
How to Use Water Pump: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Water Pump in Cirkit Designer
Design with Water Pump in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A water pump is an electronic device designed to move water from one location to another. It is commonly used in applications such as irrigation systems, drainage systems, water supply systems, aquariums, and cooling systems. Water pumps are available in various types, including submersible pumps, centrifugal pumps, and diaphragm pumps, each suited for specific use cases.
Water pumps are essential in both residential and industrial settings, providing efficient water transfer and circulation. They are often controlled electronically, making them compatible with microcontrollers like Arduino for automation purposes.
Explore Projects Built with Water Pump
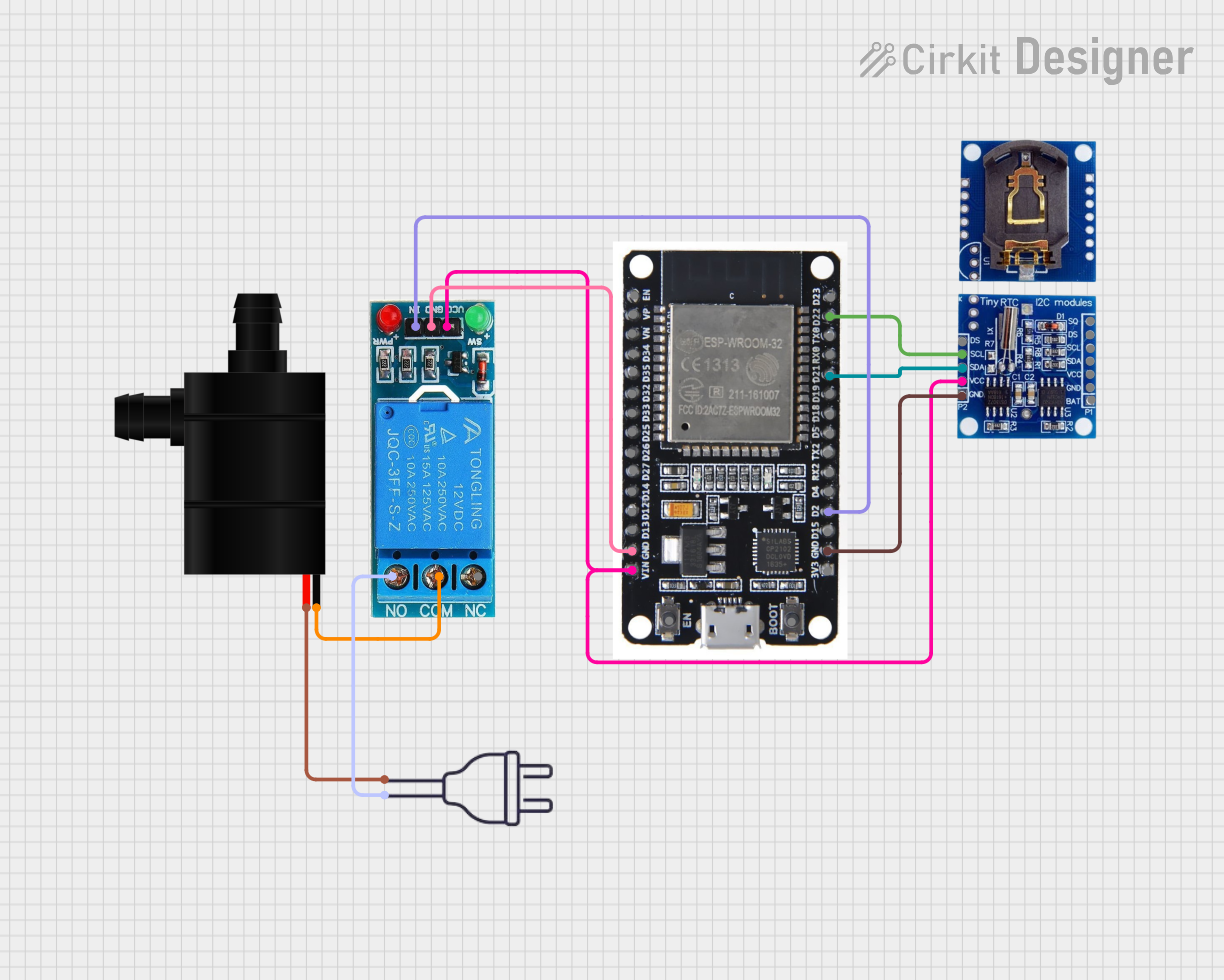
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer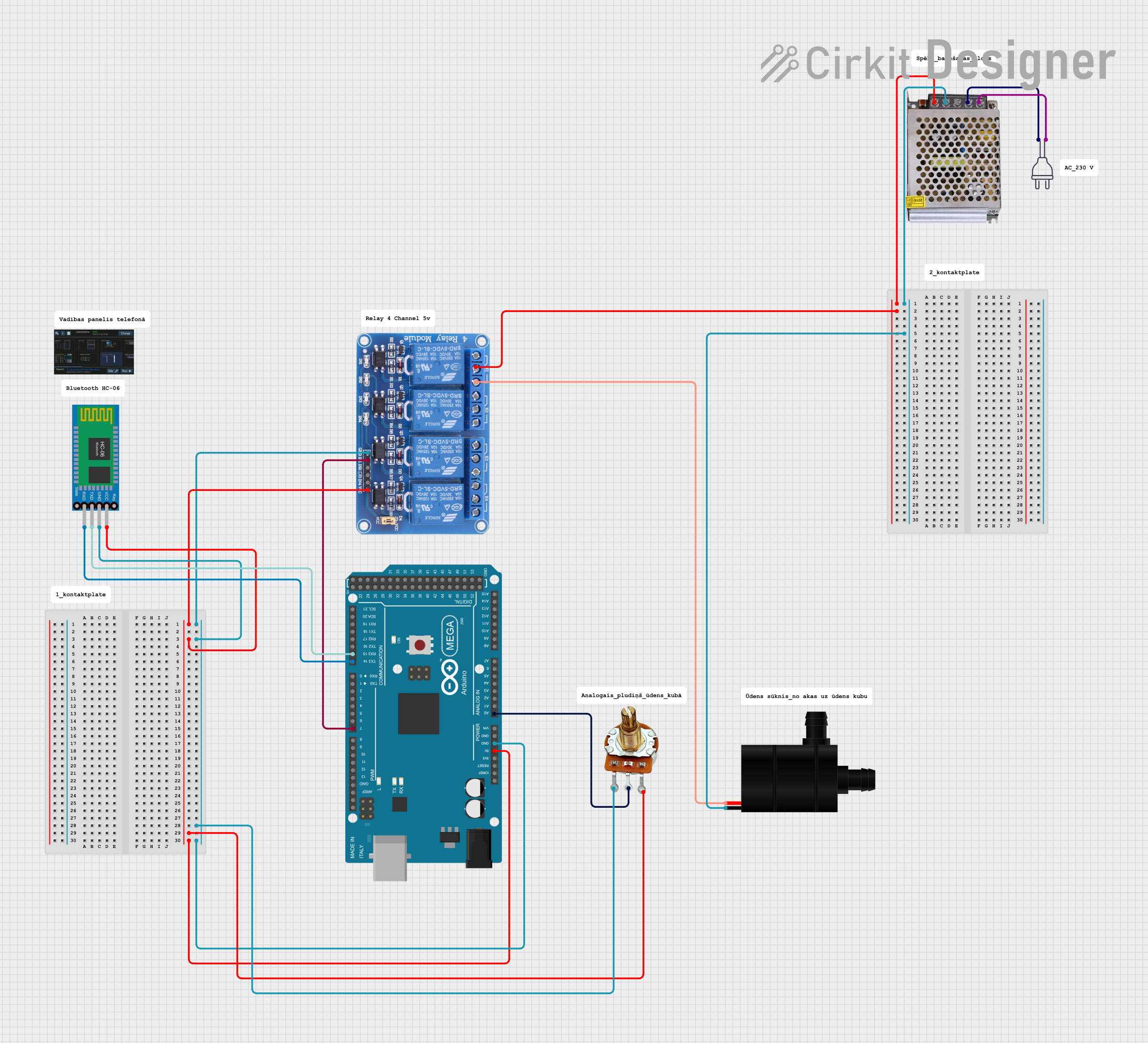
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer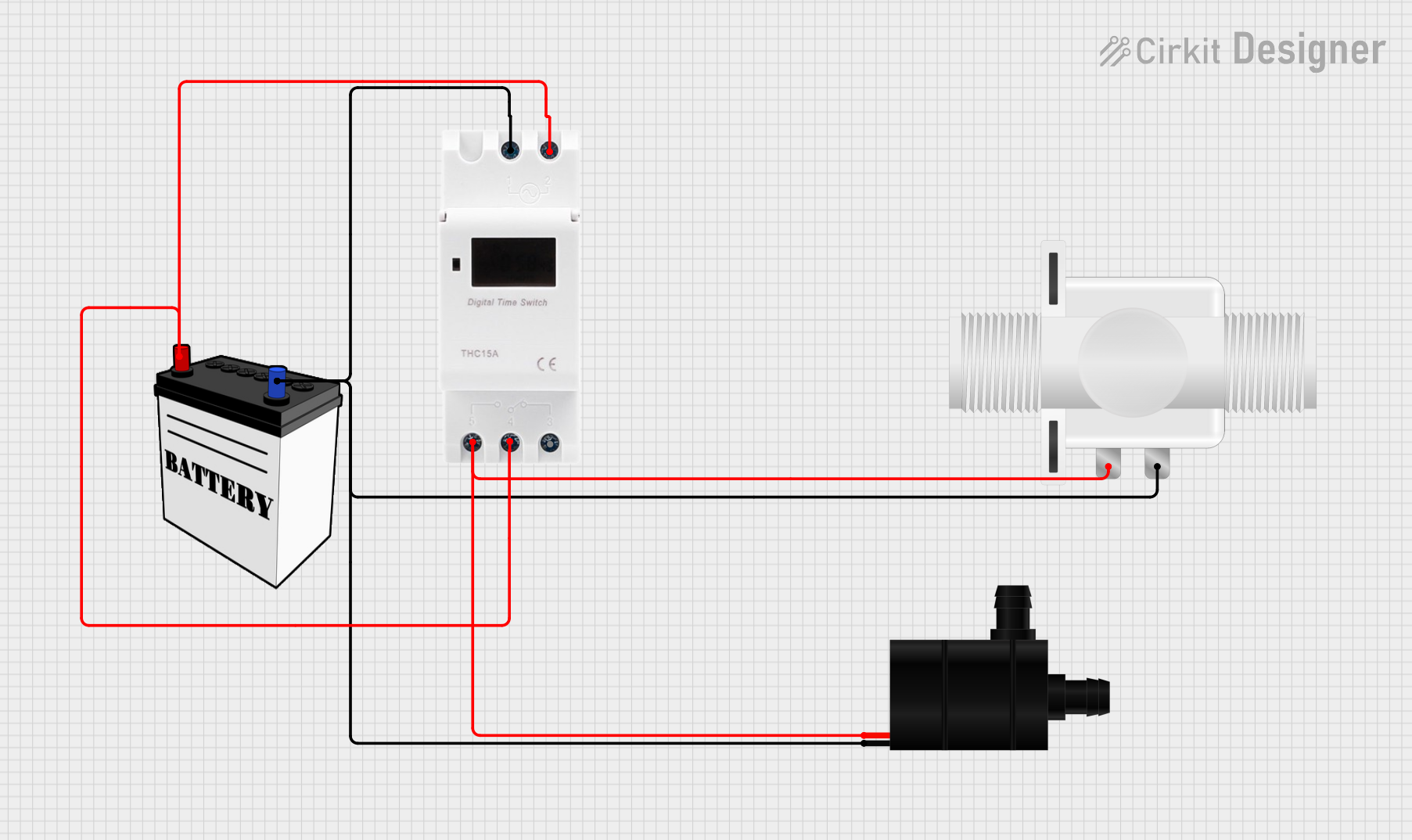
