
How to Use nanoESP32-C6 DevKit: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with nanoESP32-C6 DevKit in Cirkit Designer
Design with nanoESP32-C6 DevKit in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The nanoESP32-C6 DevKit is a compact development board manufactured by MuseLab, featuring the powerful ESP32-C6 chip. This board integrates Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth 5.0, and IEEE 802.15.4 (Thread/Zigbee) capabilities, making it an ideal choice for IoT applications, smart home devices, and wireless communication projects. Its small form factor and robust features make it suitable for rapid prototyping and deployment in space-constrained environments.
Explore Projects Built with nanoESP32-C6 DevKit
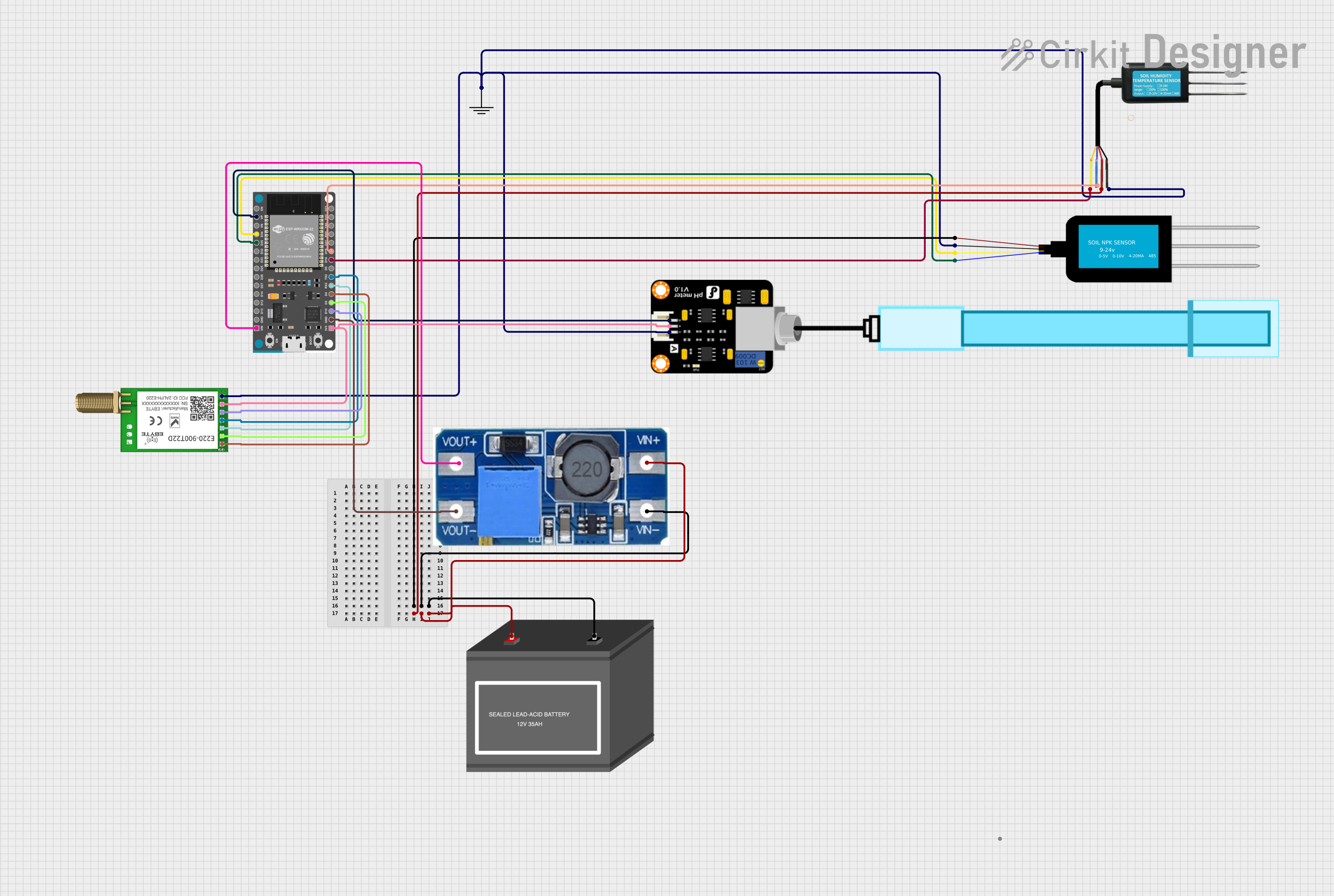
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer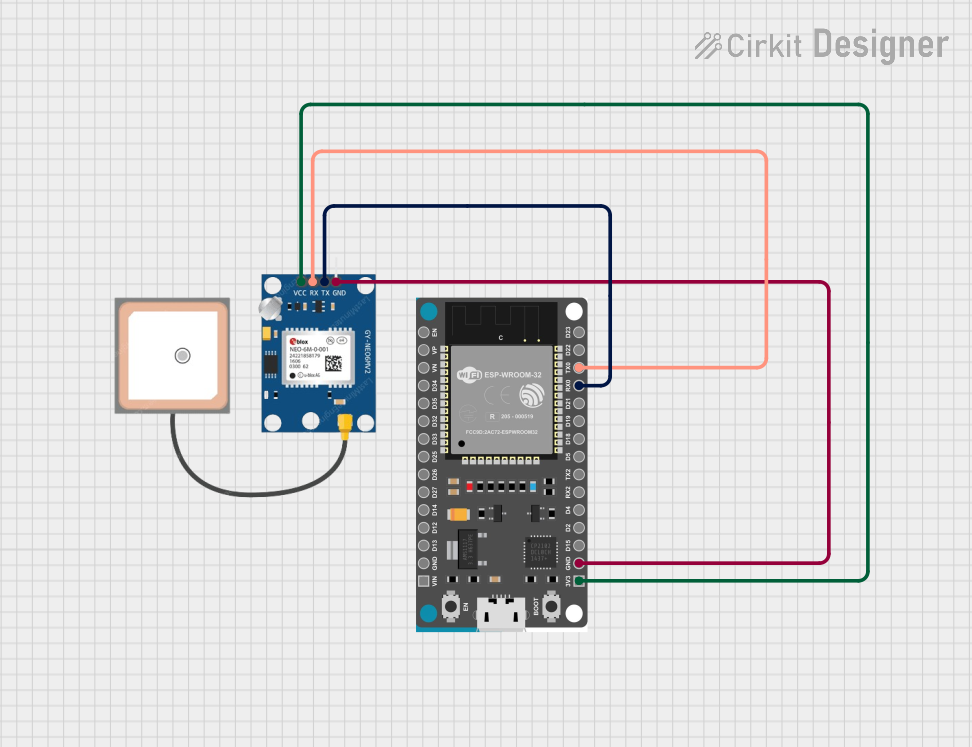
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer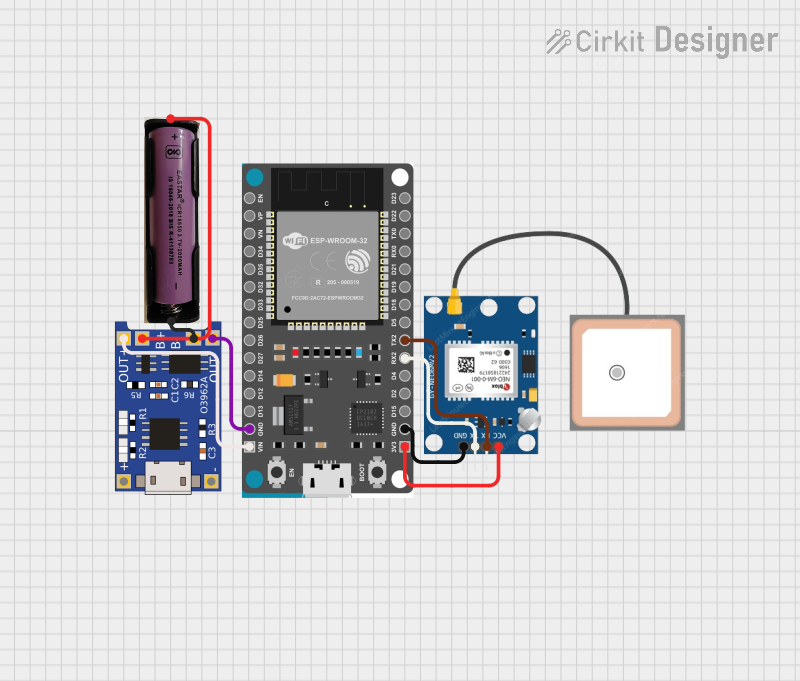
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer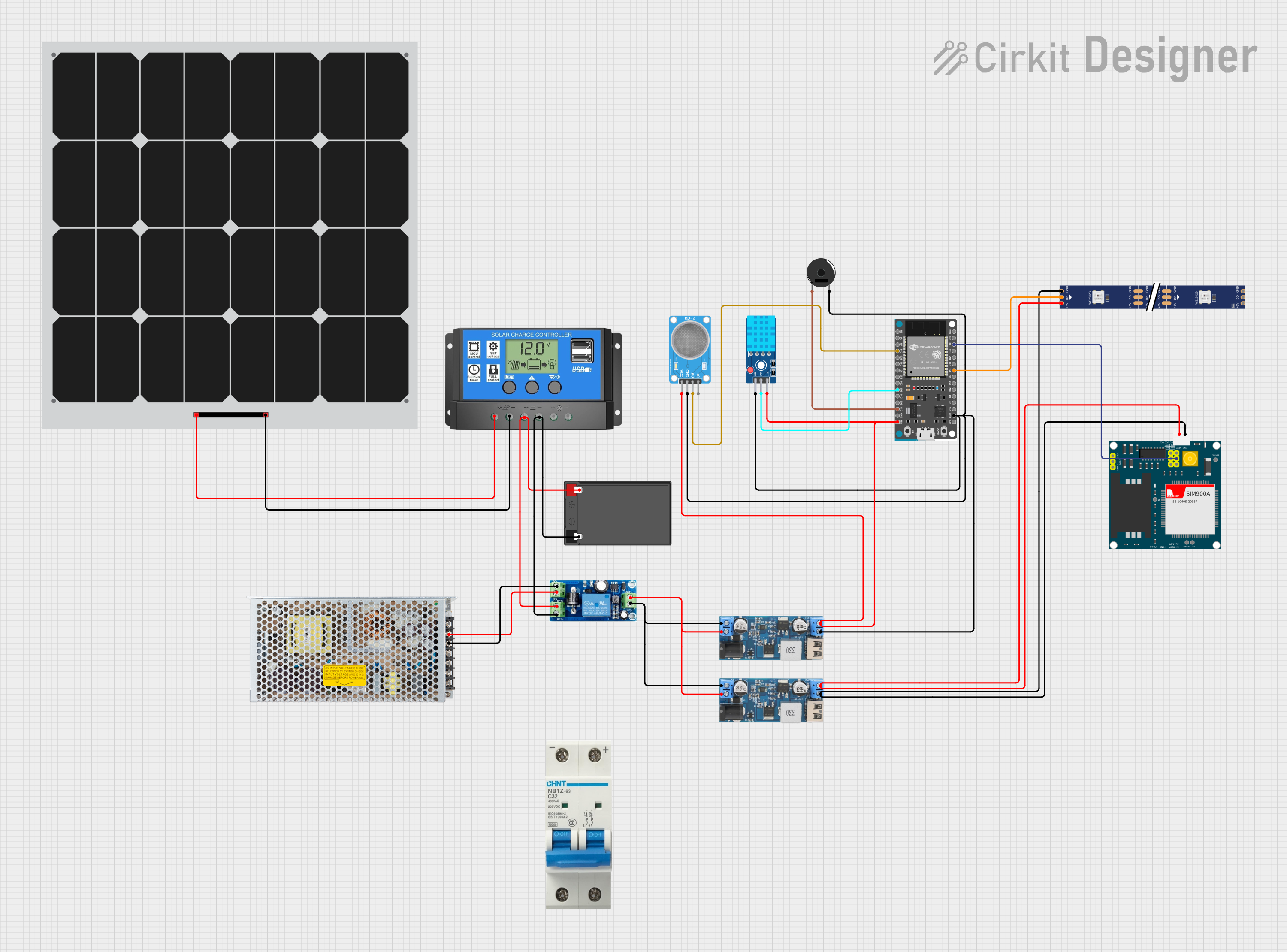
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with nanoESP32-C6 DevKit

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- IoT devices and smart home automation
- Wireless sensor networks
- Bluetooth-enabled devices
- Zigbee/Thread-based communication systems
- Low-power, high-performance embedded systems
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details and pin configuration for the nanoESP32-C6 DevKit:
