
How to Use TP4056 Battery Charging Protection Module (Type C): Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
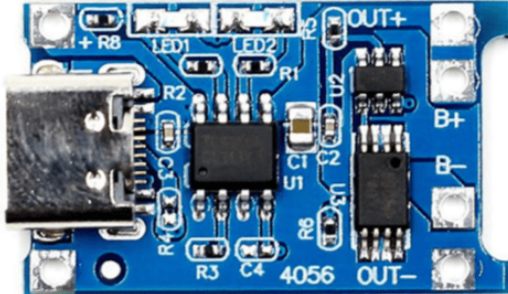
 Design with TP4056 Battery Charging Protection Module (Type C) in Cirkit Designer
Design with TP4056 Battery Charging Protection Module (Type C) in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TP4056 Battery Charging Protection Module (Type C) is a compact, highly integrated solution for charging and protecting single-cell lithium-ion or lithium polymer batteries. It is equipped with a USB Type-C input port and is designed for portable electronic devices, such as power banks, DIY electronics projects, and any application that requires battery management. The module's built-in protection features safeguard the battery from overcharging, over-discharging, and overcurrent conditions, ensuring safe and reliable operation.
Explore Projects Built with TP4056 Battery Charging Protection Module (Type C)

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer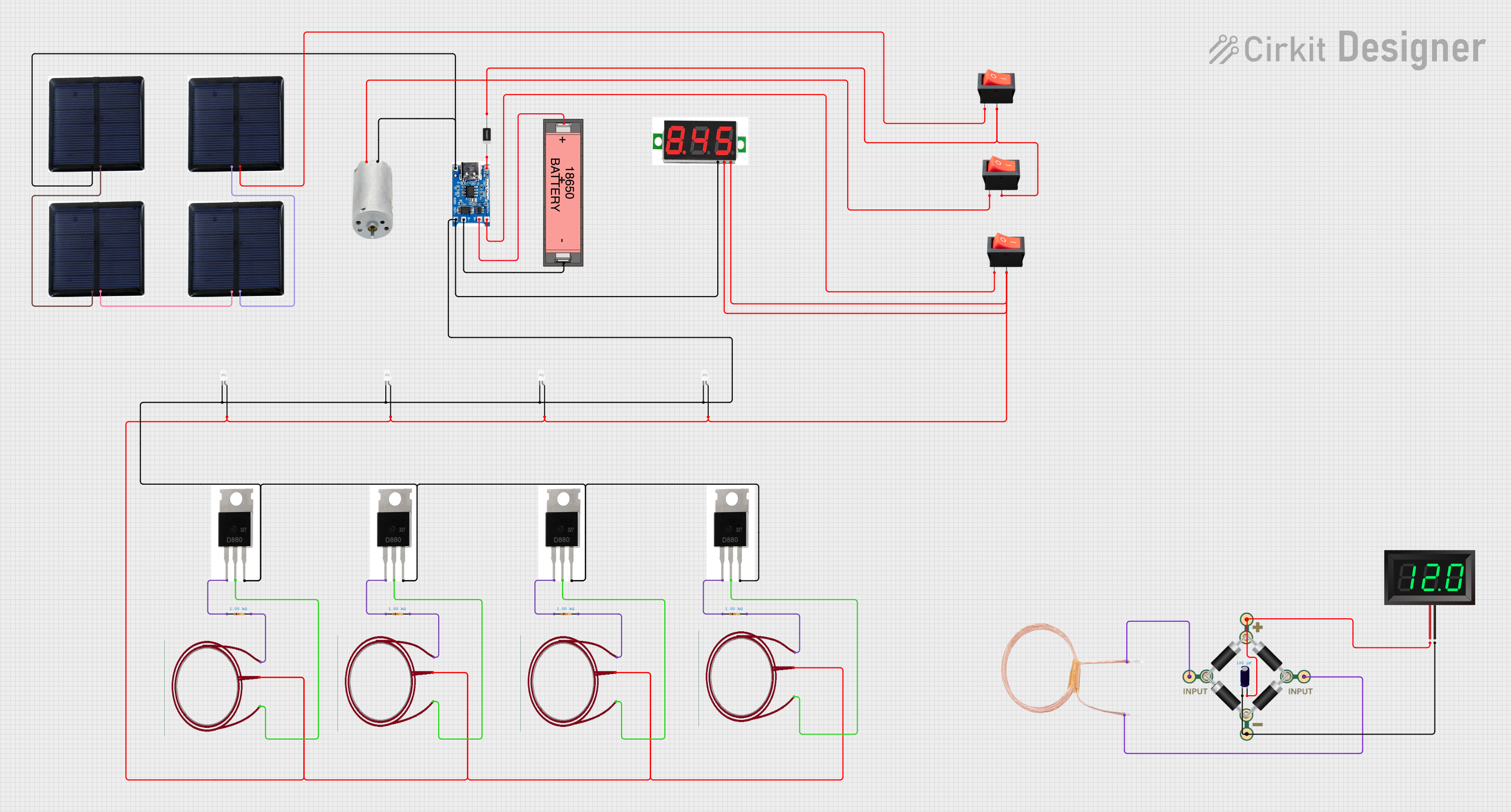
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer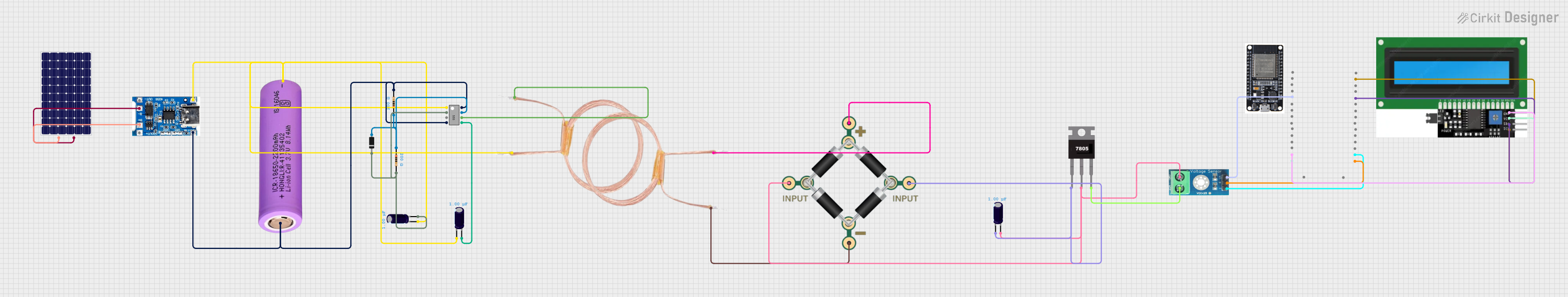
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TP4056 Battery Charging Protection Module (Type C)

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Input Voltage (VIN): 4.5V to 5.5V
- Charge Current (ICHG): Programmable up to 1A via resistor
- Battery Voltage (VBAT): 4.2V precision charging voltage
- Operating Temperature: -10°C to +85°C
- Charging Indicator: LED status for charging and full charge
- Protection Features: Overcharge, over-discharge, and overcurrent protection
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | B+ | Battery positive terminal |
| 2 | B- | Battery negative terminal |
| 3 | OUT+ | Output positive terminal |
| 4 | OUT- | Output negative terminal |
| 5 | IN+ | USB Type-C positive input |
| 6 | IN- | USB Type-C negative input |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connecting the Battery:
- Connect the positive terminal of the battery to the B+ pin.
- Connect the negative terminal of the battery to the B- pin.
Power Supply:
- Connect a 5V power supply to the USB Type-C input (IN+ and IN- pins).
Load Connection:
- Connect the load to the OUT+ and OUT- pins.
Charging:
- When the module is powered via USB Type-C, the charging process starts automatically if the battery voltage is below 4.2V.
