
How to Use CAC: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
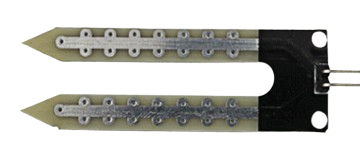
 Design with CAC in Cirkit Designer
Design with CAC in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Capacitor-AC (CAC) is a specialized type of capacitor designed to function in alternating current (AC) circuits. Unlike capacitors intended for direct current (DC) applications, CACs are built to handle the continuous polarity changes inherent in AC systems. These capacitors are widely used for filtering, coupling, energy storage, and power factor correction in various electronic and electrical systems.
Explore Projects Built with CAC
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer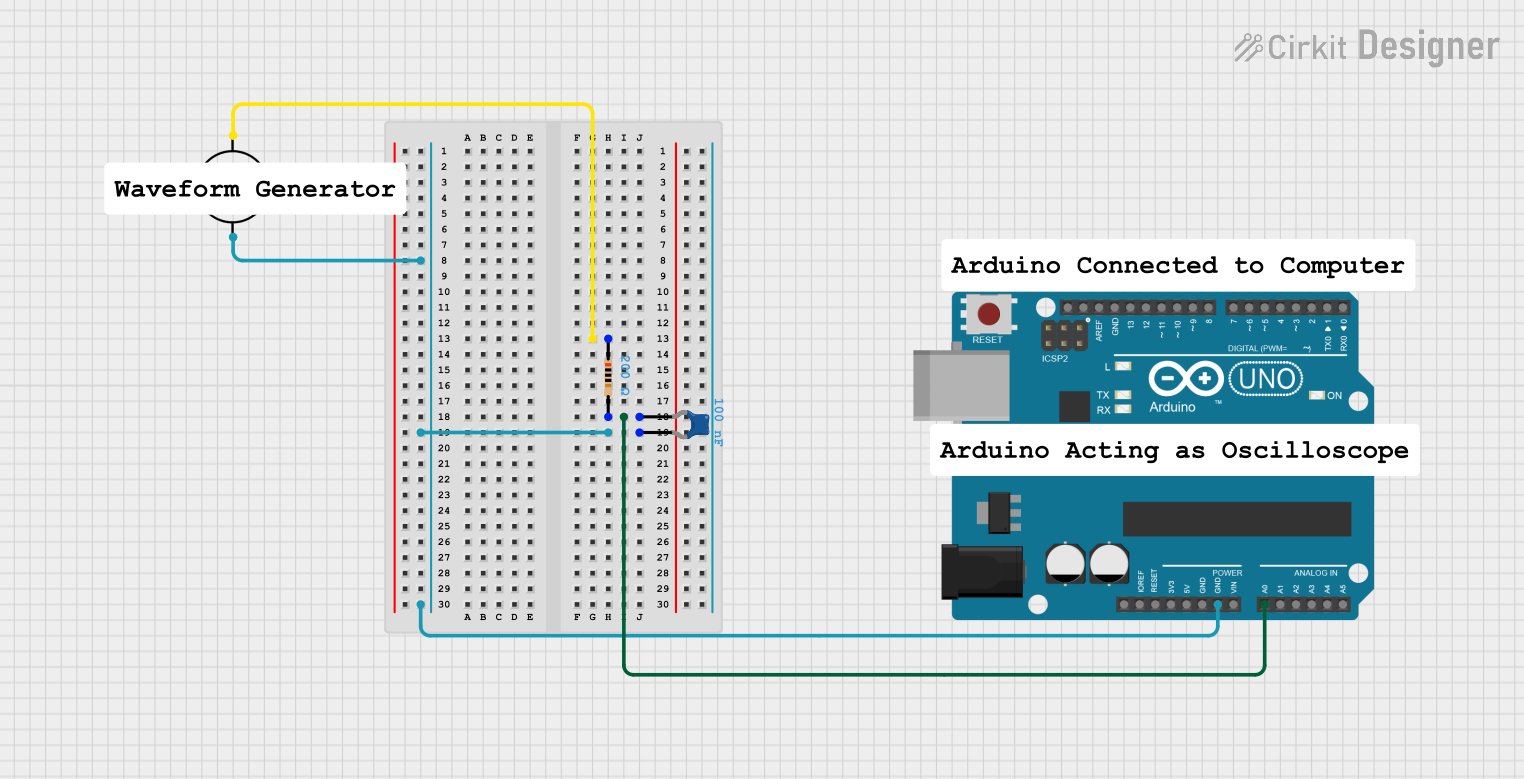
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with CAC

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- AC Signal Filtering: Removes unwanted noise or harmonics from AC signals.