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Chipset | ESP32-C6 |
| Wi-Fi | Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), 2.4 GHz |
| Bluetooth | Bluetooth 5.0 (LE) |
| Zigbee/Thread | IEEE 802.15.4 |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V |
| Input Voltage Range | 5V (via USB-C) |
| Flash Memory | 4 MB |
| SRAM | 512 KB |
| GPIO Pins | 14 |
| Communication Interfaces | UART, SPI, I2C, I2S, PWM |
| Power Consumption | Ultra-low power mode supported |
| Dimensions | 18 mm x 45 mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground |
| 2 | 3V3 | 3.3V Power Output |
| 3 | EN | Enable Pin (Active High) |
| 4 | IO0 | GPIO0, Boot Mode Selection |
| 5 | IO1 | GPIO1, General Purpose I/O |
| 6 | IO2 | GPIO2, General Purpose I/O |
| 7 | IO3 | GPIO3, General Purpose I/O |
| 8 | IO4 | GPIO4, General Purpose I/O |
| 9 | IO5 | GPIO5, General Purpose I/O |
| 10 | RXD | UART Receive |
| 11 | TXD | UART Transmit |
| 12 | SCL | I2C Clock Line |
| 13 | SDA | I2C Data Line |
| 14 | RST | Reset Pin |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Powering the Board:
- Connect the nanoESP32-C6 DevKit to a 5V power source using the USB-C port. The onboard voltage regulator will step down the voltage to 3.3V for the ESP32-C6 chip.
- Alternatively, you can power the board directly via the 3V3 pin.
Programming the Board:
- Use the Arduino IDE or ESP-IDF (Espressif IoT Development Framework) to program the board.
- Select the appropriate board type (
ESP32-C6) and port in the IDE settings.
Connecting Peripherals:
