
How to Use INA149: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with INA149 in Cirkit Designer
Design with INA149 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The INA149 is a precision instrumentation amplifier designed for low-power applications. It is specifically engineered to amplify small differential signals while rejecting large common-mode voltages. With its high input impedance, low offset voltage, and low noise characteristics, the INA149 is well-suited for applications requiring accurate signal amplification in challenging environments.
Explore Projects Built with INA149
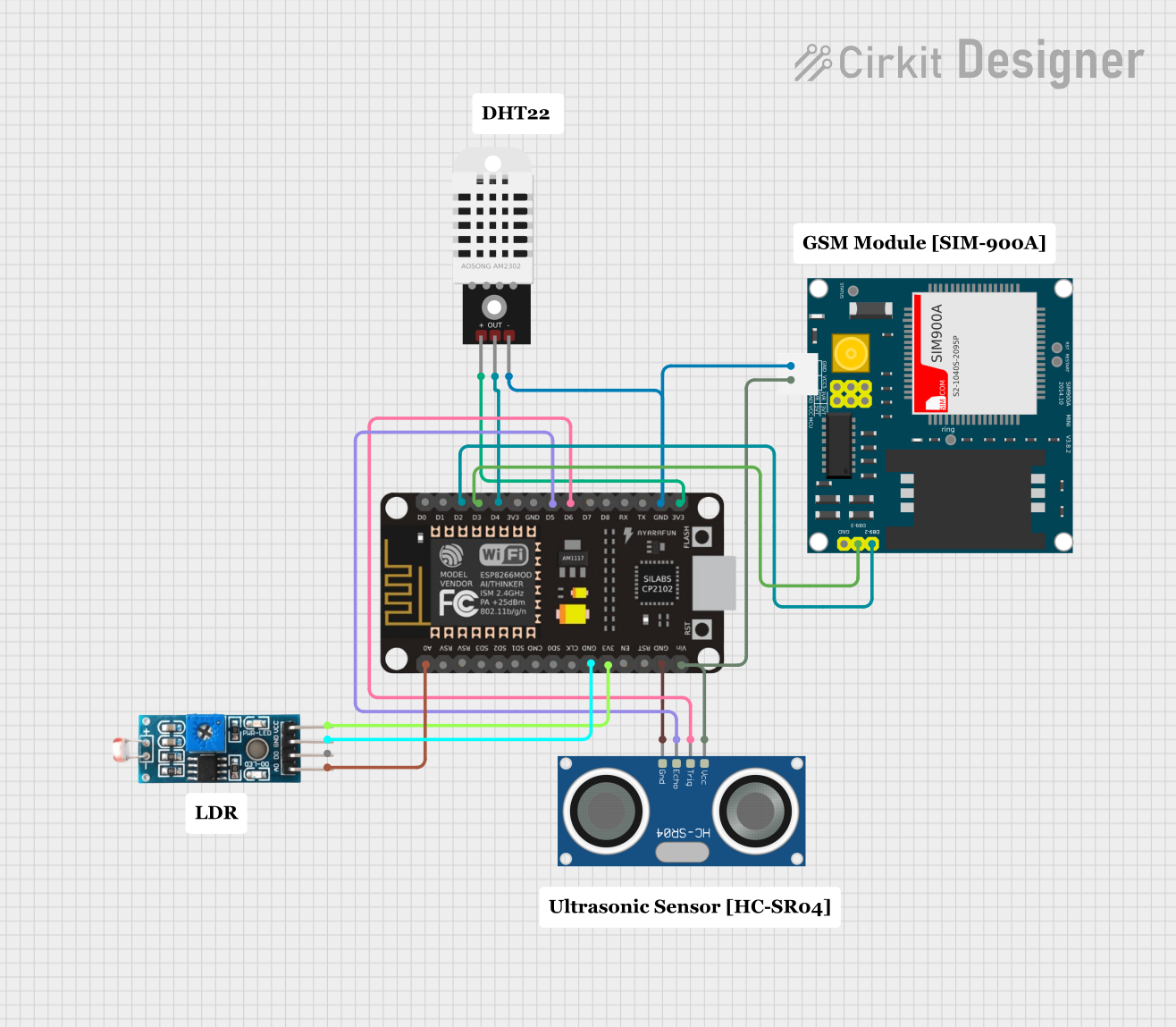
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer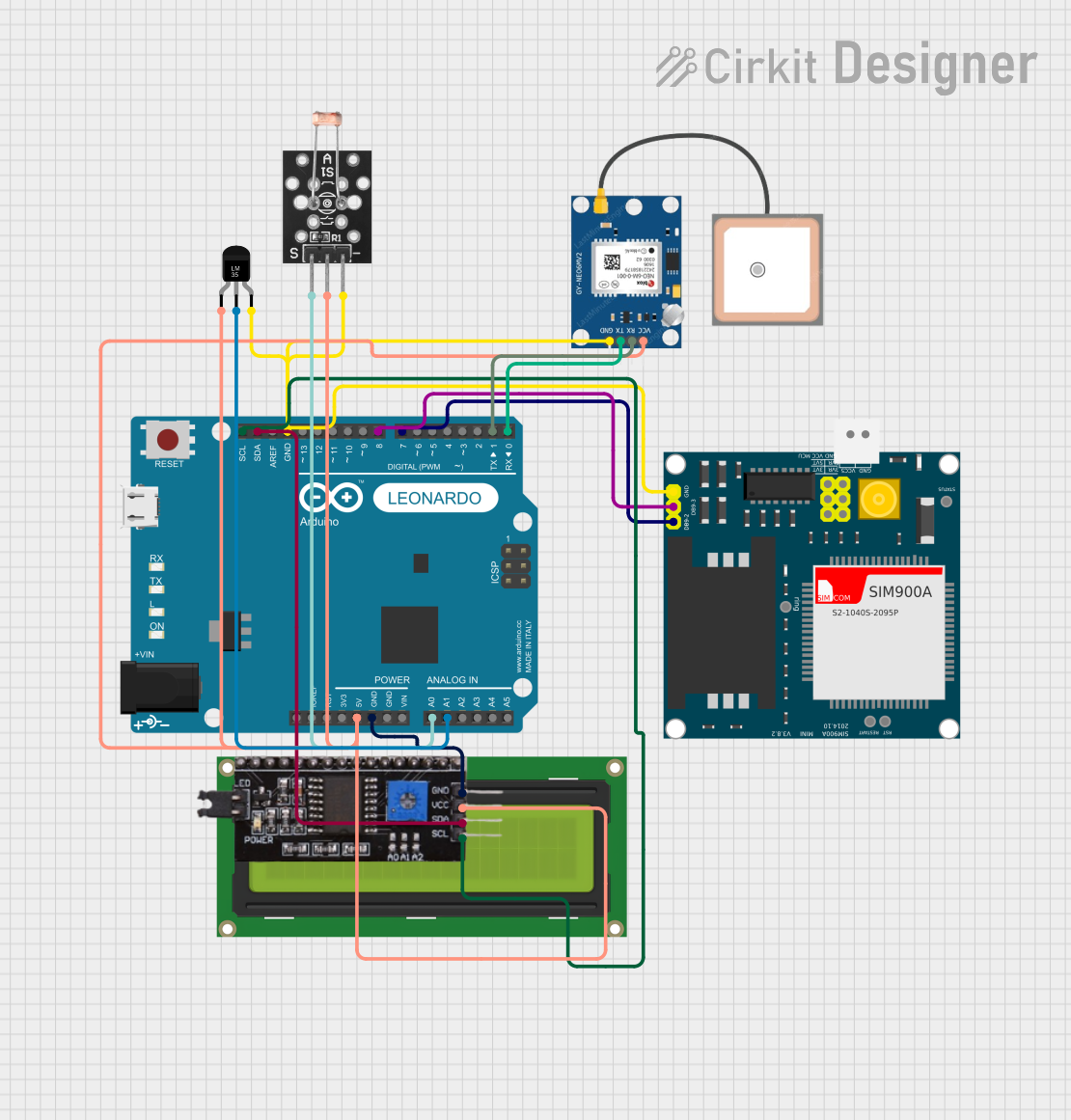
