
How to Use L298P: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with L298P in Cirkit Designer
Design with L298P in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The L298P is a dual H-bridge motor driver IC manufactured by Arduino. It is designed to control the direction and speed of DC motors and stepper motors. With the ability to drive two motors simultaneously and handle up to 2A per channel, the L298P is a versatile and robust solution for robotics, automation, and other motor control applications.
Explore Projects Built with L298P
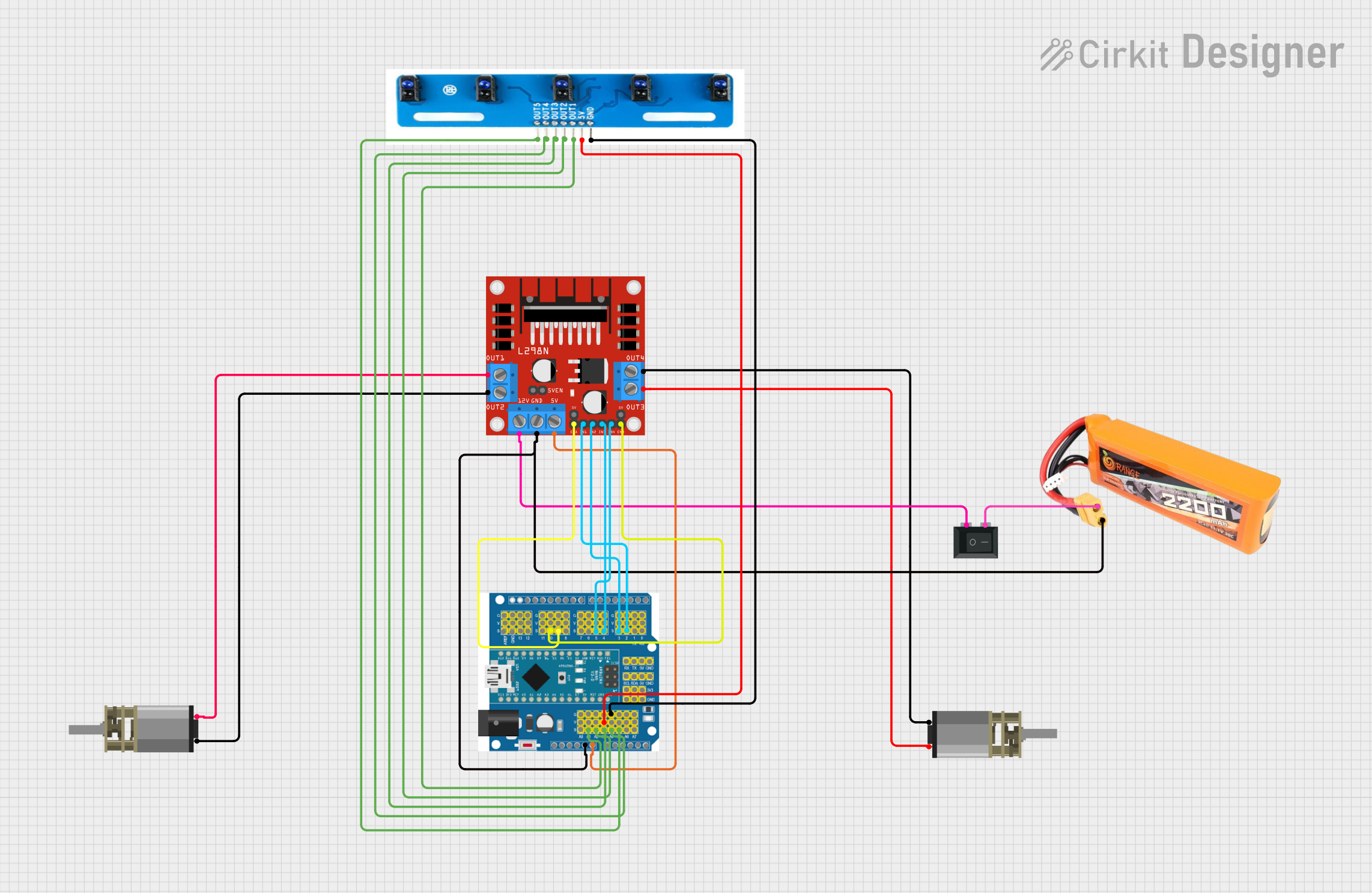
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer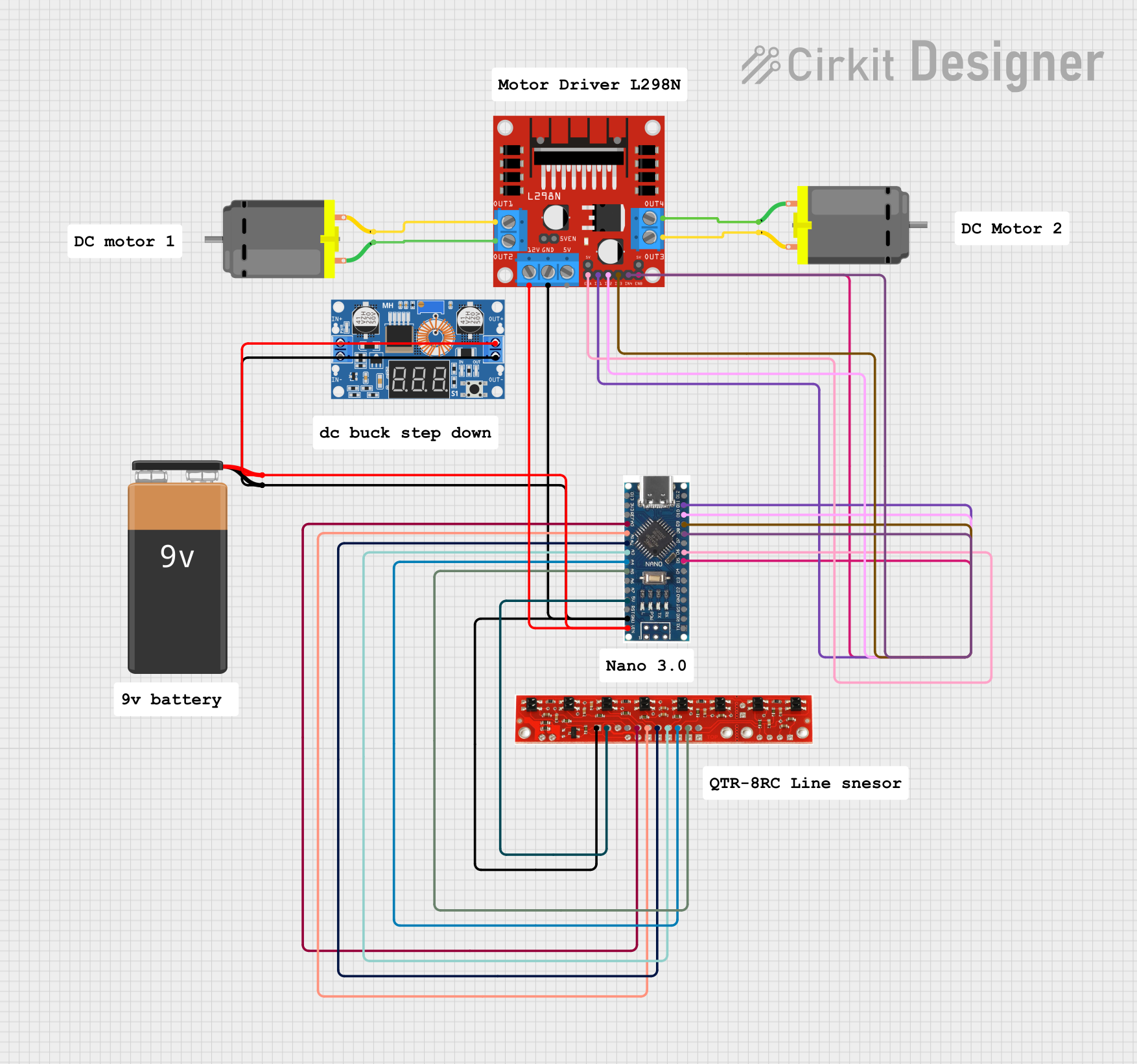
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer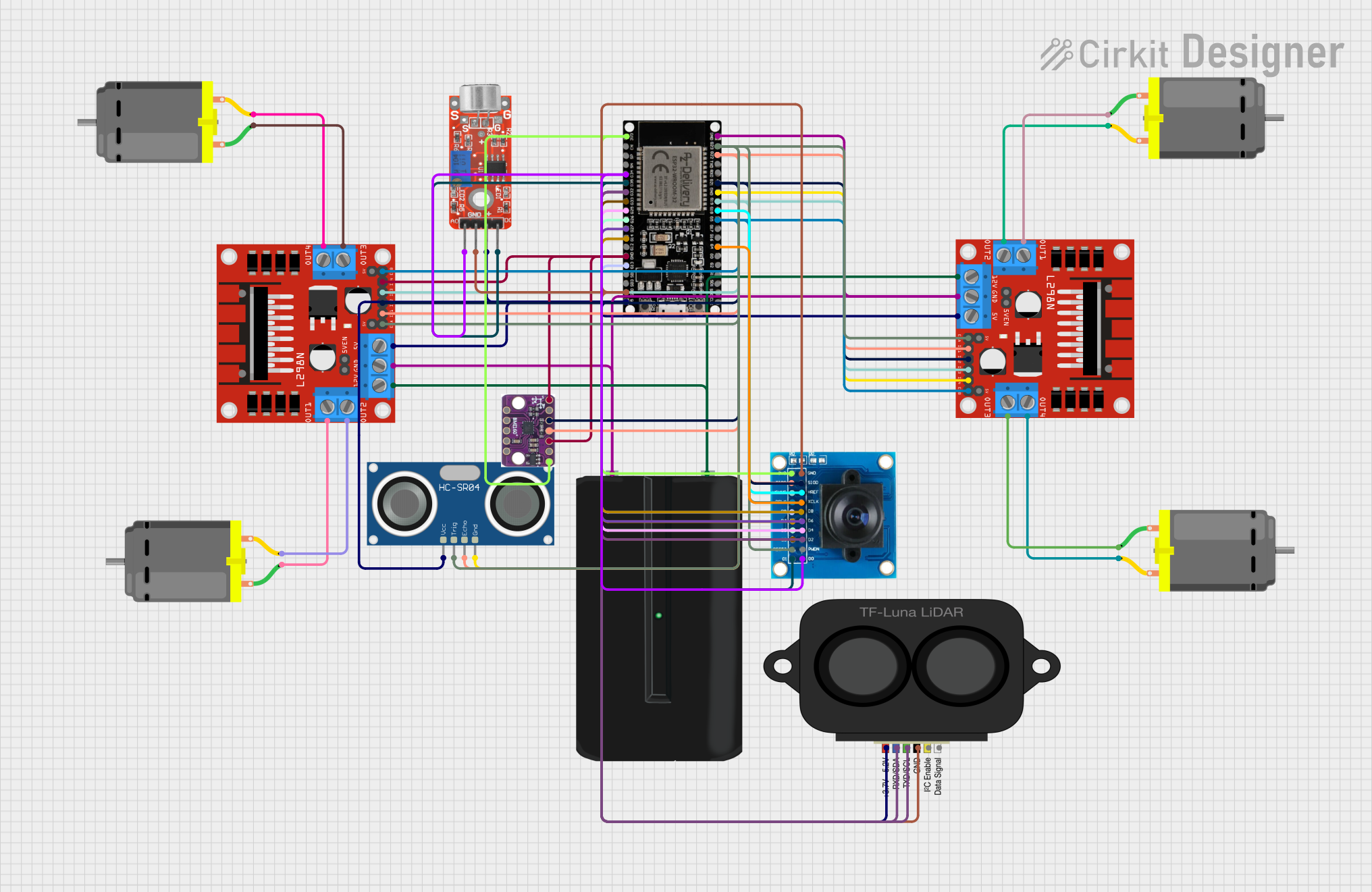
