
How to Use opt_8ch: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
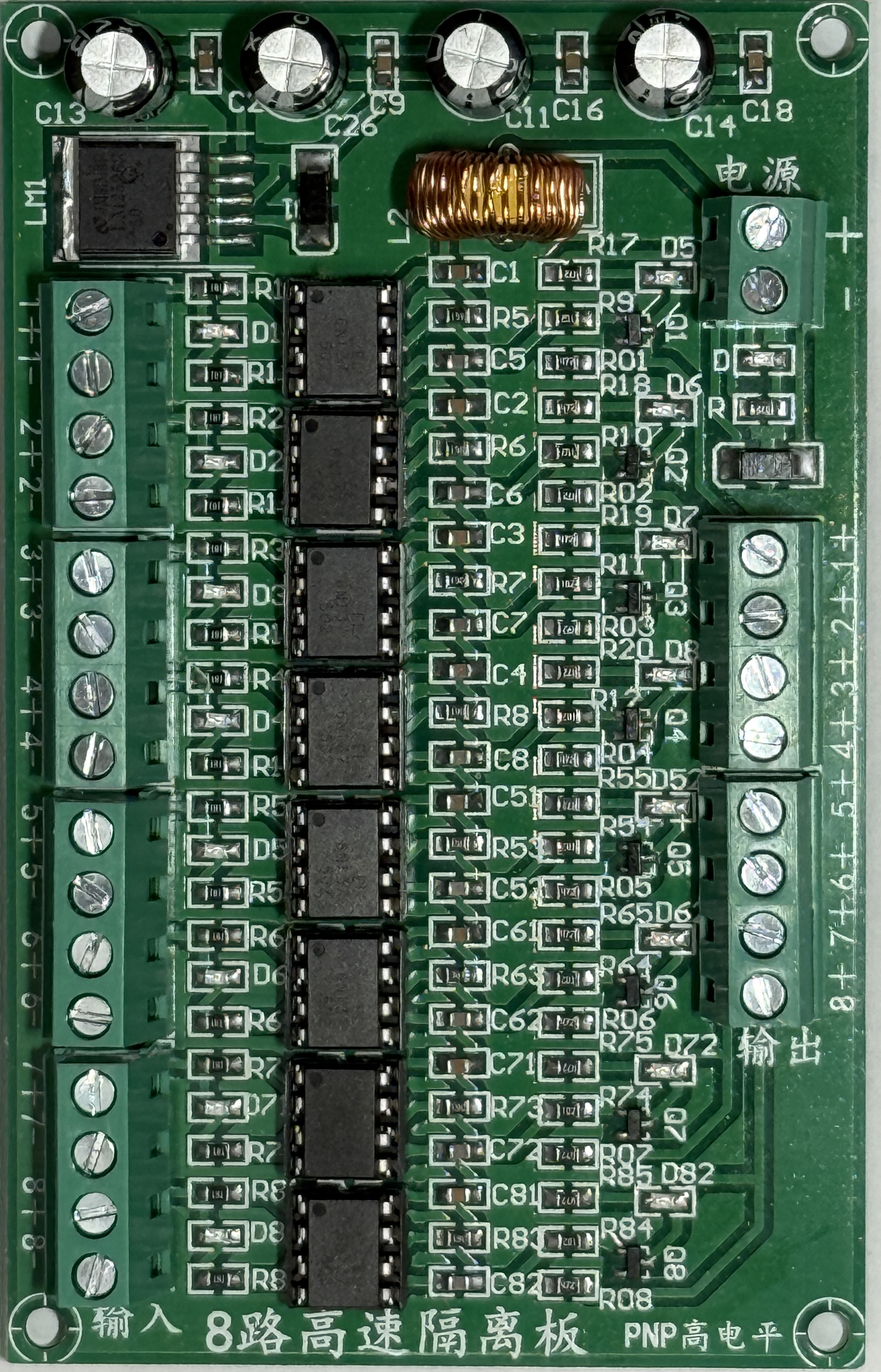
 Design with opt_8ch in Cirkit Designer
Design with opt_8ch in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The OPT_8CH is an 8-channel optical multiplexer/demultiplexer designed for routing multiple optical signals through a single optical fiber. This component significantly enhances data transmission efficiency by enabling multiple data streams to share the same fiber, reducing the need for additional cabling and infrastructure. It is widely used in optical communication systems, including telecommunications, data centers, and fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) networks.
