
How to Use TIP31C: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with TIP31C in Cirkit Designer
Design with TIP31C in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TIP31C is an NPN power transistor designed for high-speed switching and amplification applications. Manufactured by Arduino with the part ID "uno," this versatile component is widely used in circuits requiring moderate power handling. With a maximum collector current of 3A and a collector-emitter voltage of 40V, the TIP31C is ideal for driving loads such as motors, LEDs, and other electronic devices. Its robust design and reliability make it a popular choice for hobbyists and professionals alike.
Explore Projects Built with TIP31C
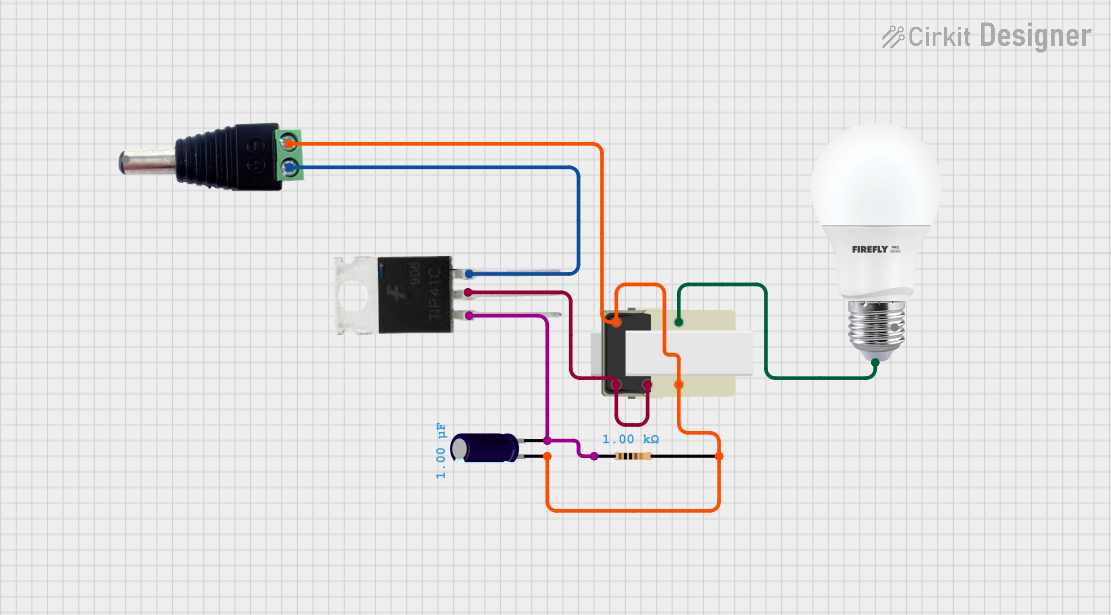
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer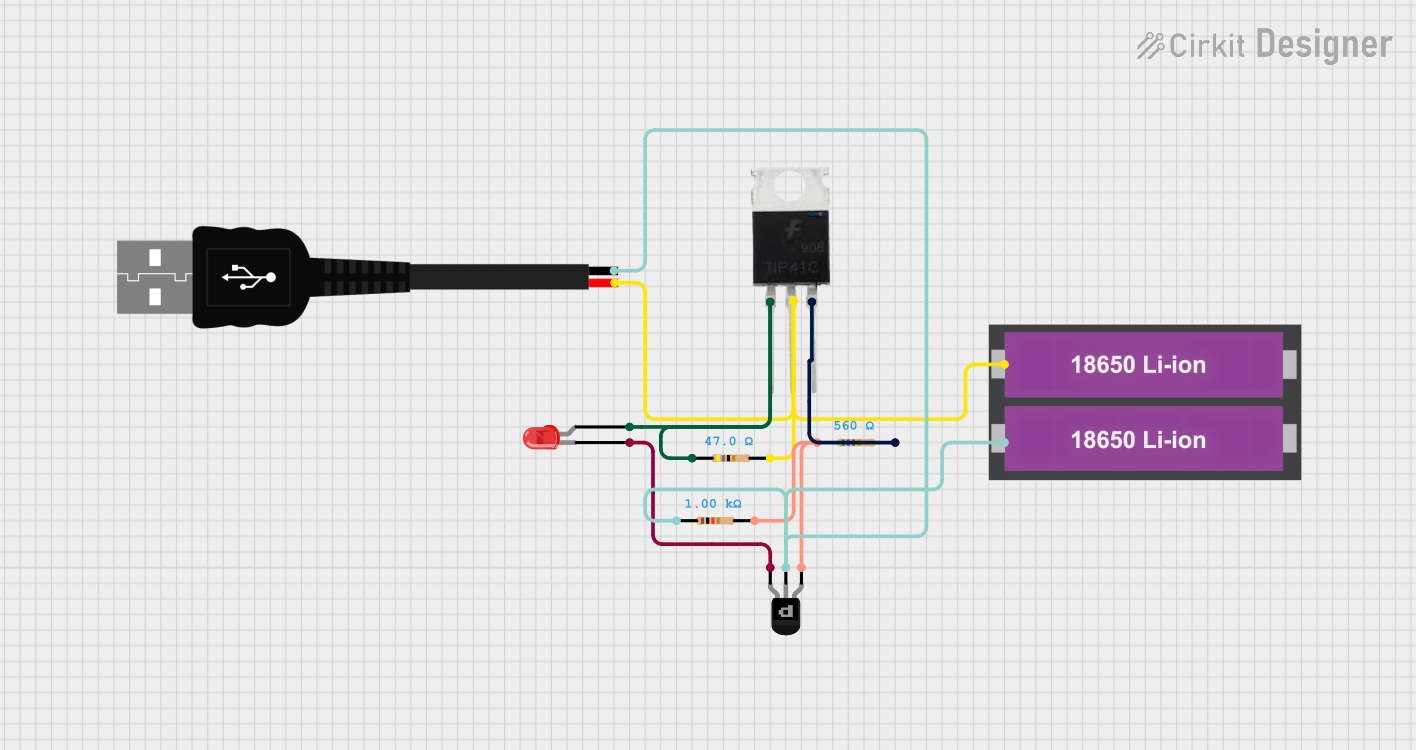
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer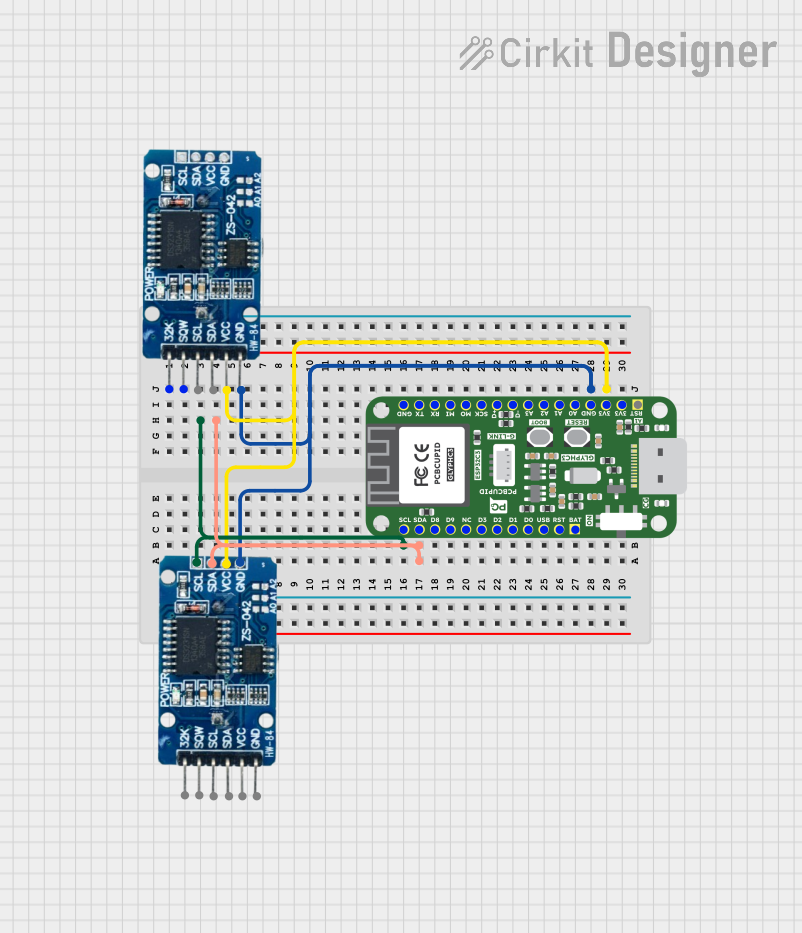
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer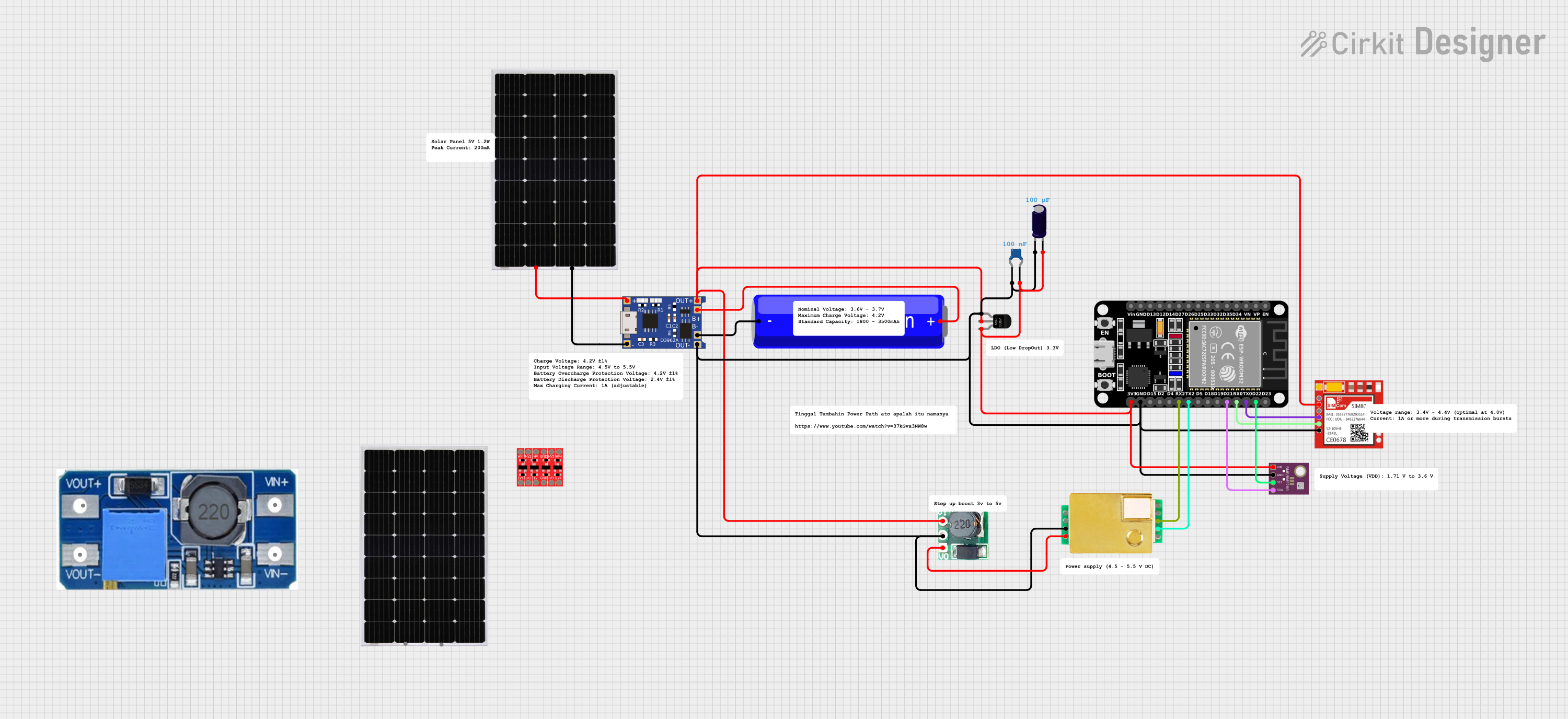
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TIP31C

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Audio amplification circuits
- Motor control and driving inductive loads
- LED dimming and control
- General-purpose switching in power electronics
- Signal amplification in analog circuits
Technical Specifications