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer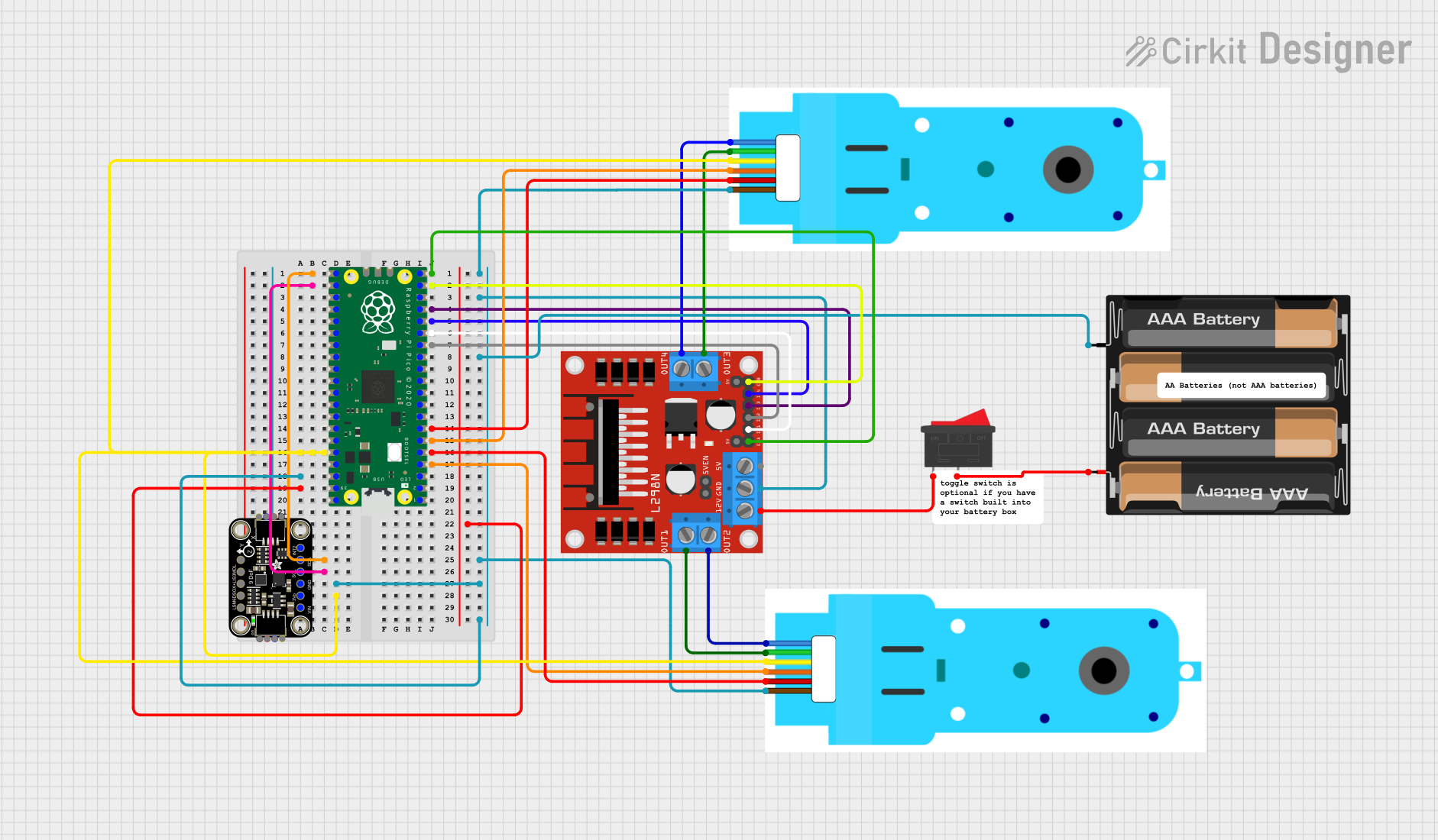
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with L298P

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Robotics and automation systems
- Motorized vehicles and drones
- Conveyor belts and industrial machinery
- Stepper motor control for CNC machines and 3D printers
- DIY electronics and hobby projects
Technical Specifications
The L298P is a high-performance motor driver IC with the following key specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Arduino |
| Part ID | L298P |
| Operating Voltage | 5V to 46V |
| Maximum Output Current | 2A per channel (continuous) |
| Peak Output Current | 3A per channel (short duration) |
