
How to Use AD620: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
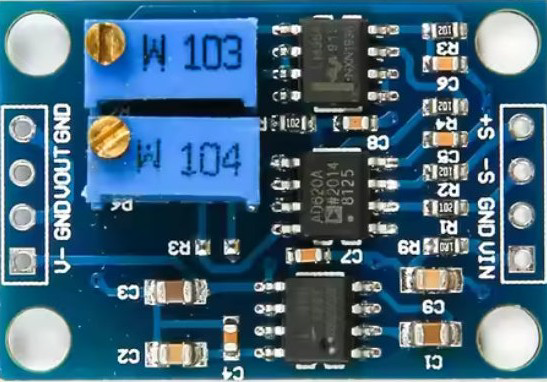
 Design with AD620 in Cirkit Designer
Design with AD620 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The AD620 is a low-power, high-accuracy instrumentation amplifier designed for precision signal amplification. It is widely used in applications requiring the amplification of small differential signals in the presence of large common-mode voltages. With its high common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR) and low noise performance, the AD620 is ideal for sensor signal conditioning, medical instrumentation, and data acquisition systems. Its low power consumption and compact design make it suitable for portable and battery-powered devices.
Explore Projects Built with AD620
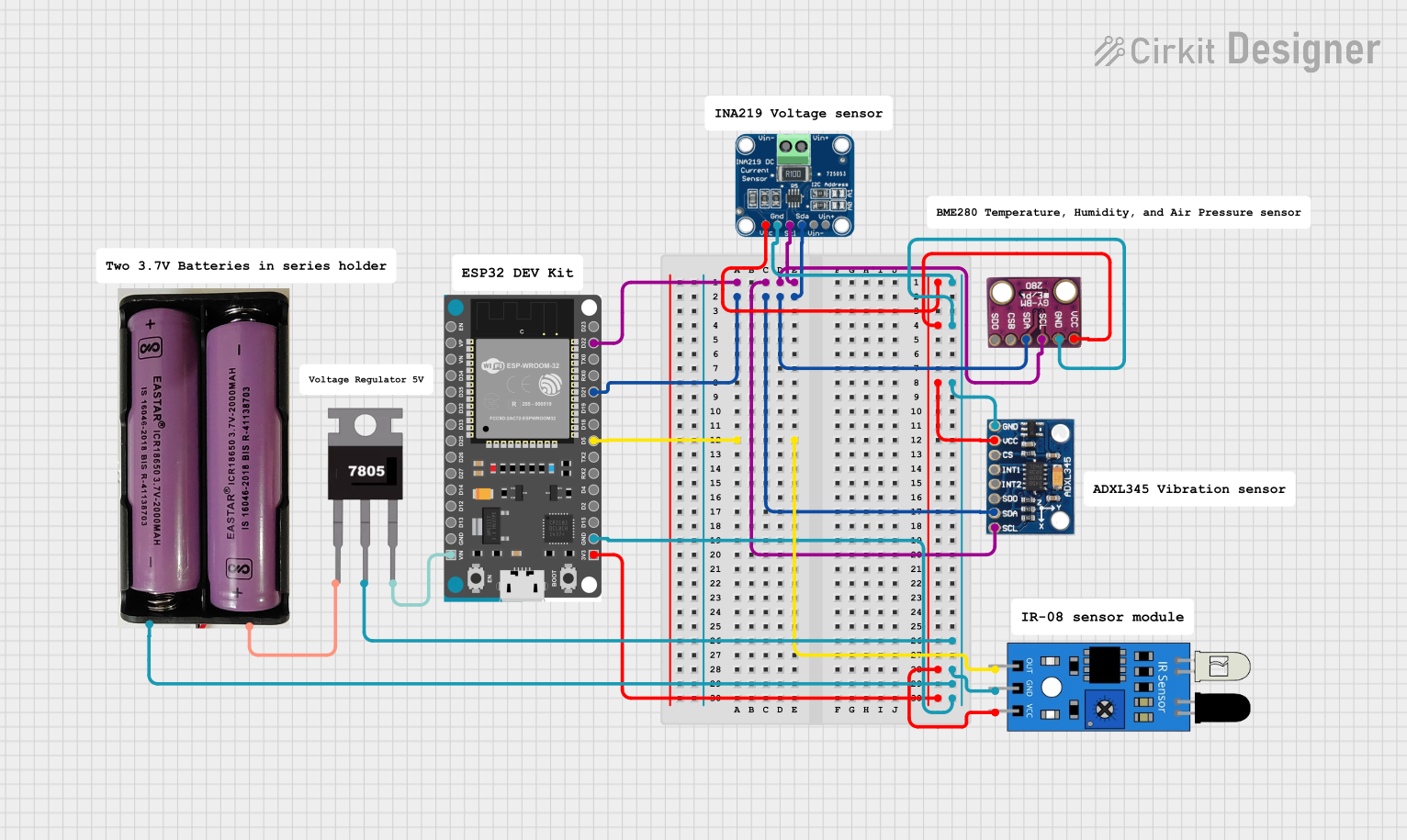
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer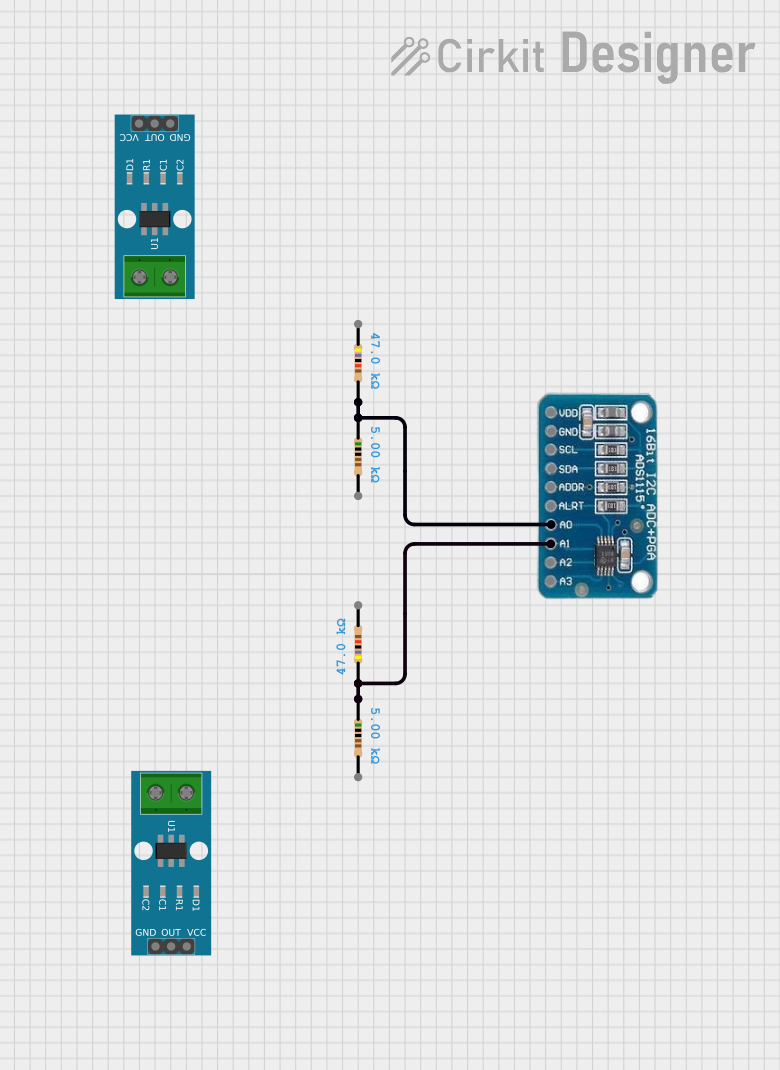