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer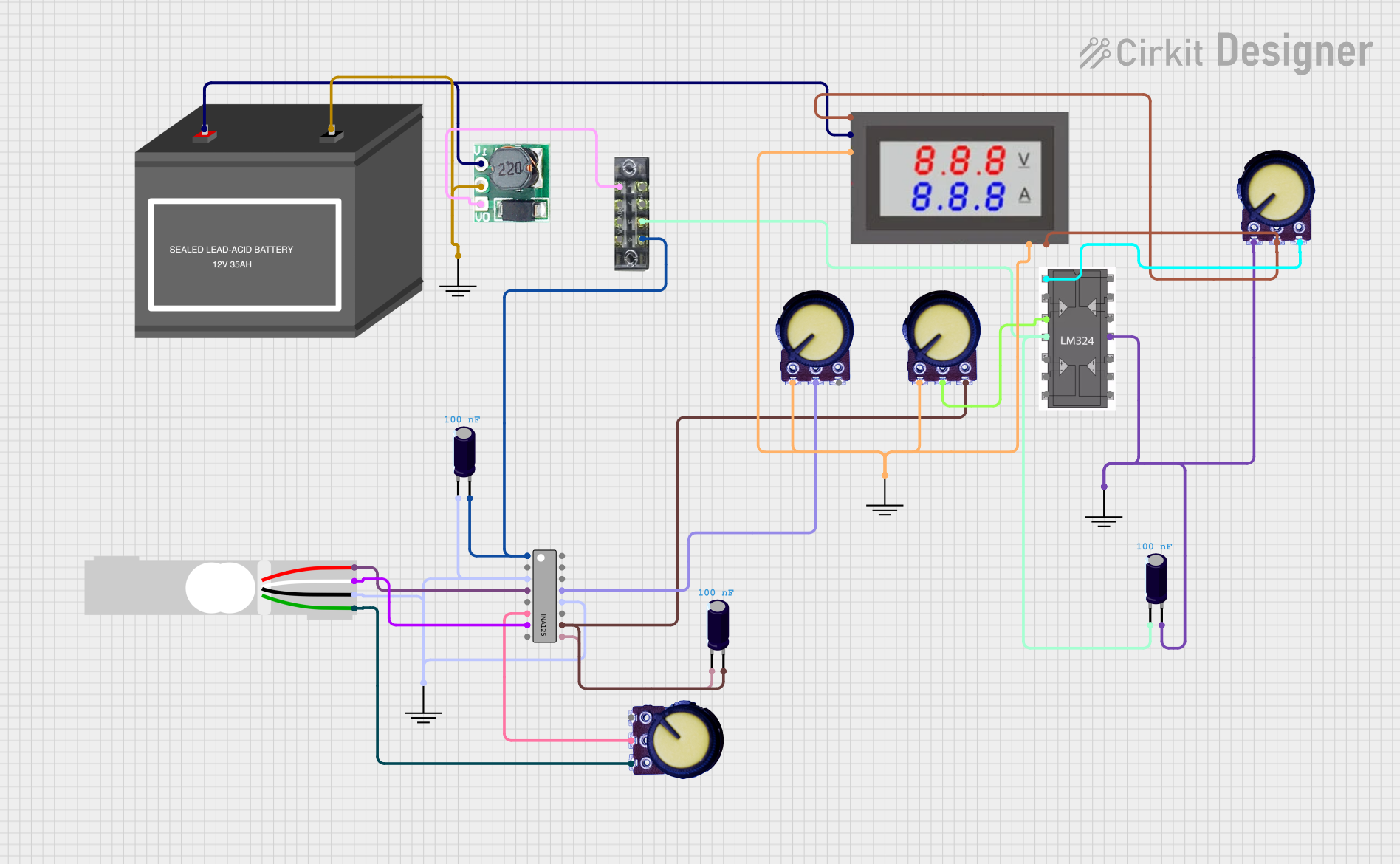
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with INA149

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Industrial process control
- Data acquisition systems
- Medical instrumentation
- High-voltage monitoring
- Precision measurement systems
- Bridge sensor amplification
Technical Specifications
The INA149 offers robust performance and is designed to handle a wide range of operating conditions. Below are the key technical specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage Range | ±2.25 V to ±18 V |
| Input Impedance | 10 GΩ (typical) |
| Common-Mode Voltage Range | ±275 V |
| Gain | Fixed at 1 V/V |
| Offset Voltage | ±1 mV (maximum) |
| Bandwidth | 500 kHz |
| Slew Rate | 1 V/μs |
| Quiescent Current | 700 μA (typical) |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +125°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The INA149 is typically available in an 8-pin SOIC package. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | -IN | Inverting input of the differential amplifier |
| 2 | +IN | Non-inverting input of the differential amplifier |
| 3 | V- | Negative power supply |
| 4 | REF | Reference voltage input |
| 5 | OUT | Amplifier output |
| 6 | NC | No connection (leave unconnected) |
| 7 | V+ | Positive power supply |
| 8 | NC | No connection (leave unconnected) |
Usage Instructions
The INA149 is straightforward to use in a circuit, but proper design considerations are essential to ensure optimal performance.
