
How to Use RFID MFRC522: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
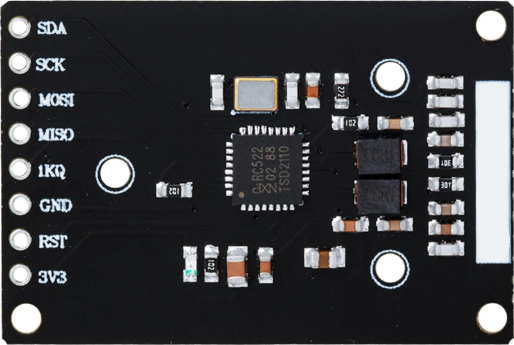
 Design with RFID MFRC522 in Cirkit Designer
Design with RFID MFRC522 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The MFRC522, manufactured by NXP, is a highly integrated RFID reader/writer IC designed for contactless communication at 13.56 MHz. It supports ISO/IEC 14443 A/MIFARE protocols, making it ideal for reading and writing RFID tags and cards. The MFRC522 is widely used in applications such as access control, payment systems, inventory management, and other systems requiring secure and efficient data exchange.
Its compact design, low power consumption, and versatile communication interfaces make it a popular choice for embedded systems and microcontroller-based projects.
Explore Projects Built with RFID MFRC522

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer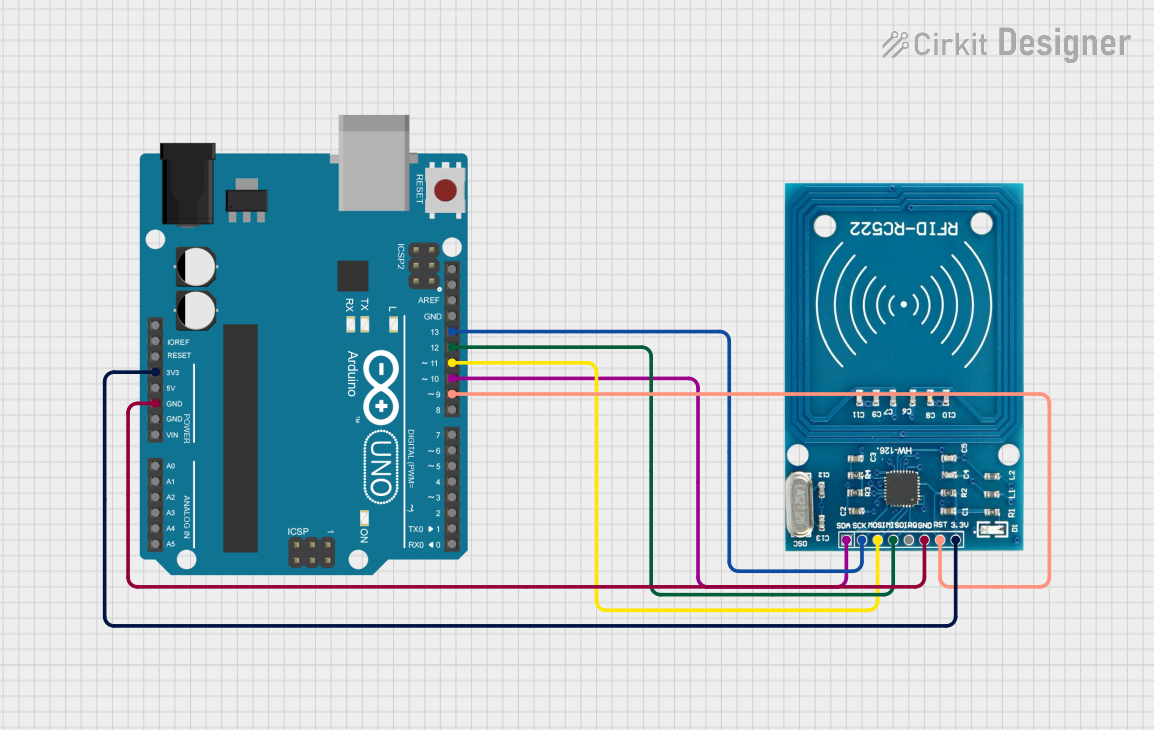
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer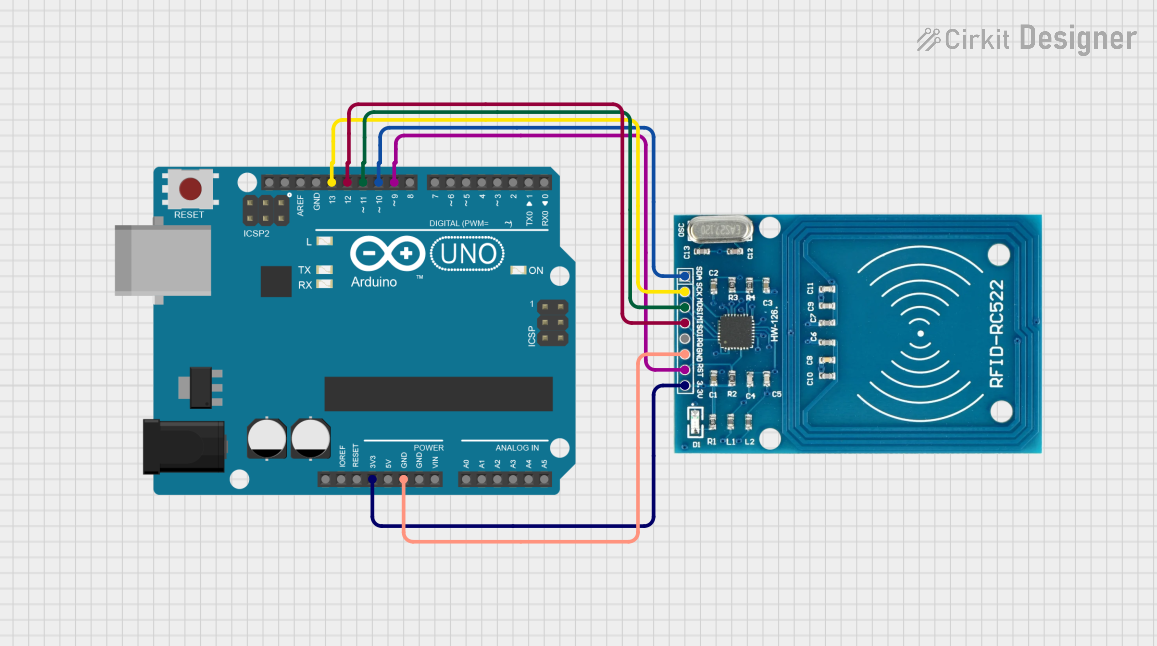
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer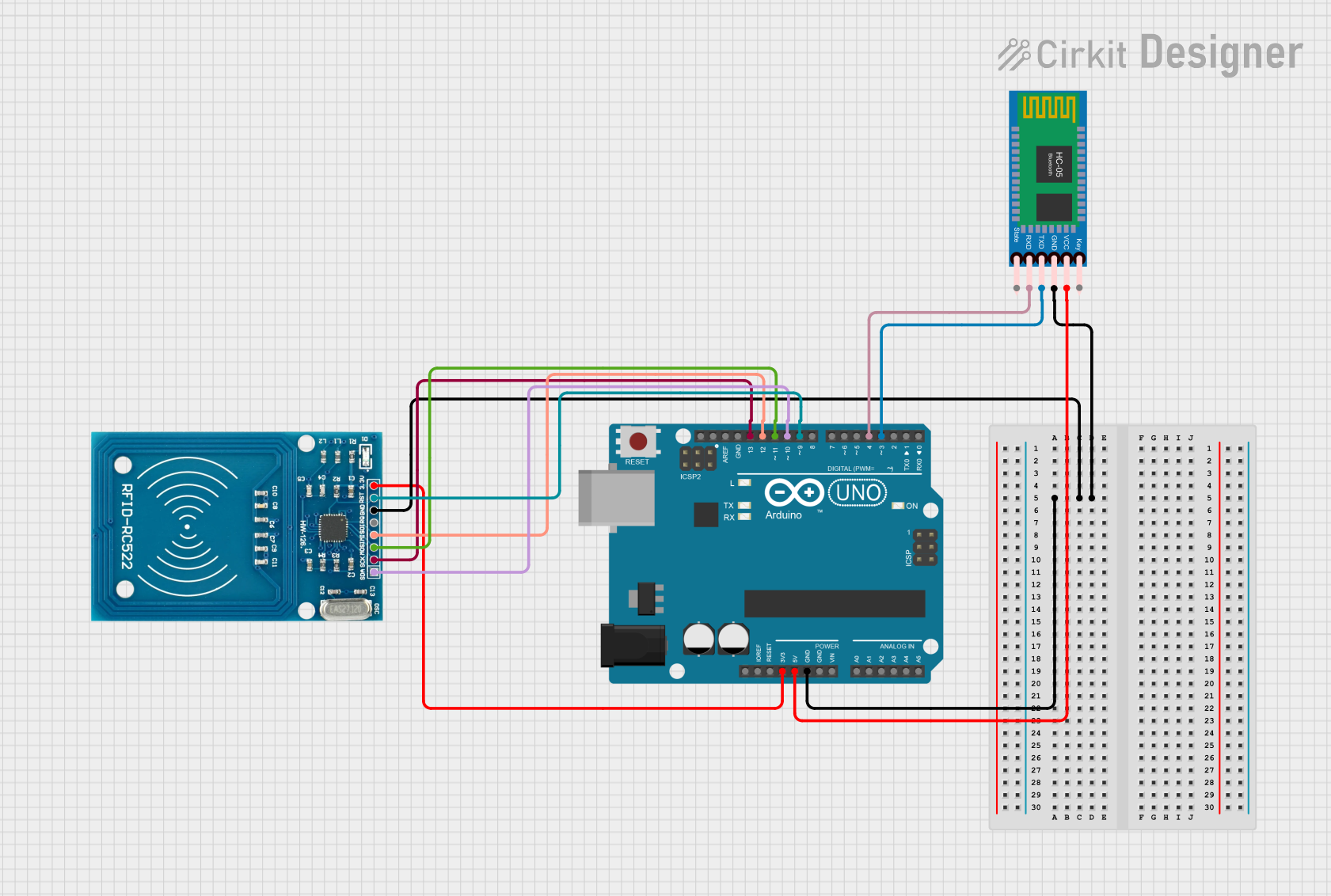
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with RFID MFRC522

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
The following are the key technical details of the MFRC522:
- Operating Frequency: 13.56 MHz
- Supported Protocols: ISO/IEC 14443 A/MIFARE
- Operating Voltage: 2.5 V to 3.3 V (logic level)
- Current Consumption: 13-26 mA (typical during operation)
- Communication Interface: SPI, I²C, UART (default: SPI)
- Maximum Data Rate: 10 Mbit/s (SPI)
- Operating Temperature: -30°C to +85°C
- Package: HVQFN32 (32-pin)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The MFRC522 IC has 32 pins, but in most breakout boards, only the essential pins are exposed. Below is the pin configuration for a typical MFRC522 breakout board:
| Pin Name | Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | 1 | Power supply input (3.3 V). |
| GND | 2 | Ground connection. |
| RST | 3 | Reset pin. Active LOW. Used to reset the IC. |
