
How to Use M100-5883 GPS: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with M100-5883 GPS in Cirkit Designer
Design with M100-5883 GPS in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The M100-5883 GPS is a compact and high-performance GPS module manufactured by HGLRC. It is designed to provide accurate positioning and navigation data for a wide range of applications. With its low power consumption, high sensitivity, and fast time-to-first-fix (TTFF), the M100-5883 GPS is ideal for integration into drones, robotics, IoT devices, and other electronic systems requiring reliable location tracking.
Explore Projects Built with M100-5883 GPS
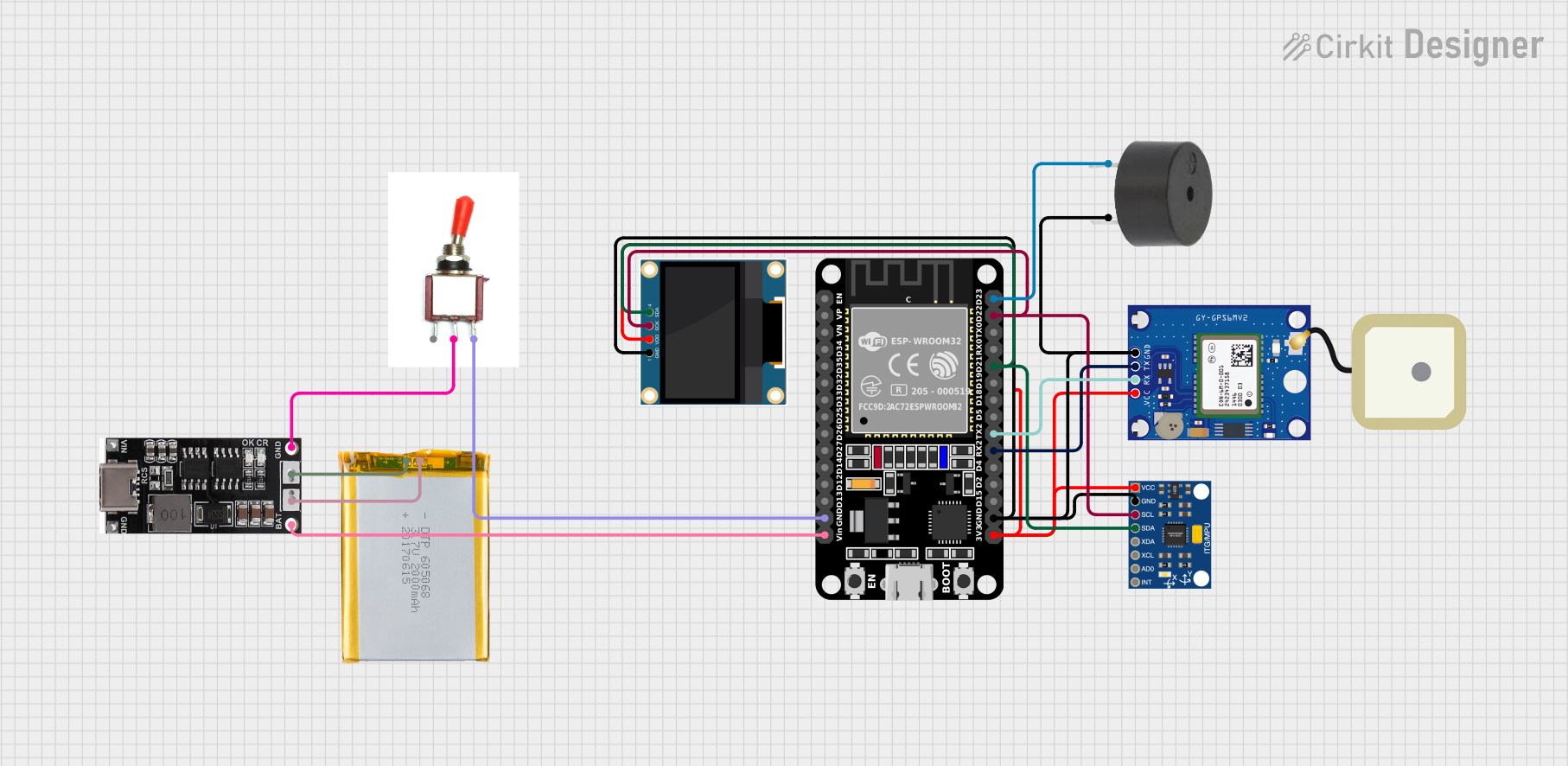
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer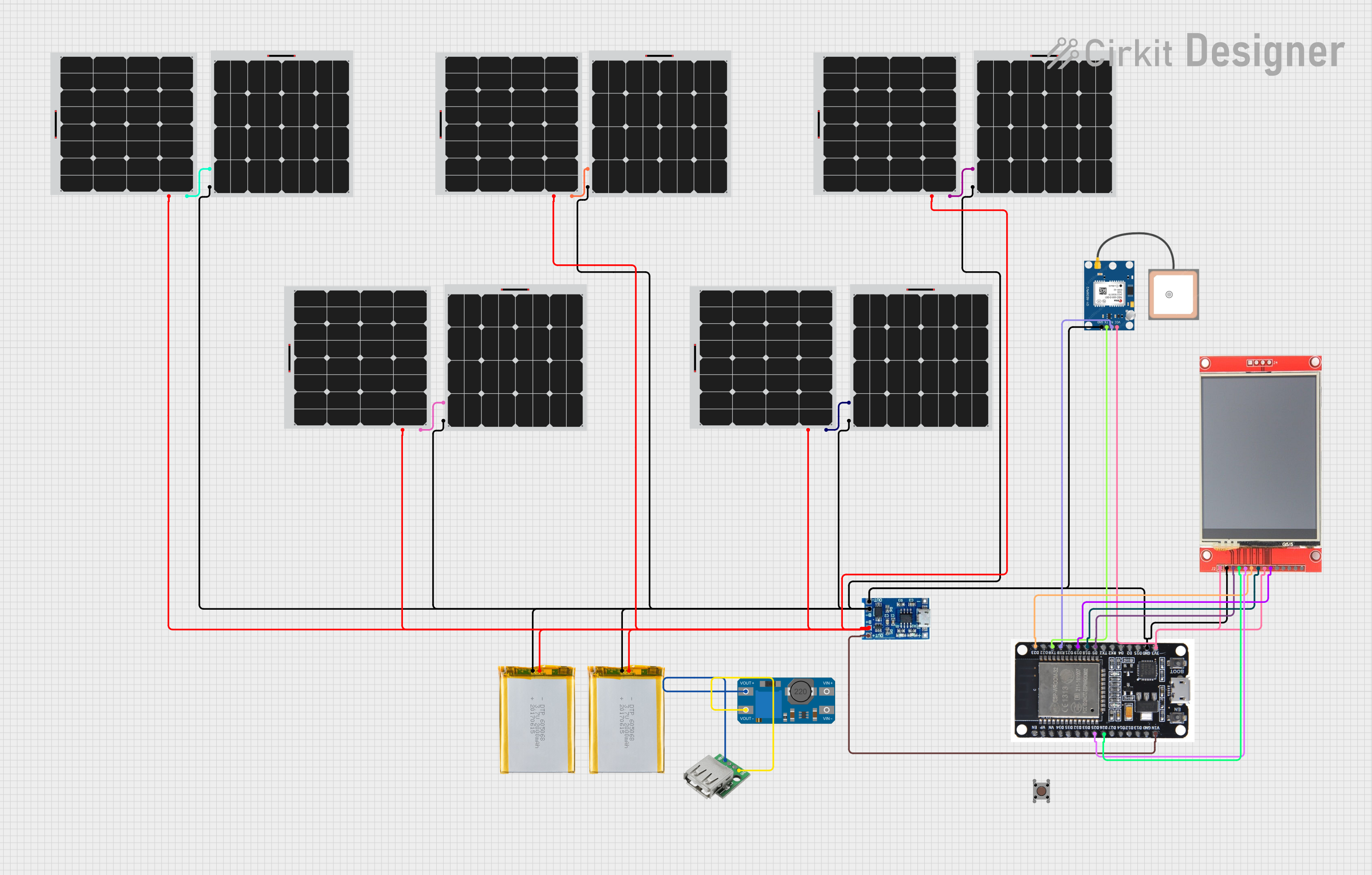
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer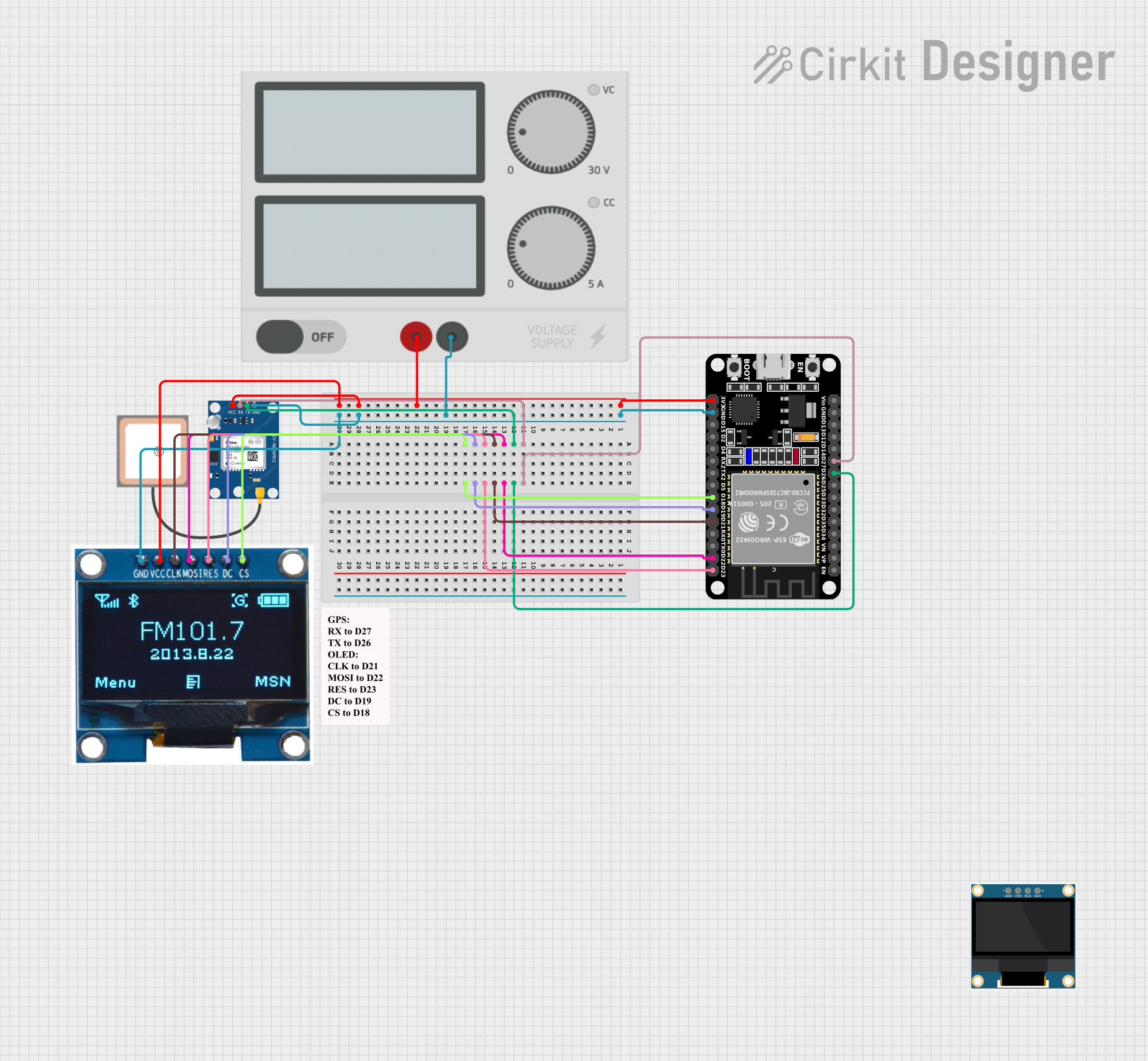
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with M100-5883 GPS

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Drones and UAVs for navigation and positioning
- Robotics for autonomous movement and mapping
- IoT devices for geolocation services
- Vehicle tracking systems
- Outdoor navigation devices
Technical Specifications
The M100-5883 GPS module is built to deliver reliable performance in a compact form factor. Below are its key technical details:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | HGLRC |
| Model | M100-5883 |
| GPS Chipset | MTK3333 |
| Frequency | L1, 1575.42 MHz |
| Positioning Accuracy | < 2.5 meters CEP |
| Time-to-First-Fix (TTFF) | Cold Start: < 35s, Hot Start: < 1s |
| Sensitivity | Tracking: -165 dBm, Acquisition: -148 dBm |
| Update Rate | 1 Hz (default), up to 10 Hz |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V - 5.0V |
| Power Consumption | < 50 mA @ 3.3V |
| Dimensions | 18mm x 18mm x 6mm |
| Weight | 5 grams |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The M100-5883 GPS module has a simple pinout for easy integration into circuits. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (3.3V - 5.0V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | TX | UART Transmit (GPS data output) |
| 4 | RX | UART Receive (for configuration commands) |
| 5 | SDA | I2C Data Line (for compass functionality) |
| 6 | SCL | I2C Clock Line (for compass functionality) |
Usage Instructions
The M100-5883 GPS module is straightforward to use and can be integrated into a variety of systems. Below are the steps and best practices for using the module:
Connecting the M100-5883 GPS to an Arduino UNO
Wiring the Module:
- Connect the VCC pin of the GPS module to the 5V pin on the Arduino UNO.