- The charging status is indicated by the onboard LED.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Input Voltage: Ensure that the input voltage does not exceed the specified range to prevent damage to the module.
- Current Rating: Do not exceed the maximum charging current of 1A; select an appropriate resistor to set the desired charging current.
- Heat Dissipation: Provide adequate ventilation around the module as it may generate heat during operation.
- Battery Type: Use the module only with lithium-ion or lithium polymer batteries.
- Protection: Do not disable the onboard protection features as they are critical for battery safety.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- LED Not Lighting Up: Ensure the power supply is connected correctly and the battery is properly seated.
- Battery Not Charging: Check the battery connections and verify that the battery is not already fully charged or damaged.
- Module Overheating: Reduce the charging current if the module is too hot during operation.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Check Connections: Verify all connections are secure and correct.
- Inspect Battery: Ensure the battery is in good condition and compatible with the module.
- Current Setting: Confirm the charging current is set correctly for your battery.
FAQs
Q: Can I charge multiple batteries with this module? A: No, the TP4056 is designed for single-cell lithium-ion or lithium polymer batteries.
Q: What should I do if the module gets too hot? A: Reduce the charging current, ensure proper ventilation, and check for any shorts or excessive load on the output.
Q: How do I know when the battery is fully charged? A: The onboard LED will change its status, typically turning off or changing color, to indicate a full charge.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
// There is no direct interaction code for the TP4056 with Arduino as it is a standalone charging module.
// However, you can monitor the battery voltage using Arduino's ADC.
const int batteryPin = A0; // Connect battery to A0 through a voltage divider
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(batteryPin);
float voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0); // Convert the reading to voltage
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.println(voltage);
delay(1000); // Wait for a second between readings
}
Note: When measuring battery voltage, ensure that the voltage at the analog pin does not exceed 5V. Use a voltage divider if necessary to bring the voltage within a safe range for the Arduino ADC.