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer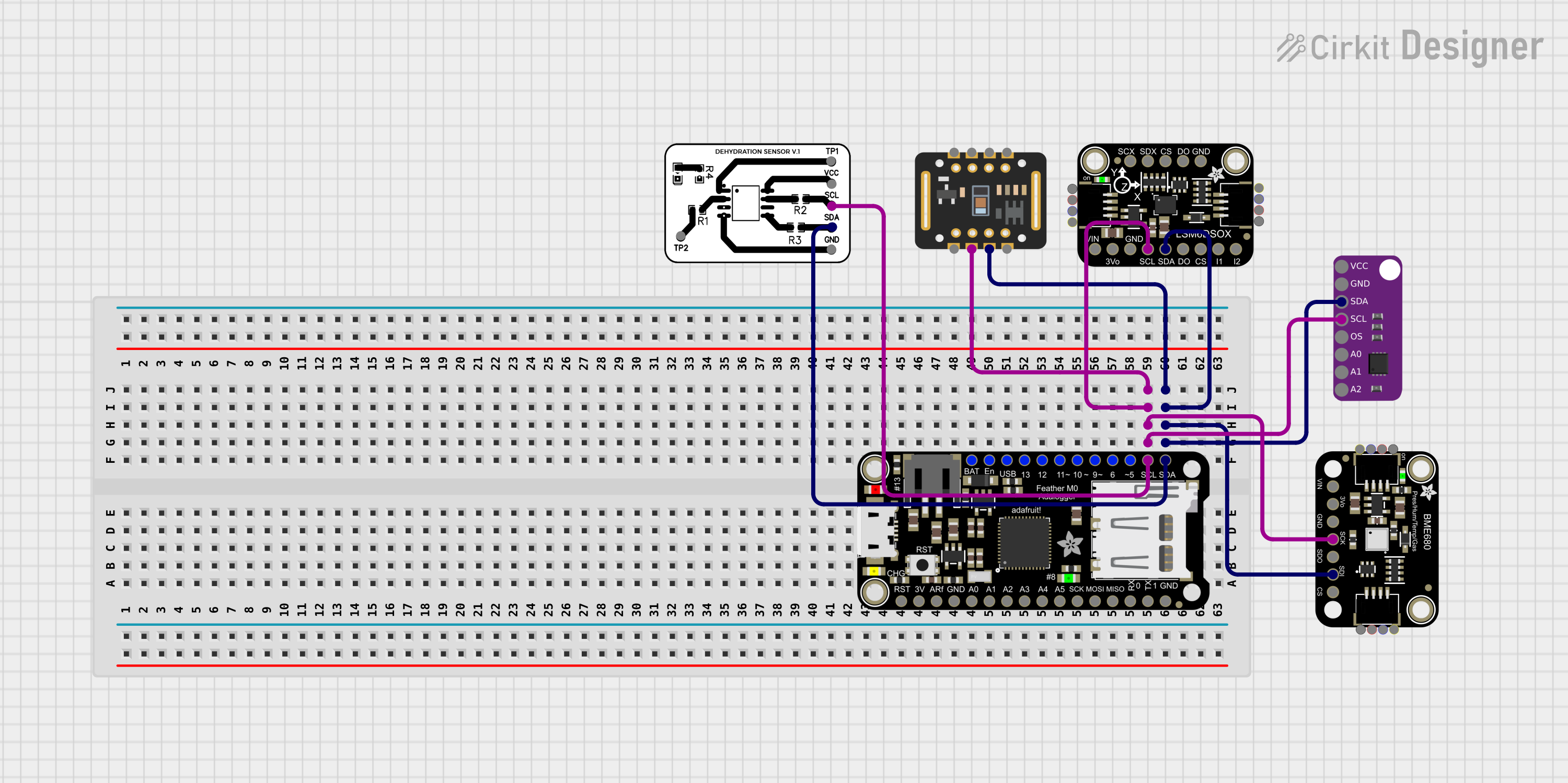
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with AD620

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Medical instrumentation (e.g., ECG, EEG)
- Sensor signal amplification (e.g., strain gauges, thermocouples)
- Data acquisition systems
- Industrial process controls
- Portable and battery-powered devices
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Supply Voltage: ±2.3V to ±18V (dual supply) or 4.6V to 36V (single supply)
- Input Impedance: 10 GΩ (differential), 10 GΩ (common-mode)
- Gain Range: 1 to 10,000 (set by an external resistor)
- Gain Equation: ( G = 1 + \frac{49.4k\Omega}{R_G} )
- Common-Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR): 100 dB (typical at G = 10)
- Input Offset Voltage: 50 µV (typical)
- Bandwidth: 120 kHz (at G = 1)
- Quiescent Current: 1.3 mA (typical)
- Package Options: 8-pin DIP, SOIC, and MSOP
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The AD620 is available in an 8-pin package. The pinout and descriptions are as follows:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ref | Reference voltage input. Sets the output voltage reference level. |
| 2 | -In | Inverting input of the differential amplifier. |
| 3 | +In | Non-inverting input of the differential amplifier. |
| 4 | -Vs | Negative power supply (e.g., -5V for dual supply or GND for single supply). |
| 5 | RG | Gain-setting resistor connection. |
| 6 | Output | Amplifier output. |
| 7 | +Vs | Positive power supply (e.g., +5V for dual supply or +5V to +36V for single). |
| 8 | RG | Gain-setting resistor connection (same as Pin 5). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the AD620 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the AD620 to a dual power supply (e.g., ±5V) or a single power supply (e.g., 5V and GND). Ensure the supply voltage is within the specified range.