How to Use the INA149 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the V+ and V- pins to the appropriate positive and negative supply voltages. Ensure the supply voltage is within the specified range (±2.25 V to ±18 V).
- Input Signal: Connect the differential signal to the +IN and -IN pins. The INA149 can handle large common-mode voltages (up to ±275 V), but ensure the differential voltage is within the amplifier's linear range.
- Reference Voltage: The REF pin sets the output reference voltage. For single-supply operation, connect REF to mid-supply (e.g., V+/2). For dual-supply operation, REF is typically connected to ground.
- Output Signal: The amplified differential signal is available at the OUT pin. Connect this pin to the next stage of your circuit (e.g., an ADC or microcontroller).
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Bypass Capacitors: Place decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1 μF and 10 μF) close to the V+ and V- pins to reduce power supply noise.
- Input Protection: If the input signals may exceed the INA149's input voltage range, use external resistors or diodes to protect the inputs.
- PCB Layout: Use a clean and low-noise PCB layout. Keep input traces short and away from noisy signals.
- Common-Mode Voltage: Ensure the common-mode voltage is within the specified range to avoid saturation or damage to the device.
Example: Using the INA149 with an Arduino UNO
The INA149 can be used to amplify a small differential signal for measurement by an Arduino UNO's ADC. Below is an example circuit and code:
Circuit Description
- Connect the INA149's +IN and -IN pins to the differential signal source.
- Connect the REF pin to the Arduino's GND to set the output reference to 0 V.
- Connect the OUT pin to one of the Arduino's analog input pins (e.g., A0).
- Power the INA149 with a dual supply (e.g., ±12 V) or a single supply (e.g., 5 V and GND).
Arduino Code Example
// INA149 Example: Reading a differential signal with Arduino UNO
// Connect the INA149 OUT pin to Arduino analog pin A0
const int analogPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to INA149 OUT
float voltage = 0.0; // Variable to store the measured voltage
const float vRef = 5.0; // Arduino reference voltage (5V for default)
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int adcValue = analogRead(analogPin); // Read ADC value (0-1023)
// Convert ADC value to voltage
voltage = (adcValue / 1023.0) * vRef;
// Print the measured voltage
Serial.print("Measured Voltage: ");
Serial.print(voltage, 3); // Print voltage with 3 decimal places
Serial.println(" V");
delay(500); // Wait 500ms before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Signal
- Cause: Incorrect power supply connections.
- Solution: Verify that V+ and V- are connected to the correct supply voltages.
Output Saturation
- Cause: Common-mode voltage exceeds the specified range.
- Solution: Ensure the common-mode voltage is within ±275 V.
High Noise on Output
- Cause: Insufficient power supply decoupling or noisy input signals.
- Solution: Add bypass capacitors near the power supply pins and use shielded cables for inputs.
Incorrect Output Voltage
- Cause: REF pin not properly connected.
- Solution: Verify the REF pin is connected to the desired reference voltage.
FAQs
Q: Can the INA149 be used with a single power supply?
A: Yes, the INA149 can operate with a single supply. Connect V- to GND and ensure the input and output signals remain within the device's operating range.
Q: What is the maximum differential input voltage?
A: The INA149 does not have a strict differential input voltage limit, but the output will saturate if the differential input exceeds the linear range of the amplifier.
Q: How do I handle high common-mode voltages?
A: The INA149 is designed to reject high common-mode voltages (up to ±275 V). Ensure the differential signal is within the linear range and the common-mode voltage does not exceed the specified limits.