
How to Use 74HC595: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
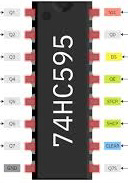
 Design with 74HC595 in Cirkit Designer
Design with 74HC595 in Cirkit Designer74HC595 Shift Register Documentation
1. Introduction
The 74HC595 is an 8-bit serial-in, parallel-out shift register with a storage register and tri-state outputs. It is widely used in electronics to expand the number of output pins available on a microcontroller, such as an Arduino. By using a serial data input, the 74HC595 allows you to control up to 8 output pins with just 3 control pins from the microcontroller. Additionally, multiple 74HC595 chips can be cascaded to control even more outputs.
Common Applications
- Driving LED arrays or 7-segment displays
- Controlling relays or other digital outputs
- Expanding GPIO pins on microcontrollers
- Multiplexing and demultiplexing signals
- Building digital counters or shift registers
2. Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the 74HC595:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (Vcc) | 2V to 6V |
| Input Voltage (VI) | 0V to Vcc |
| Output Current (IO) | ±6 mA per pin |
| Maximum Clock Frequency | 25 MHz (at 4.5V) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +125°C |
| Propagation Delay | ~20 ns (at 5V) |
| Package Types | DIP-16, SOIC-16, TSSOP-16 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 74HC595 has 16 pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Q1 | Parallel output pin 1 |
| 2 | Q2 | Parallel output pin 2 |
| 3 | Q3 | Parallel output pin 3 |
| 4 | Q4 | Parallel output pin 4 |
| 5 | Q5 | Parallel output pin 5 |
| 6 | Q6 | Parallel output pin 6 |
| 7 | Q7 | Parallel output pin 7 |
| 8 | GND | Ground (0V) |
| 9 | Q7' | Serial data output for cascading additional 74HC595 chips |
| 10 | MR | Master Reset (active LOW) - Clears all outputs |
| 11 | SH_CP | Shift Register Clock Input - Shifts data into the register on rising edge |
| 12 | ST_CP | Storage Register Clock Input (Latch) - Transfers data to output on rising edge |
| 13 | OE | Output Enable (active LOW) - Enables/disables outputs |
| 14 | DS | Serial Data Input |
| 15 | Q0 | Parallel output pin 0 |
| 16 | Vcc | Positive supply voltage |
3. Usage Instructions
Connecting the 74HC595 to a Microcontroller
To use the 74HC595, connect it to your microcontroller as follows:
- Power Supply: Connect
Vccto the microcontroller's 5V pin andGNDto ground. - Control Pins:
- Connect
DS(Pin 14) to the microcontroller's data pin (e.g., ArduinoD11). - Connect
SH_CP(Pin 11) to the microcontroller's clock pin (e.g., ArduinoD12). - Connect
ST_CP(Pin 12) to the microcontroller's latch pin (e.g., ArduinoD8).
- Connect
- Output Enable: Connect
OE(Pin 13) to ground to enable the outputs. - Master Reset: Connect
MR(Pin 10) to Vcc to disable the reset function.
Cascading Multiple 74HC595 Chips
To control more than 8 outputs, you can cascade multiple 74HC595 chips:
- Connect the
Q7'(Pin 9) of the first chip to theDS(Pin 14) of the second chip. - Share the
SH_CP,ST_CP, andOEpins across all chips.