- Input Connections: Connect the differential signal to the +In (Pin 3) and -In (Pin 2) pins. Ensure the input signal is within the common-mode voltage range.
- Gain Setting: Select the desired gain by connecting a resistor (( R_G )) between the RG pins (Pins 5 and 8). Use the gain equation ( G = 1 + \frac{49.4k\Omega}{R_G} ) to calculate the resistor value.
- Output Reference: Connect the Ref pin (Pin 1) to a reference voltage (e.g., GND for single-supply operation or a mid-supply voltage for dual-supply operation).
- Output Connection: The amplified signal will be available at the Output pin (Pin 6). Connect this pin to the next stage of your circuit.
Important Considerations
- Use precision resistors for ( R_G ) to ensure accurate gain settings.
- Decouple the power supply with capacitors (e.g., 0.1 µF ceramic and 10 µF electrolytic) close to the power pins to reduce noise.
- Avoid exceeding the input voltage range to prevent distortion or damage to the device.
- For single-supply operation, ensure the input signal and reference voltage are within the allowable range.
Example: Connecting the AD620 to an Arduino UNO
The AD620 can be used to amplify a sensor signal for an Arduino UNO. Below is an example of interfacing the AD620 with a strain gauge sensor:
Circuit Connections
- Connect the strain gauge output to the +In and -In pins of the AD620.
- Set the gain using a resistor ( R_G ) (e.g., 10 kΩ for a gain of approximately 5).
- Connect the AD620 output to an analog input pin (e.g., A0) of the Arduino UNO.
- Power the AD620 with a 5V single supply (connect +Vs to 5V and -Vs to GND).
Arduino Code
// Example code for reading AD620 output with Arduino UNO
const int sensorPin = A0; // AD620 output connected to analog pin A0
float sensorValue = 0; // Variable to store the sensor reading
float voltage = 0; // Variable to store the calculated voltage
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin); // Read the analog value from AD620
voltage = (sensorValue / 1023.0) * 5.0; // Convert to voltage (5V reference)
// Print the voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Voltage: ");
Serial.print(voltage, 3); // Print voltage with 3 decimal places
Serial.println(" V");
delay(500); // Wait for 500 ms before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Signal:
- Verify the power supply connections and ensure the AD620 is powered correctly.
- Check the input signal and ensure it is within the allowable range.
- Confirm that the gain-setting resistor (( R_G )) is properly connected.
Distorted Output:
- Ensure the input signal is within the common-mode voltage range.
- Check for excessive gain settings that may cause the output to saturate.
High Noise in Output:
- Use proper decoupling capacitors on the power supply pins.
- Minimize noise in the input signal by using shielded cables or twisted pairs.
Incorrect Gain:
- Double-check the value of the gain-setting resistor (( R_G )).
- Ensure the resistor is connected securely between Pins 5 and 8.
FAQs
Q1: Can the AD620 operate with a single power supply?
Yes, the AD620 can operate with a single supply voltage (e.g., 5V). Ensure the input signal and reference voltage are within the allowable range for single-supply operation.
Q2: How do I calculate the gain for the AD620?
The gain is calculated using the formula ( G = 1 + \frac{49.4k\Omega}{R_G} ), where ( R_G ) is the resistor connected between Pins 5 and 8.
Q3: What is the maximum gain I can achieve with the AD620?
The AD620 can achieve a maximum gain of 10,000. However, high gains may reduce bandwidth and increase noise, so choose the gain carefully based on your application.
Q4: Can I use the AD620 for AC signals?
Yes, the AD620 can amplify AC signals. Ensure proper coupling and biasing for AC signal applications.