| Logic Voltage | 5V |
| Power Dissipation | 25W (with proper heat sinking) |
| Control Inputs | TTL-compatible |
| Operating Temperature | -25°C to +130°C |
| Motor Types Supported | DC motors, stepper motors |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The L298P IC has 15 pins, each serving a specific function. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Enable A | Enables or disables the motor connected to OUT1 and OUT2 |
| 2 | Input 1 | Logic input to control the direction of motor A |
| 3 | Input 2 | Logic input to control the direction of motor A |
| 4 | Output 1 | Motor A output terminal 1 |
| 5 | Output 2 | Motor A output terminal 2 |
| 6 | VSS | Logic voltage supply (5V) |
| 7 | GND | Ground connection |
| 8 | VS | Motor power supply (up to 46V) |
| 9 | Enable B | Enables or disables the motor connected to OUT3 and OUT4 |
| 10 | Input 3 | Logic input to control the direction of motor B |
| 11 | Input 4 | Logic input to control the direction of motor B |
| 12 | Output 3 | Motor B output terminal 1 |
| 13 | Output 4 | Motor B output terminal 2 |
| 14 | Sense A | Current sensing pin for motor A (optional, connect to GND if unused) |
| 15 | Sense B | Current sensing pin for motor B (optional, connect to GND if unused) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the L298P in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the motor power supply (VS) to pin 8. Ensure the voltage matches the motor's requirements (up to 46V). Connect the logic voltage (5V) to pin 6.