- Connect the GND pin of the GPS module to the GND pin on the Arduino UNO.
- Connect the TX pin of the GPS module to the RX pin (Pin 0) on the Arduino UNO.
- Connect the RX pin of the GPS module to the TX pin (Pin 1) on the Arduino UNO.
- If using the compass functionality, connect the SDA and SCL pins to the corresponding I2C pins on the Arduino UNO.
Installing Required Libraries:
- Install the
TinyGPS++library for parsing GPS data. - Install the
Wirelibrary (built-in) for I2C communication if using the compass.
- Install the
Sample Code: Below is an example Arduino sketch to read GPS data from the M100-5883 module:
#include <TinyGPS++.h> // Include TinyGPS++ library for GPS parsing #include <SoftwareSerial.h> // Include SoftwareSerial for UART communication // Define GPS module RX and TX pins SoftwareSerial gpsSerial(4, 3); // RX = Pin 4, TX = Pin 3 TinyGPSPlus gps; // Create a TinyGPS++ object void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize Serial Monitor gpsSerial.begin(9600); // Initialize GPS module communication Serial.println("M100-5883 GPS Module Test"); } void loop() { // Read data from GPS module while (gpsSerial.available() > 0) { char c = gpsSerial.read(); if (gps.encode(c)) { // Parse GPS data if (gps.location.isUpdated()) { // Print latitude and longitude to Serial Monitor Serial.print("Latitude: "); Serial.print(gps.location.lat(), 6); Serial.print(", Longitude: "); Serial.println(gps.location.lng(), 6); } } } }
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the GPS module has a clear view of the sky for optimal satellite reception.
- Avoid placing the module near sources of electromagnetic interference (e.g., motors, power supplies).
- Use a decoupling capacitor (e.g., 10 µF) between VCC and GND to stabilize the power supply.
- If using the compass functionality, calibrate the compass in your application for accurate readings.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No GPS Data Received:
- Ensure the module is powered correctly (3.3V - 5.0V).
- Verify the TX and RX connections between the GPS module and the microcontroller.
- Check for a clear view of the sky to acquire satellite signals.
Incorrect or No Location Data:
- Wait for the module to acquire a fix (can take up to 35 seconds in a cold start).
- Ensure the antenna is properly connected and oriented.
Compass Not Working:
- Verify the SDA and SCL connections for I2C communication.
- Use a compatible library for reading compass data (e.g.,
Wirelibrary).
Intermittent GPS Signal:
- Minimize interference by keeping the module away from high-frequency devices.
- Use a ground plane or shielding to improve signal stability.
FAQs
Q: Can the M100-5883 GPS module be used indoors?
A: While the module can function indoors, GPS signal strength may be significantly reduced. For best results, use the module outdoors with a clear view of the sky.
Q: What is the default baud rate of the GPS module?
A: The default baud rate is 9600 bps.
Q: Can I increase the update rate of the GPS module?
A: Yes, the update rate can be configured up to 10 Hz using specific configuration commands sent via UART.
Q: Does the module support GLONASS or other GNSS systems?
A: No, the M100-5883 GPS module is designed to work with GPS satellites only.
Q: How do I calibrate the compass?
A: Calibration typically involves rotating the module in all three axes while collecting data. Refer to your application or library documentation for specific calibration procedures.