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer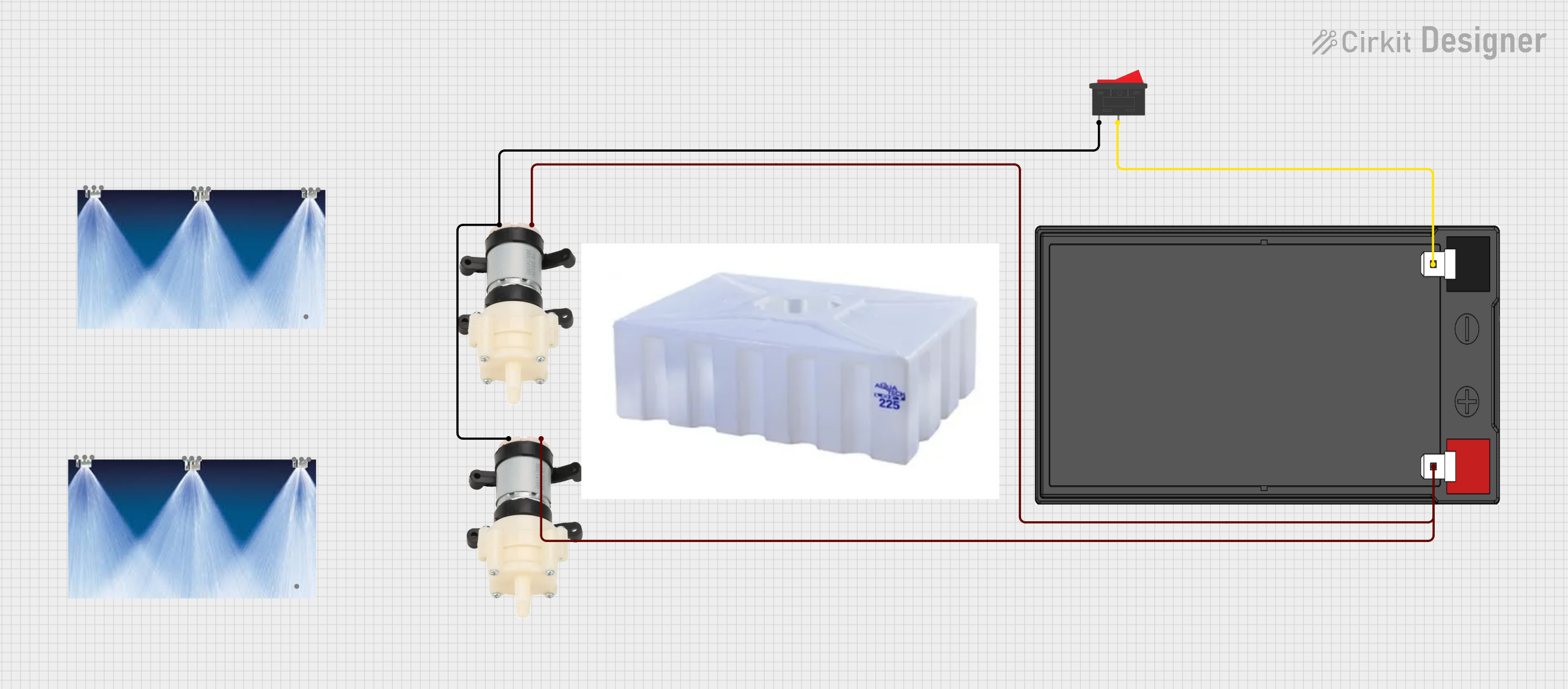
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Water Pump

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a typical DC water pump. Specifications may vary depending on the specific model.