The TIP31C's key technical details are summarized below:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Arduino |
| Part ID | uno |
| Transistor Type | NPN |
| Maximum Collector Current | 3A |
| Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (Vce) | 40V |
| Maximum Collector-Base Voltage (Vcb) | 100V |
| Maximum Emitter-Base Voltage (Veb) | 5V |
| Power Dissipation (Pd) | 40W |
| DC Current Gain (hFE) | 10 to 50 |
| Transition Frequency (fT) | 3 MHz |
| Package Type | TO-220 |
Pin Configuration
The TIP31C has three pins, as detailed in the table below:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Base (B) | Controls the transistor's operation. |
| 2 | Collector (C) | Current flows from collector to emitter. |
| 3 | Emitter (E) | Current exits the transistor. |
Usage Instructions
Using the TIP31C in a Circuit
The TIP31C is commonly used as a switch or amplifier in electronic circuits. Below are the steps to use it effectively:
Determine the Operating Mode:
- Switching Mode: Use the TIP31C to control high-current loads by applying a small base current.
- Amplification Mode: Use the TIP31C to amplify small input signals.
Connect the Pins:
- Connect the emitter to ground (for NPN configuration).
- Connect the collector to the load (e.g., motor, LED) and then to the power supply.
- Apply a small current to the base to control the transistor.