Example Circuit
Below is an example of connecting a single 74HC595 to an Arduino UNO to control 8 LEDs:
74HC595 Pin 14 (DS) -> Arduino Pin 11
74HC595 Pin 11 (SH_CP) -> Arduino Pin 12
74HC595 Pin 12 (ST_CP) -> Arduino Pin 8
74HC595 Pin 13 (OE) -> GND
74HC595 Pin 10 (MR) -> Vcc
74HC595 Pin 16 (Vcc) -> Arduino 5V
74HC595 Pin 8 (GND) -> Arduino GND
74HC595 Pins Q0-Q7 -> LEDs (with current-limiting resistors)
4. Arduino Code Example
Here is an example Arduino sketch to control 8 LEDs using the 74HC595:
// Define 74HC595 control pins
const int dataPin = 11; // DS (Serial Data Input)
const int clockPin = 12; // SH_CP (Shift Register Clock)
const int latchPin = 8; // ST_CP (Storage Register Clock)
// Function to send data to the 74HC595
void shiftOutData(byte data) {
digitalWrite(latchPin, LOW); // Disable latch to update data
shiftOut(dataPin, clockPin, MSBFIRST, data); // Send data (MSB first)
digitalWrite(latchPin, HIGH); // Enable latch to output data
}
void setup() {
// Set control pins as outputs
pinMode(dataPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(clockPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(latchPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Turn on LEDs one by one
for (byte i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
shiftOutData(1 << i); // Shift a single HIGH bit through the register
delay(200); // Wait 200ms
}
// Turn off LEDs one by one
for (byte i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
shiftOutData(~(1 << i)); // Shift a single LOW bit through the register
delay(200); // Wait 200ms
}
}
5. Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| LEDs not lighting up | Incorrect wiring or loose connections | Double-check all connections and ensure proper wiring. |
| Outputs not updating | Latch pin (ST_CP) not toggled correctly |