General Specifications
- Operating Voltage: 3V to 12V DC
- Operating Current: 0.1A to 0.5A
- Power Consumption: 1W to 6W
- Flow Rate: 80 L/h to 300 L/h (liters per hour)
- Maximum Lift: 1m to 3m (depending on the model)
- Pump Type: Submersible or non-submersible
- Material: Plastic or metal housing (waterproof for submersible models)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Most DC water pumps have two wires for operation. The table below describes the connections:
| Wire Color | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Red | Positive (+) | Connect to the positive terminal of the power supply or motor driver. |
| Black | Negative (-) | Connect to the ground (GND) of the power supply or motor driver. |
For advanced pumps with additional features (e.g., speed control or sensors), refer to the specific model's datasheet for pinout details.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Water Pump in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Ensure the pump is powered within its operating voltage range (e.g., 5V or 12V DC). Use a regulated power supply to avoid damage.
- Connections:
- Connect the red wire to the positive terminal of the power supply or motor driver.
- Connect the black wire to the ground terminal.
- Control: For automated control, use a relay module or a motor driver to switch the pump on and off. This can be controlled by a microcontroller like an Arduino.
- Water Source: Submerge the pump (if submersible) or place the inlet hose in the water source. Ensure the pump is primed (filled with water) before operation to prevent dry running.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Dry Running: Avoid running the pump without water, as this can damage the motor or impeller.
- Voltage Compatibility: Always check the pump's voltage rating and use a compatible power source.
- Filtration: Use a filter to prevent debris from entering the pump and causing blockages or damage.
- Cooling: Ensure proper cooling for non-submersible pumps to prevent overheating.
- Polarity: Double-check the wire connections to avoid reversing polarity, which may damage the pump.
Example: Controlling a Water Pump with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control a water pump using an Arduino UNO and a relay module.
// Example: Controlling a water pump with Arduino and a relay module
// Ensure the relay module is connected to the Arduino and the pump is powered
// by an external power source within its voltage range.
const int relayPin = 7; // Pin connected to the relay module
void setup() {
pinMode(relayPin, OUTPUT); // Set the relay pin as an output
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // Ensure the relay is off at startup
}
void loop() {
// Turn the pump ON
digitalWrite(relayPin, HIGH); // Activate the relay
delay(5000); // Keep the pump on for 5 seconds
// Turn the pump OFF
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // Deactivate the relay
delay(5000); // Keep the pump off for 5 seconds
}
Note: Ensure the relay module is rated for the pump's voltage and current. Use an external power source for the pump, as the Arduino cannot supply sufficient power.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Pump Does Not Start:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Verify the connections and ensure the power supply matches the pump's voltage and current requirements.
Low Water Flow:
- Cause: Blocked inlet or outlet, or insufficient power.
- Solution: Check for debris in the inlet or outlet and clean if necessary. Ensure the power supply is adequate.
Pump Overheats:
- Cause: Dry running or prolonged operation without cooling.
- Solution: Ensure the pump is submerged (if submersible) or has adequate cooling. Avoid running the pump without water.
Noise or Vibration:
- Cause: Loose mounting or debris in the impeller.
- Solution: Secure the pump properly and inspect the impeller for debris.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a water pump with an AC power source?
- A: No, most small water pumps are designed for DC power. Use a DC power supply or a compatible motor driver.
Q: How do I control the pump's speed?
- A: Use a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal with a motor driver to control the pump's speed.
Q: Can the pump run continuously?
- A: Yes, but ensure proper cooling and avoid dry running to prevent damage.
Q: Is the pump waterproof?
- A: Only submersible pumps are waterproof. Non-submersible pumps must be kept dry.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use and troubleshoot a water pump in various applications.