
How to Use CD4051: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with CD4051 in Cirkit Designer
Design with CD4051 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The CD4051 is an 8-channel analog multiplexer/demultiplexer that allows the selection of one of eight input signals to be routed to a single output, or vice versa. It is a versatile component that operates with a wide supply voltage range (3V to 18V), making it suitable for both low-power and high-voltage applications. The CD4051 is commonly used in signal routing, data acquisition systems, audio switching, and sensor interfacing.
Explore Projects Built with CD4051

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer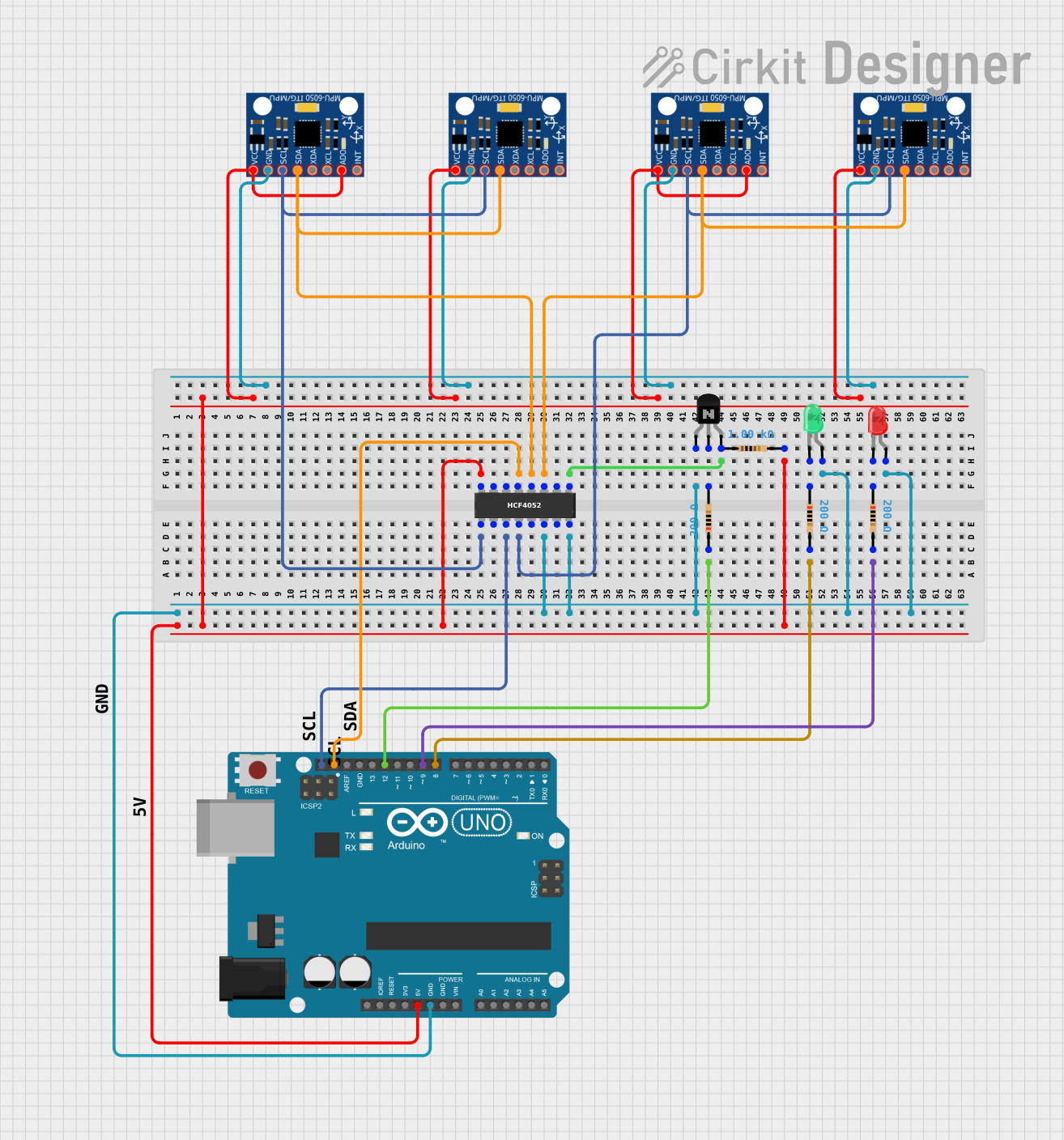
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer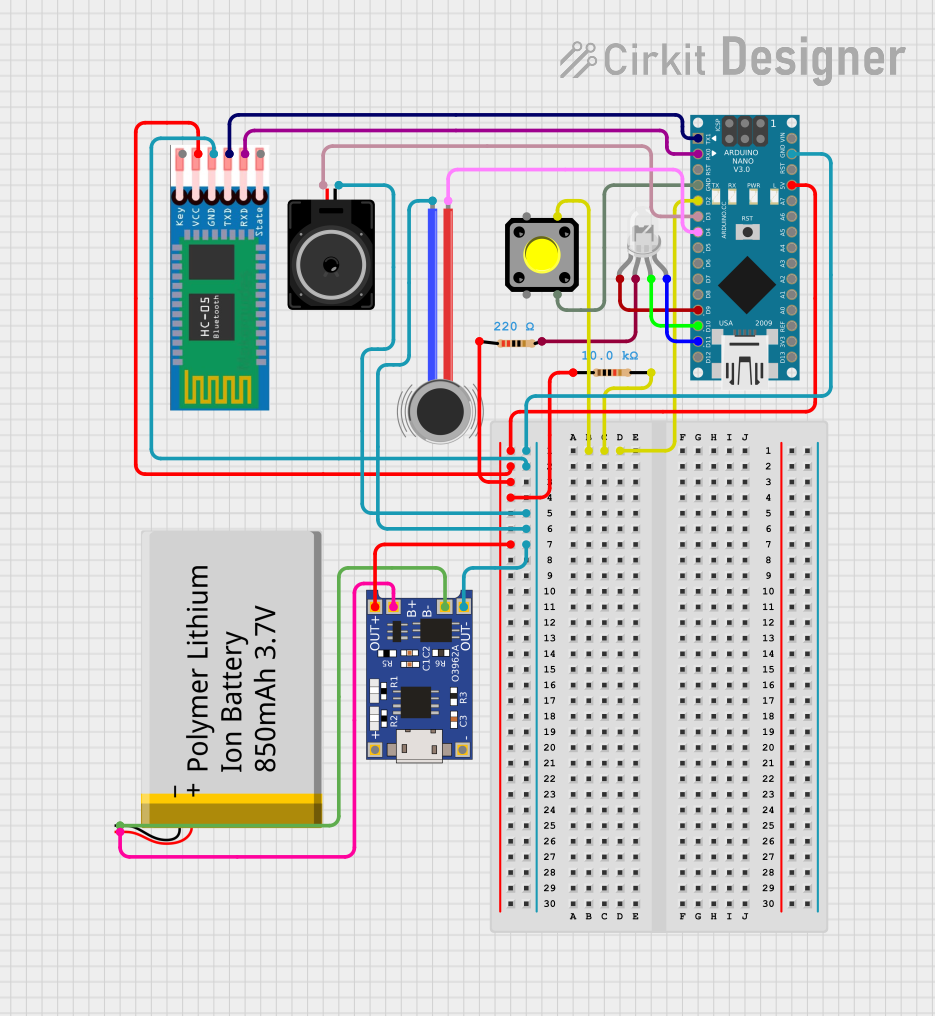
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with CD4051

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications:
- Signal routing in data acquisition systems
- Audio signal switching
- Sensor multiplexing
- Analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) channel selection
- Test equipment and instrumentation
Technical Specifications
Key Specifications:
- Supply Voltage (VDD - VSS): 3V to 18V
- Analog Signal Range: 0V to VDD
- Control Logic Voltage Range: 0V to VDD