| IRQ | 4 | Interrupt request pin. Indicates events like data reception. |
| MISO/SCL/TX | 5 | SPI MISO (Master In Slave Out) / I²C Clock / UART TX (transmit) pin. |
| MOSI/SDA/RX | 6 | SPI MOSI (Master Out Slave In) / I²C Data / UART RX (receive) pin. |
| SCK | 7 | SPI Clock pin. |
| NSS/SDA | 8 | SPI Chip Select (active LOW) / I²C Address Select pin. |
| ANT1 | 9 | Antenna connection pin 1. |
| ANT2 | 10 | Antenna connection pin 2. |
Note: The exact pinout may vary depending on the breakout board. Always refer to the specific board's datasheet.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the MFRC522 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3 V power source and GND to ground.
- Communication Interface: Use SPI for communication with a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO). Connect the SPI pins (MISO, MOSI, SCK, NSS) to the corresponding pins on the microcontroller.
- Antenna: Ensure the antenna pins (ANT1 and ANT2) are connected to the onboard antenna for proper RFID communication.
- Reset: Connect the RST pin to a GPIO pin on the microcontroller for resetting the module when needed.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: The MFRC522 operates at 3.3 V logic levels. If using a 5 V microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO), use a level shifter to avoid damaging the IC.
- Antenna Placement: Ensure the antenna is not obstructed by metal objects, as this can interfere with RFID communication.
- SPI Speed: Use a moderate SPI clock speed (e.g., 4 MHz) to ensure reliable communication.
- Tag Distance: The effective range for reading RFID tags is typically 2-5 cm, depending on the tag and antenna design.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the MFRC522 with an Arduino UNO to read an RFID tag:
#include <SPI.h>
#include <MFRC522.h>
// Define MFRC522 pins
#define RST_PIN 9 // Reset pin connected to Arduino pin 9
#define SS_PIN 10 // Slave Select pin connected to Arduino pin 10
MFRC522 rfid(SS_PIN, RST_PIN); // Create an instance of the MFRC522 class