- Motor Connections:
- For motor A, connect the motor terminals to pins 4 (OUT1) and 5 (OUT2).
- For motor B, connect the motor terminals to pins 12 (OUT3) and 13 (OUT4).
- Control Inputs: Use pins 2, 3 (for motor A) and pins 10, 11 (for motor B) to control the motor direction. Apply a HIGH or LOW signal to these pins based on the desired direction.
- Enable Pins:
- Pin 1 (Enable A) controls motor A. Set HIGH to enable or LOW to disable.
- Pin 9 (Enable B) controls motor B. Set HIGH to enable or LOW to disable.
- Current Sensing (Optional): If current sensing is required, connect pins 14 (Sense A) and 15 (Sense B) to a resistor and measure the voltage drop. Otherwise, connect these pins to GND.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Heat Dissipation: The L298P can dissipate up to 25W of power. Use a heat sink or cooling fan to prevent overheating during operation.
- Flyback Diodes: The IC includes internal flyback diodes to protect against voltage spikes caused by motor inductance.
- Power Supply Decoupling: Add decoupling capacitors (e.g., 100µF and 0.1µF) near the power supply pins to reduce noise and improve stability.
- Avoid Overcurrent: Ensure the motor's current does not exceed 2A per channel to prevent damage to the IC.
Example: Using L298P with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of controlling a DC motor using the L298P and Arduino UNO:
// Define L298P control pins
const int enableA = 9; // Enable pin for motor A
const int input1 = 8; // Input 1 for motor A
const int input2 = 7; // Input 2 for motor A
void setup() {
// Set pin modes
pinMode(enableA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(input1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(input2, OUTPUT);
// Initialize motor
digitalWrite(enableA, HIGH); // Enable motor A
digitalWrite(input1, HIGH); // Set motor A direction
digitalWrite(input2, LOW); // Set motor A direction
}
void loop() {
// Run motor at full speed for 5 seconds
analogWrite(enableA, 255); // Full speed
delay(5000);
// Stop motor for 2 seconds
analogWrite(enableA, 0); // Stop motor
delay(2000);
// Reverse motor direction and run at half speed for 5 seconds
digitalWrite(input1, LOW); // Reverse direction
digitalWrite(input2, HIGH); // Reverse direction
analogWrite(enableA, 128); // Half speed
delay(5000);
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Not Running:
- Ensure the enable pin (Enable A or Enable B) is set HIGH.
- Verify the motor power supply (VS) is connected and within the specified voltage range.
- Check the control inputs (Input 1, Input 2, etc.) for proper logic levels.
Overheating:
- Use a heat sink or cooling fan to dissipate heat.
- Ensure the motor's current does not exceed 2A per channel.
Erratic Motor Behavior:
- Add decoupling capacitors near the power supply pins to reduce noise.
- Check for loose or incorrect wiring connections.
No Current Sensing Output:
- Ensure the Sense pins (Sense A and Sense B) are connected to a resistor for current measurement.
- If current sensing is not required, connect these pins to GND.
FAQs
Q: Can the L298P drive stepper motors?
A: Yes, the L298P can drive stepper motors by controlling the sequence of inputs to the H-bridges.
Q: What is the maximum voltage the L298P can handle?
A: The L298P can handle up to 46V on the motor power supply (VS) pin.
Q: Do I need external diodes for motor protection?
A: No, the L298P includes internal flyback diodes to protect against voltage spikes.
Q: Can I use the L298P with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: The L298P requires a 5V logic voltage. Use a level shifter if interfacing with a 3.3V microcontroller.