- On-Resistance (RON): ~125Ω (typical at VDD = 10V)
- Maximum Input Current: ±10mA
- Propagation Delay: ~50ns (typical at VDD = 10V)
- Operating Temperature Range: -55°C to +125°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions:
The CD4051 is available in a 16-pin DIP, SOIC, or TSSOP package. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin No. | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VEE | Negative supply voltage (commonly connected to GND for single-supply use). |
| 2 | A | Address select input A (LSB). |
| 3 | B | Address select input B. |
| 4 | C | Address select input C (MSB). |
| 5 | IN/OUT 4 | Analog input/output channel 4. |
| 6 | IN/OUT 6 | Analog input/output channel 6. |
| 7 | IN/OUT 7 | Analog input/output channel 7. |
| 8 | VSS | Ground (0V reference). |
| 9 | IN/OUT 8 | Analog input/output channel 8. |
| 10 | IN/OUT 5 | Analog input/output channel 5. |
| 11 | IN/OUT 3 | Analog input/output channel 3. |
| 12 | IN/OUT 2 | Analog input/output channel 2. |
| 13 | IN/OUT 1 | Analog input/output channel 1. |
| 14 | IN/OUT 0 | Analog input/output channel 0. |
| 15 | ENABLE | Active LOW enable pin (must be LOW for normal operation). |
| 16 | VDD | Positive supply voltage. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the CD4051 in a Circuit:
Power Supply:
- Connect the VDD pin to the positive supply voltage (3V to 18V).