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
SPI.begin(); // Initialize SPI bus
rfid.PCD_Init(); // Initialize the MFRC522 module
Serial.println("Place an RFID tag near the reader...");
}
void loop() {
// Check if a new card is present
if (!rfid.PICC_IsNewCardPresent()) {
return; // No card detected
}
// Check if the card can be read
if (!rfid.PICC_ReadCardSerial()) {
return; // Failed to read card
}
// Print the UID of the card
Serial.print("Card UID: ");
for (byte i = 0; i < rfid.uid.size; i++) {
Serial.print(rfid.uid.uidByte[i], HEX); // Print each byte in hexadecimal
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
rfid.PICC_HaltA(); // Halt communication with the card
}
Note: This code requires the
MFRC522library, which can be installed via the Arduino Library Manager.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
No Response from the Module:
- Ensure the module is powered correctly (3.3 V).
- Verify the SPI connections and pin assignments in the code.
- Check for loose or faulty wiring.
Unable to Read RFID Tags:
- Ensure the tag is within the effective range (2-5 cm).
- Verify that the tag is compatible with the MFRC522 (e.g., MIFARE cards).
- Check for interference from nearby metal objects.
Communication Errors:
- Reduce the SPI clock speed if communication is unreliable.
- Ensure proper grounding between the module and the microcontroller.
FAQs
Q: Can the MFRC522 work with 5 V microcontrollers?
- A: Yes, but you must use a level shifter to convert 5 V signals to 3.3 V.
Q: What is the maximum range of the MFRC522?
- A: The typical range is 2-5 cm, depending on the tag and antenna design.
Q: Can the MFRC522 write data to RFID tags?
- A: Yes, the MFRC522 supports both reading and writing to compatible RFID tags.
Q: How do I increase the range of the MFRC522?
- A: Use a larger or more efficient antenna, but note that the range is inherently limited by the IC's design.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the MFRC522 into your projects and troubleshoot common issues.