Ensure the latch pin is toggled HIGH after sending data. |
| Cascaded chips not working | Incorrect connection of Q7' to DS |
Verify the Q7' of the first chip is connected to the DS of the next chip. |
| Flickering LEDs | Clock signal is noisy or too fast | Use a lower clock frequency or add decoupling capacitors near the chip. |
| Outputs always HIGH or LOW | OE or MR pins not properly connected |
Ensure OE is grounded and MR is connected to Vcc. |
FAQs
Can I use the 74HC595 with 3.3V microcontrollers?
- Yes, the 74HC595 operates at voltages as low as 2V. Ensure the output current is within limits.
How many 74HC595 chips can I cascade?
- Theoretically, you can cascade as many as you want, but practical limits depend on signal integrity and timing.
Do I need resistors for LEDs connected to the 74HC595?
- Yes, always use current-limiting resistors to protect the LEDs and the 74HC595 outputs.
What is the purpose of the
OEpin?- The
OEpin enables or disables the outputs. When HIGH, all outputs are in a high-impedance state.
- The
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to using the 74HC595 shift register. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced user, the 74HC595 is a versatile and essential component for expanding your microcontroller's output capabilities.
Explore Projects Built with 74HC595
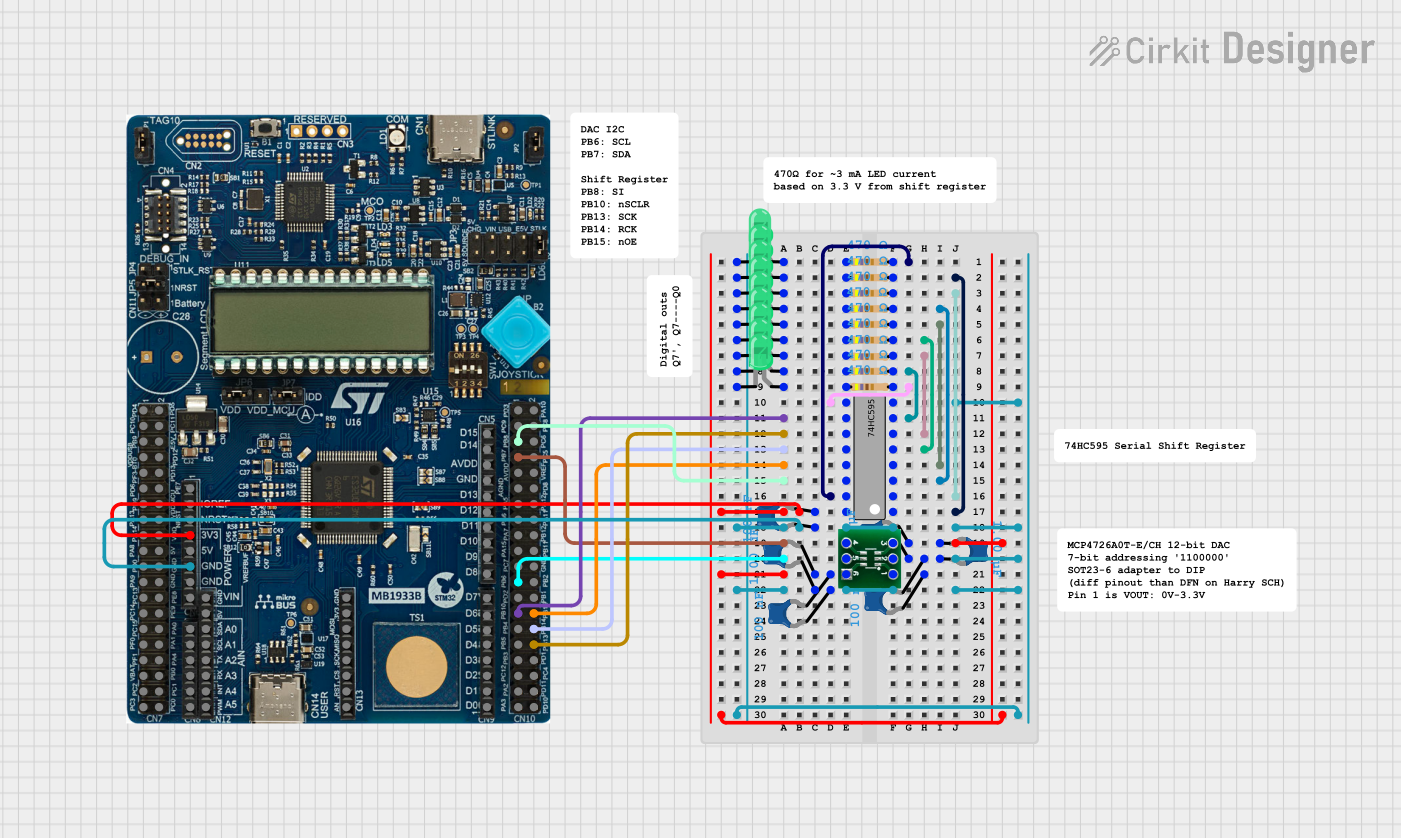
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer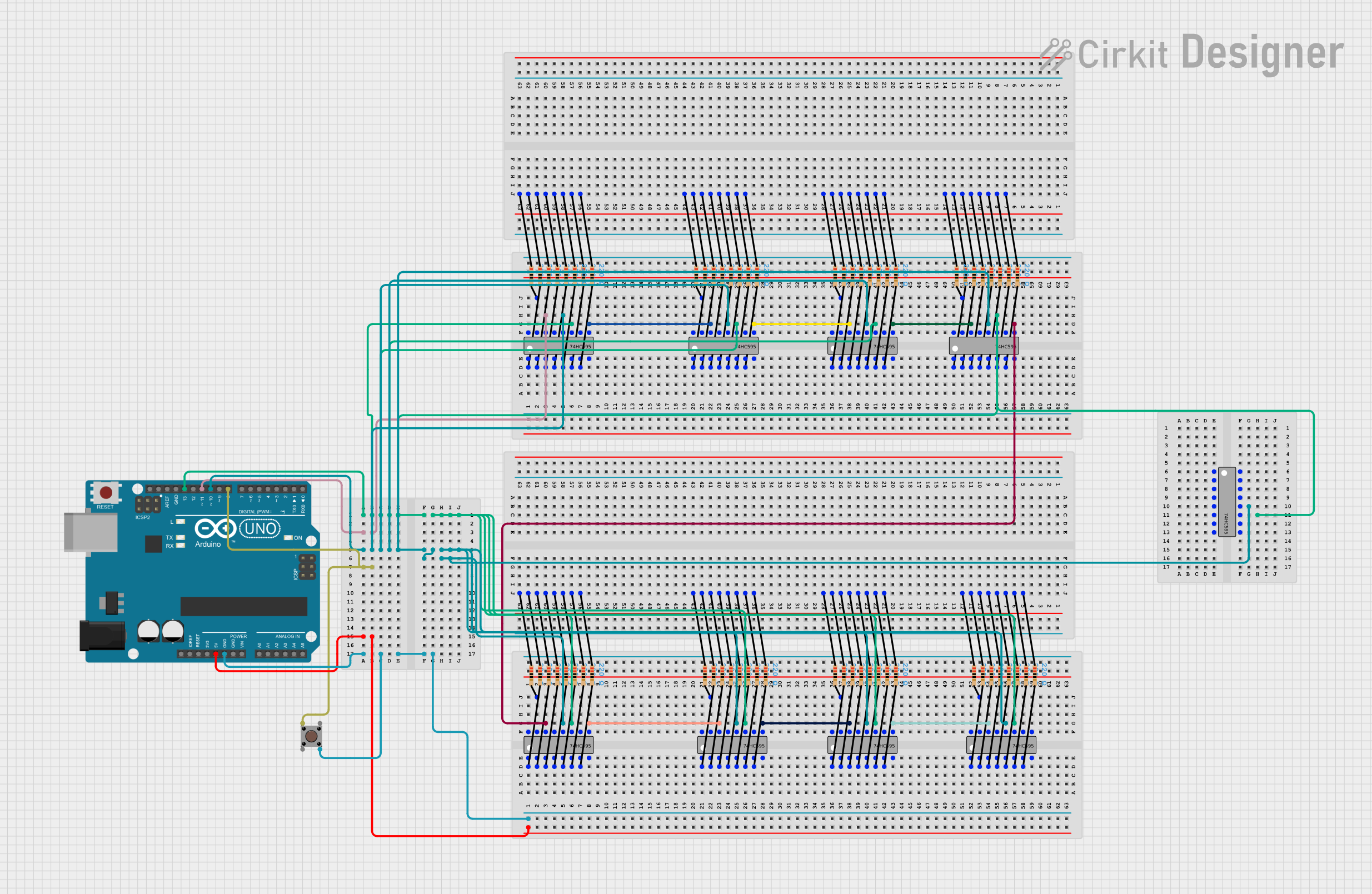
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer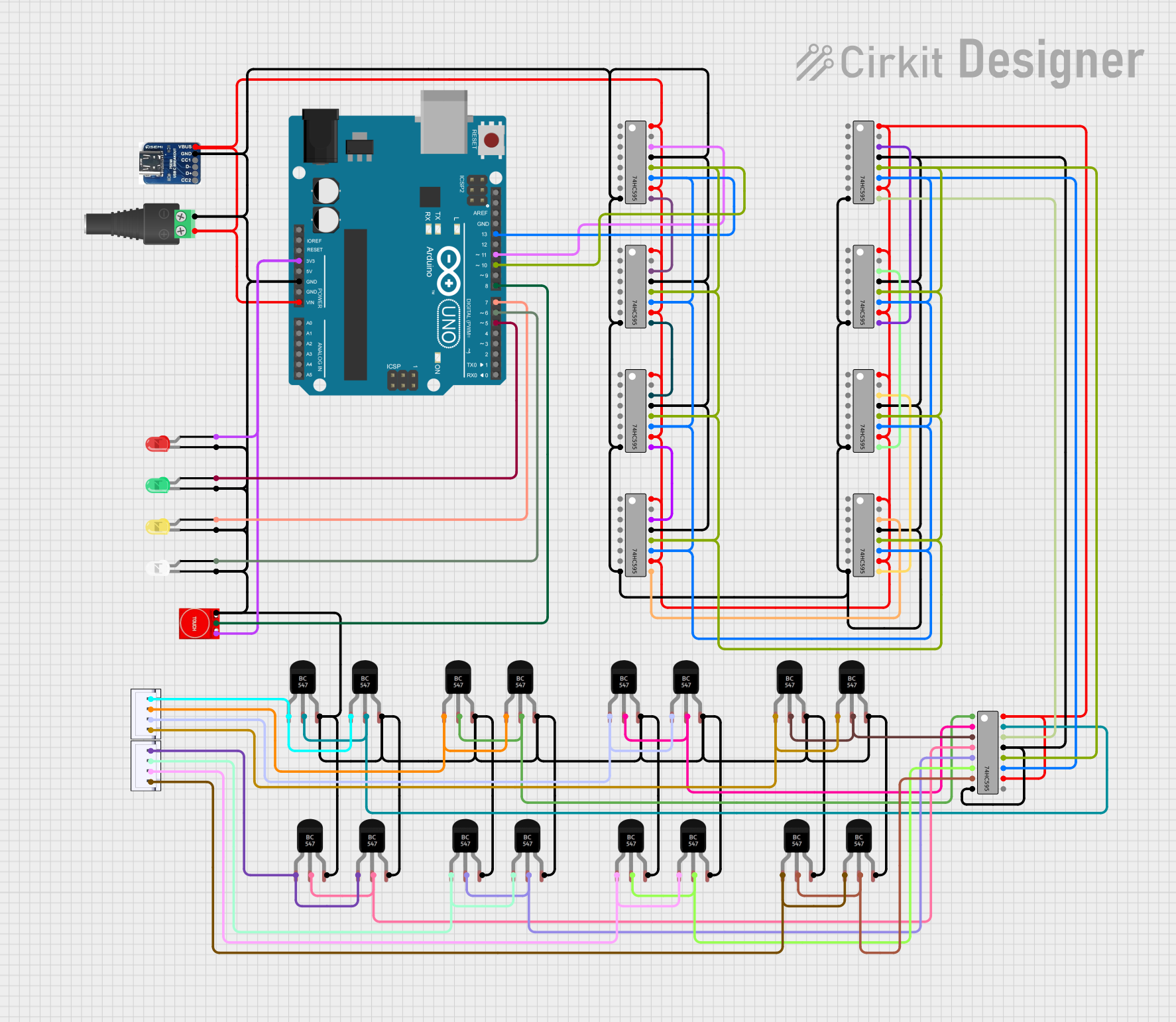
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer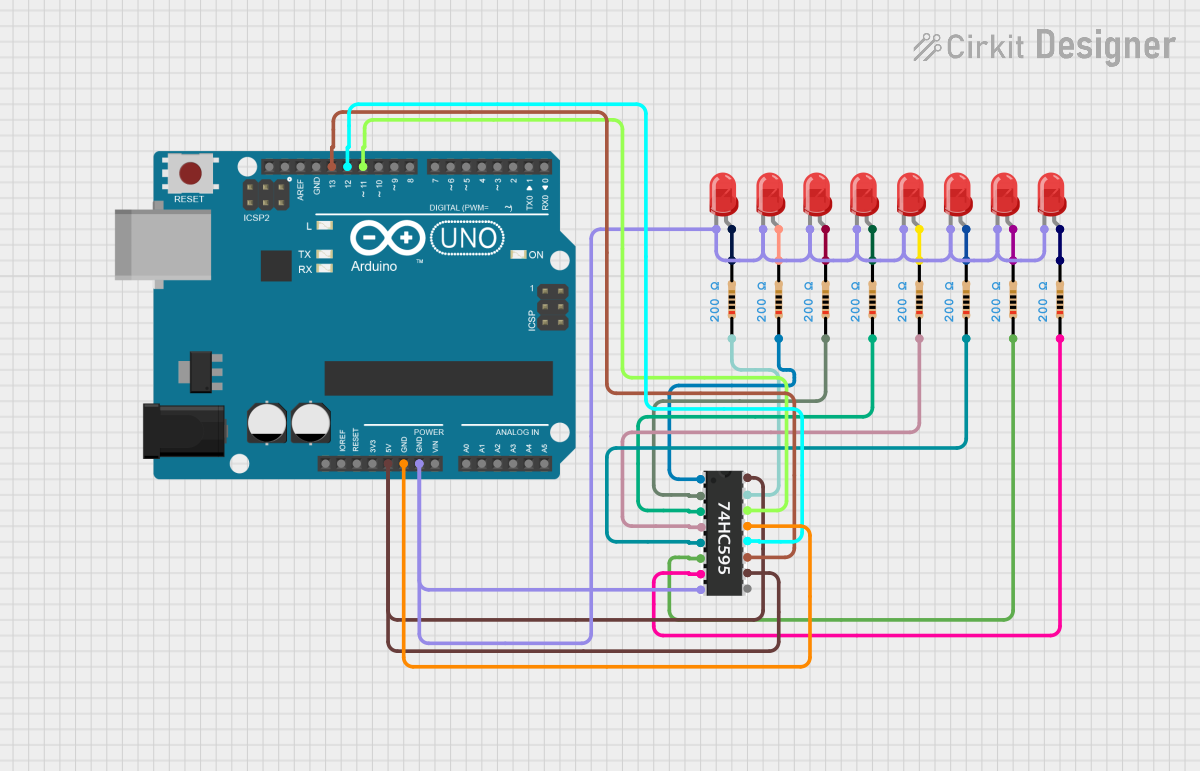
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 74HC595

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer