
How to Use gy-us-42: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with gy-us-42 in Cirkit Designer
Design with gy-us-42 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The GY-US-42 is an ultrasonic distance sensor designed to measure the distance to an object using sonar technology. It emits ultrasonic waves and calculates the time taken for the echo to return, providing precise distance measurements. This sensor is widely used in applications such as robotics, obstacle detection, level measurement, and proximity sensing. Its compact design and high accuracy make it a popular choice for both hobbyists and professionals.
Explore Projects Built with gy-us-42

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer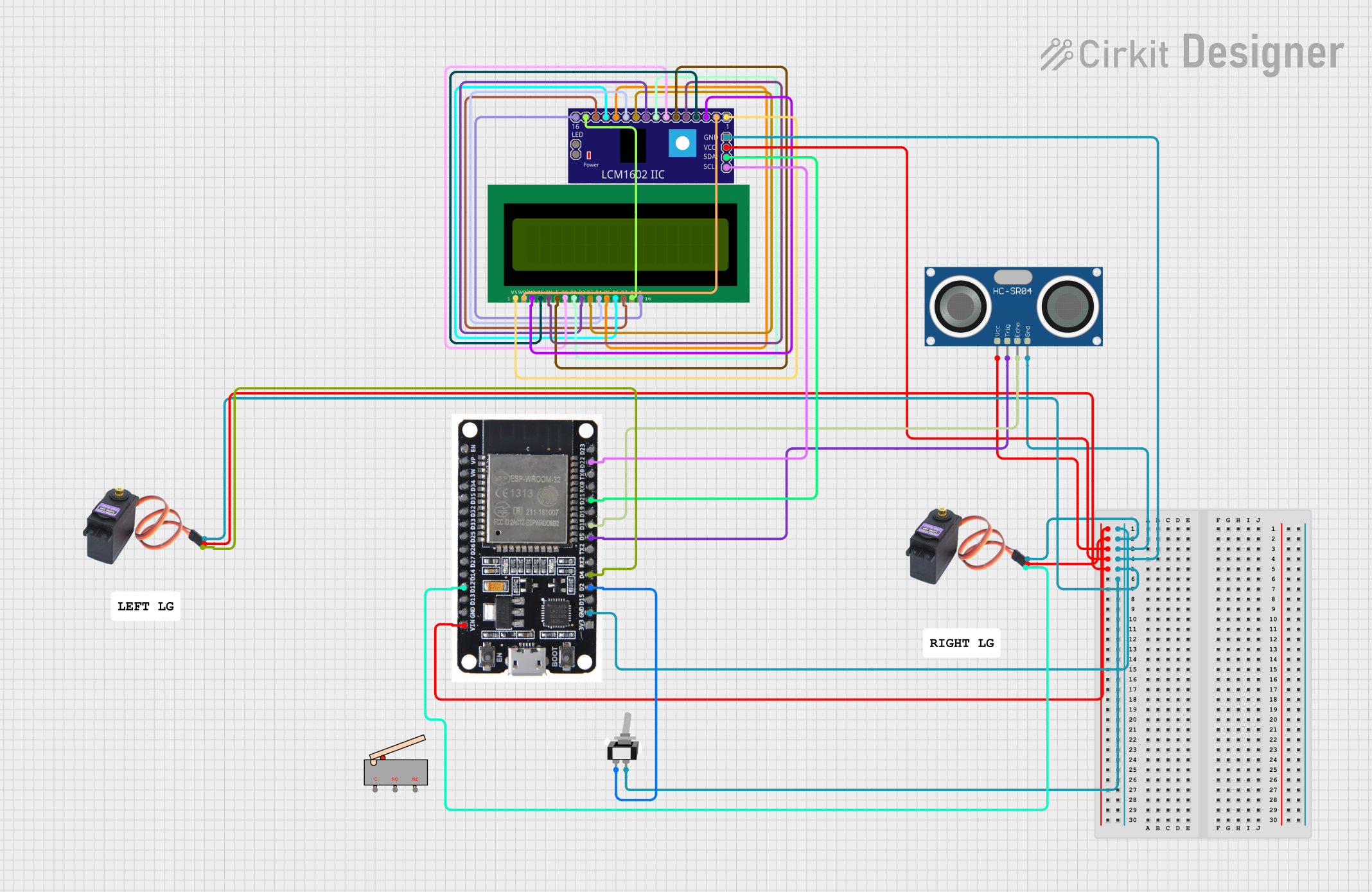
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer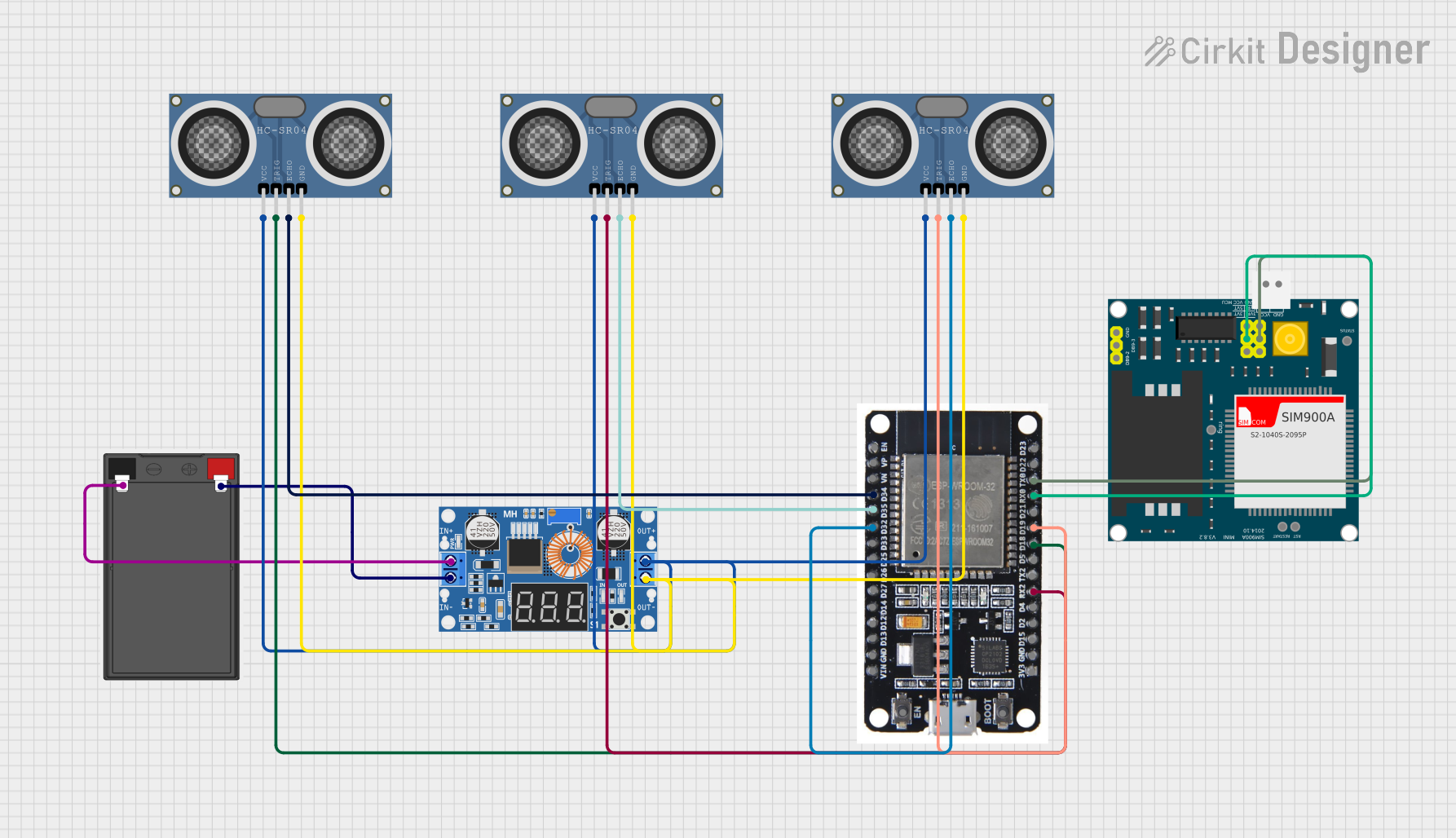
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with gy-us-42

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V to 5V DC
- Operating Current: ≤ 15mA
- Measuring Range: 2cm to 450cm
- Measuring Accuracy: ±1mm
- Output Modes: UART (serial) or PWM
- Communication Protocol: UART (9600 baud rate)
- Operating Temperature: -15°C to 60°C
- Dimensions: 45mm x 20mm x 15mm
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The GY-US-42 sensor has 4 pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (3.3V to 5V DC). |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection. |
| 3 | TXD | UART transmit pin for serial communication. |
| 4 | RXD | UART receive pin for serial communication. |
Alternatively, the sensor can operate in PWM mode. In this case, the TXD pin outputs a PWM signal representing the measured distance.
Usage Instructions
Connecting the GY-US-42 to an Arduino UNO
The GY-US-42 can be easily interfaced with an Arduino UNO using its UART communication mode. Follow these steps to connect and use the sensor:
Wiring:
- Connect the VCC pin of the GY-US-42 to the 5V pin on the Arduino.
- Connect the GND pin of the GY-US-42 to the GND pin on the Arduino.
- Connect the TXD pin of the GY-US-42 to the Arduino's RX (Pin 0).
- Connect the RXD pin of the GY-US-42 to the Arduino's TX (Pin 1).
Arduino Code: Use the following example code to read distance measurements from the GY-US-42:
// GY-US-42 Ultrasonic Distance Sensor Example Code // This code reads distance data from the sensor via UART and displays it // on the Serial Monitor. void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud delay(100); // Allow time for the sensor to initialize } void loop() { if (Serial.available() > 0) { // Check if data is available from the sensor int highByte = Serial.read(); // Read the high byte of the distance int lowByte = Serial.read(); // Read the low byte of the distance int distance = (highByte << 8) + lowByte; // Combine high and low bytes // Display the distance in centimeters Serial.print("Distance: "); Serial.print(distance); Serial.println(" cm"); } delay(100); // Add a small delay to avoid overwhelming the sensor }
Important Considerations
- Ensure the sensor is powered within its operating voltage range (3.3V to 5V). Exceeding this range may damage the sensor.
- Avoid placing the sensor in environments with excessive noise or vibrations, as this may affect measurement accuracy.
- When using the sensor in PWM mode, refer to the datasheet for details on interpreting the PWM signal.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Data Received from the Sensor:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or baud rate mismatch.
- Solution: Double-check the wiring connections and ensure the Arduino's baud rate is set to 9600.
Inaccurate Distance Measurements:
- Cause: Obstructions or reflective surfaces near the sensor.
- Solution: Ensure the sensor has a clear line of sight to the target object. Avoid using the sensor near highly reflective or absorbent surfaces.
Sensor Not Powering On:
- Cause: Insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Verify that the power supply provides a stable voltage between 3.3V and 5V.
FAQs
Q1: Can the GY-US-42 measure distances below 2cm?
A1: No, the minimum measurable distance for the GY-US-42 is 2cm. Objects closer than this may not be detected accurately.
Q2: Can I use the GY-US-42 with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A2: Yes, the GY-US-42 is compatible with 3.3V systems. Ensure the power supply and logic levels match the microcontroller's specifications.
Q3: How do I switch between UART and PWM modes?
A3: The GY-US-42 defaults to UART mode. Refer to the sensor's datasheet for instructions on enabling PWM mode if needed.