Base Resistor:
- Use a resistor between the base and the control signal to limit the base current. Calculate the resistor value using Ohm's law: [ R_b = \frac{V_{control} - V_{be}}{I_b} ] where ( V_{be} ) is typically 0.7V for the TIP31C.
Heat Dissipation:
- If the transistor operates near its maximum power dissipation (40W), attach a heatsink to the TO-220 package to prevent overheating.
Example: Controlling an LED with Arduino UNO
The following example demonstrates how to use the TIP31C to control a high-power LED with an Arduino UNO:
// TIP31C Example: Controlling an LED with Arduino UNO
// Connect the TIP31C emitter to ground, collector to the LED's cathode, and
// the LED's anode to a 12V power supply. Use a 1kΩ resistor between the
// Arduino pin and the TIP31C base.
const int ledControlPin = 9; // Arduino pin connected to TIP31C base
void setup() {
pinMode(ledControlPin, OUTPUT); // Set the control pin as output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledControlPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledControlPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Important Considerations
- Base Current: Ensure the base current does not exceed the maximum rating to avoid damaging the transistor.
- Voltage Ratings: Do not exceed the maximum collector-emitter voltage (40V) or emitter-base voltage (5V).
- Heat Management: Use a heatsink if the transistor dissipates significant power.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Transistor Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive power dissipation.
- Solution: Attach a heatsink to the TIP31C and ensure proper ventilation.
Load Not Turning On:
- Cause: Insufficient base current or incorrect wiring.
- Solution: Verify the base resistor value and check all connections.
Low Amplification:
- Cause: Incorrect biasing or low DC current gain (hFE).
- Solution: Adjust the base resistor or use a Darlington pair for higher gain.
Transistor Not Switching:
- Cause: Base-emitter voltage too low.
- Solution: Ensure the base voltage is at least 0.7V above the emitter voltage.
FAQs
Q1: Can the TIP31C handle AC signals?
A1: Yes, the TIP31C can amplify or switch AC signals, but proper biasing is required for amplification.
Q2: What is the maximum load the TIP31C can drive?
A2: The TIP31C can handle up to 3A of collector current, but ensure the power dissipation does not exceed 40W.
Q3: Can I use the TIP31C without a heatsink?
A3: Yes, but only if the power dissipation is low. For high-power applications, a heatsink is recommended.
Q4: Is the TIP31C suitable for audio applications?
A4: Yes, the TIP31C is commonly used in audio amplification circuits due to its high-speed switching and linearity.