- Connect the VSS pin to ground (0V).
- If using a dual-supply configuration, connect VEE to the negative supply voltage.
Control Logic:
- Use the address select pins (A, B, C) to select one of the eight channels. The binary value on these pins determines the active channel.
- Ensure the ENABLE pin is set to LOW for the multiplexer to function. If HIGH, all channels are disconnected.
Signal Connections:
- Connect the analog signals to the IN/OUT 0-7 pins.
- The selected channel will route the signal to the common I/O pin (or vice versa).
Example Address Selection:
- For channel 0: A = 0, B = 0, C = 0
- For channel 7: A = 1, B = 1, C = 1
Important Considerations:
- Ensure the analog signal voltage does not exceed the supply voltage range (0V to VDD).
- Minimize the load on the selected channel to reduce signal distortion caused by the on-resistance.
- Use decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1µF) near the power supply pins to reduce noise.
Example: Connecting CD4051 to Arduino UNO
The CD4051 can be controlled using digital pins on an Arduino UNO. Below is an example code to select different channels and read analog signals:
// CD4051 Control Pins
const int pinA = 2; // Address pin A
const int pinB = 3; // Address pin B
const int pinC = 4; // Address pin C
const int enablePin = 5; // Enable pin (active LOW)
const int analogInput = A0; // Common I/O pin connected to Arduino analog input
void setup() {
// Set control pins as outputs
pinMode(pinA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinB, OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinC, OUTPUT);
pinMode(enablePin, OUTPUT);
// Enable the CD4051
digitalWrite(enablePin, LOW);
// Initialize serial communication
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
for (int channel = 0; channel < 8; channel++) {
// Set the address pins to select the channel
digitalWrite(pinA, channel & 0x01); // LSB
digitalWrite(pinB, (channel >> 1) & 0x01);
digitalWrite(pinC, (channel >> 2) & 0x01);
// Read the analog value from the selected channel
int value = analogRead(analogInput);
// Print the channel and its value
Serial.print("Channel ");
Serial.print(channel);
Serial.print(": ");
Serial.println(value);
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms before switching to the next channel
}
}
Notes:
- The ENABLE pin must remain LOW for the multiplexer to function.
- The analog signal range should not exceed the Arduino's ADC input range (0V to 5V).
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues:
No Signal Output:
- Ensure the ENABLE pin is LOW.
- Verify the address pins (A, B, C) are set correctly for the desired channel.
Signal Distortion:
- Check if the analog signal exceeds the supply voltage range (0V to VDD).
- Reduce the load on the selected channel to minimize the effect of on-resistance.
Incorrect Channel Selection:
- Verify the binary values on the address pins match the desired channel.
- Check for loose or incorrect connections to the control pins.
Noise or Interference:
- Add decoupling capacitors near the power supply pins.
- Use shielded cables for analog signals if operating in a noisy environment.
FAQs:
Q1: Can the CD4051 handle digital signals?
Yes, the CD4051 can route digital signals as long as the voltage levels are within the supply voltage range (0V to VDD).
Q2: Can I use the CD4051 with a dual power supply?
Yes, the VEE pin can be connected to a negative voltage for dual-supply operation, allowing the analog signal range to extend below 0V.
Q3: What happens if the ENABLE pin is HIGH?
When the ENABLE pin is HIGH, all channels are disconnected, and no signal will pass through the multiplexer.
Q4: How do I reduce signal loss through the CD4051?
Minimize the load on the selected channel and operate the CD4051 at a higher supply voltage to reduce the on-resistance.