- Use the GPIO pins to connect sensors, actuators, or other peripherals. Ensure that the voltage levels of connected devices are compatible with the 3.3V logic of the board.
Wireless Communication:
- Configure Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or Zigbee/Thread communication using the appropriate libraries and APIs provided by Espressif.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: Ensure all connected peripherals operate at 3.3V logic levels to avoid damaging the board.
- Boot Mode: To enter bootloader mode, hold the IO0 pin low while resetting the board.
- Antenna Placement: Avoid placing metallic objects near the onboard antenna to ensure optimal wireless performance.
- Power Consumption: Use the ultra-low power mode for battery-powered applications to extend battery life.
Example Code for Arduino UNO Integration
Below is an example of using the nanoESP32-C6 DevKit to connect to a Wi-Fi network and send data to a server:
#include <WiFi.h> // Include the Wi-Fi library
// Replace with your network credentials
const char* ssid = "Your_SSID";
const char* password = "Your_PASSWORD";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Initialize serial communication
delay(1000);
// Connect to Wi-Fi
Serial.print("Connecting to Wi-Fi");
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("\nConnected to Wi-Fi!");
Serial.print("IP Address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); // Print the device's IP address
}
void loop() {
// Add your main code here
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Board Not Detected by IDE:
- Ensure the correct USB driver is installed for the nanoESP32-C6 DevKit.
- Verify that the USB cable is functional and supports data transfer.
Wi-Fi Connection Fails:
- Double-check the SSID and password for your Wi-Fi network.
- Ensure the Wi-Fi network operates on the 2.4 GHz band, as the ESP32-C6 does not support 5 GHz.
GPIO Pins Not Responding:
- Verify that the pins are not being used for other functions (e.g., boot mode).
- Check for short circuits or incorrect wiring.
High Power Consumption:
- Enable the ultra-low power mode in your code for battery-powered applications.
- Disconnect unused peripherals to reduce power draw.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the nanoESP32-C6 DevKit with Zigbee devices?
A: Yes, the board supports IEEE 802.15.4, which is compatible with Zigbee and Thread protocols.
Q: What is the maximum Wi-Fi range of the board?
A: The range depends on environmental factors, but typically it can reach up to 50 meters indoors and 200 meters outdoors.
Q: Does the board support OTA (Over-the-Air) updates?
A: Yes, the ESP32-C6 chip supports OTA updates, allowing you to update firmware wirelessly.
Q: Can I power the board using a battery?
A: Yes, you can use a 3.7V LiPo battery with a suitable voltage regulator to provide 3.3V to the board.
Q: Is the board compatible with Arduino libraries?
A: Yes, the nanoESP32-C6 DevKit is compatible with most Arduino libraries for ESP32-based devices.