- Coupling Applications: Transfers AC signals between circuit stages while blocking DC components.
- Energy Storage: Temporarily stores energy in AC circuits for smooth operation.
- Power Factor Correction: Improves the efficiency of AC power systems by compensating for reactive power.
- Motor Start/Run Applications: Provides the necessary phase shift for starting and running AC motors.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Capacitance Range: 0.1 µF to 100 µF (varies by model)
- Voltage Rating: 250V AC to 600V AC
- Frequency Range: 50 Hz to 60 Hz (standard), up to 400 Hz for specialized models
- Dielectric Material: Polypropylene or polyester (depending on the model)
- Operating Temperature: -40°C to +85°C
- Tolerance: ±5% to ±10%
- Form Factor: Cylindrical or rectangular with insulated terminals
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Capacitor-AC typically has two terminals, which are non-polarized, meaning they can be connected in either orientation in an AC circuit.
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Terminal 1 | Connects to one side of the AC circuit |
| 2 | Terminal 2 | Connects to the other side of the AC circuit |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Determine the Required Capacitance and Voltage Rating:
- Select a CAC with a capacitance value suitable for your application (e.g., filtering or coupling).
- Ensure the voltage rating exceeds the peak voltage of your AC circuit.
Connect the Terminals:
- Since CACs are non-polarized, you can connect the terminals in either orientation.
- Use insulated wires to prevent accidental short circuits.
Placement in the Circuit:
- For filtering: Place the CAC in parallel with the load to smooth out voltage fluctuations.
- For coupling: Place the CAC in series between two circuit stages to block DC components.
Secure the Capacitor:
- Mount the capacitor securely using clamps or brackets to prevent vibration or movement.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Margin: Always choose a capacitor with a voltage rating at least 20% higher than the peak AC voltage.
- Temperature Limits: Avoid operating the capacitor near its maximum temperature rating to ensure longevity.
- Frequency Compatibility: Verify that the capacitor is rated for the frequency of your AC circuit.
- Safety Precautions: Discharge the capacitor before handling to avoid electric shock.
Example: Using a CAC with an Arduino UNO
While CACs are not directly interfaced with microcontrollers like the Arduino UNO, they can be used in circuits connected to the Arduino. For example, a CAC can filter noise from an AC power supply that powers an Arduino-based project.
/*
Example: Using a Capacitor-AC (CAC) for Noise Filtering
This example demonstrates how to use a CAC to filter noise from an AC power
supply in a circuit powering an Arduino UNO.
Note: The CAC is connected in parallel with the AC power supply to smooth
voltage fluctuations.
*/
// No direct code is required for the CAC itself, as it is a passive component.
// Ensure proper placement in the circuit as described in the usage instructions.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Excessive Heat Generation:
- Cause: Operating the capacitor beyond its voltage or temperature rating.
- Solution: Replace the capacitor with one that has a higher voltage or temperature rating.
Capacitor Failure (Short Circuit or Open Circuit):
- Cause: Aging, overvoltage, or physical damage.
- Solution: Inspect and replace the capacitor. Ensure proper voltage margins.
Noise or Ineffective Filtering:
- Cause: Incorrect capacitance value or poor connections.
- Solution: Verify the capacitance value and check all connections for reliability.
Humming or Buzzing Noise:
- Cause: Loose mounting or mechanical resonance.
- Solution: Secure the capacitor firmly and ensure proper insulation.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Measure Capacitance: Use a capacitance meter to verify the capacitor's value.
- Inspect for Damage: Look for bulging, cracks, or leaks in the capacitor body.
- Check Connections: Ensure all connections are tight and free of corrosion.
- Test with a Multimeter: Use a multimeter to check for continuity or shorts.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively use and maintain a Capacitor-AC (CAC) in your AC circuits.