dissipation. Ensure proper heat sinking if necessary.
The circuit does not power the load or charge the battery.
- Solution: Check the connections to the COUT and DOUT pins. Ensure the MOSFETs are functioning correctly.
The IC consumes too much current.
- Solution: Verify that there are no short circuits or incorrect connections. Ensure the quiescent current is within the specified range.
Tips for Troubleshooting
- Use a multimeter to measure voltages at key points in the circuit.
- Double-check the pin connections and ensure they match the pinout table.
- Refer to the IC's datasheet for detailed application notes and example circuits.