Explore Projects Built with opt_8ch
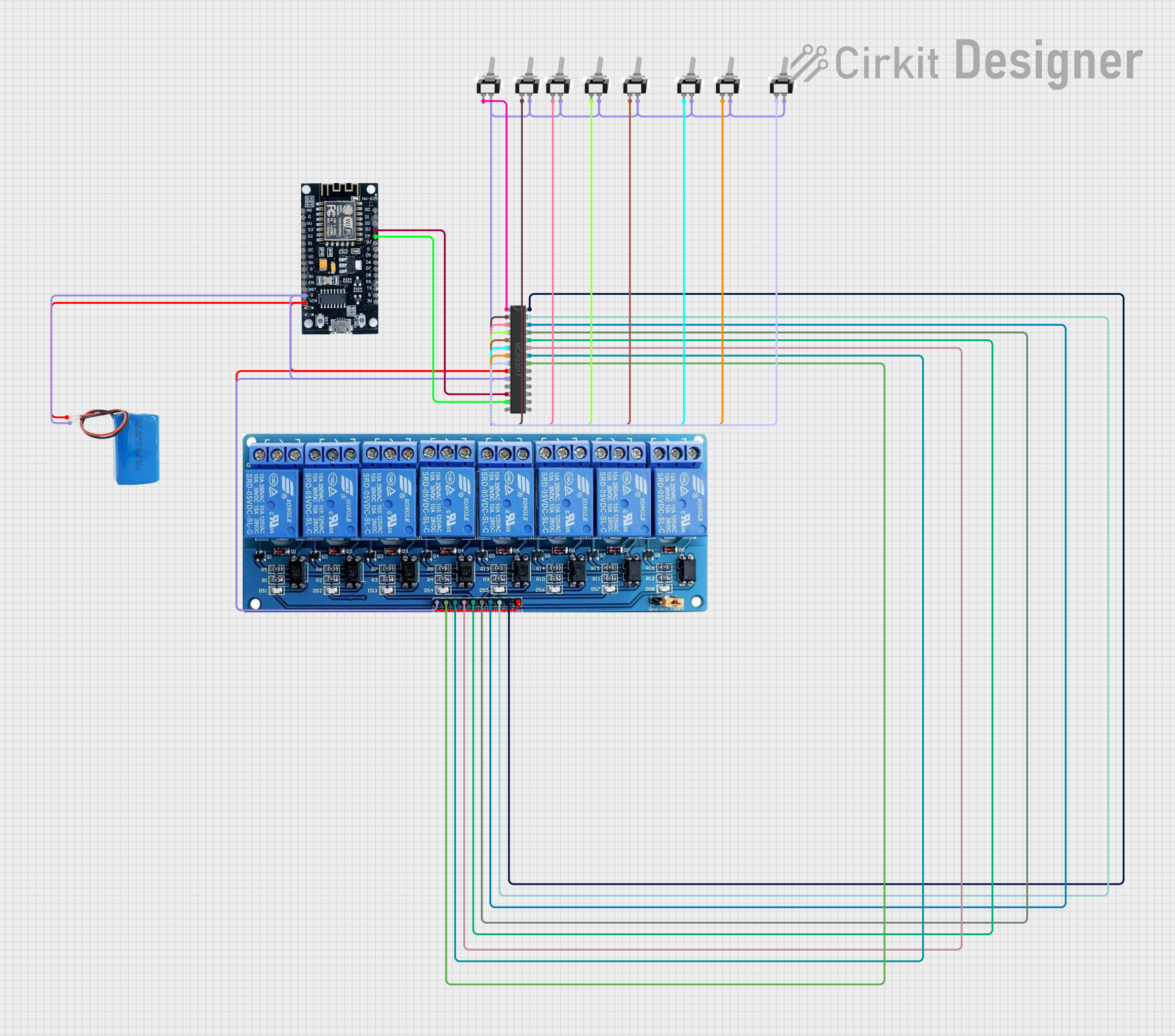
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer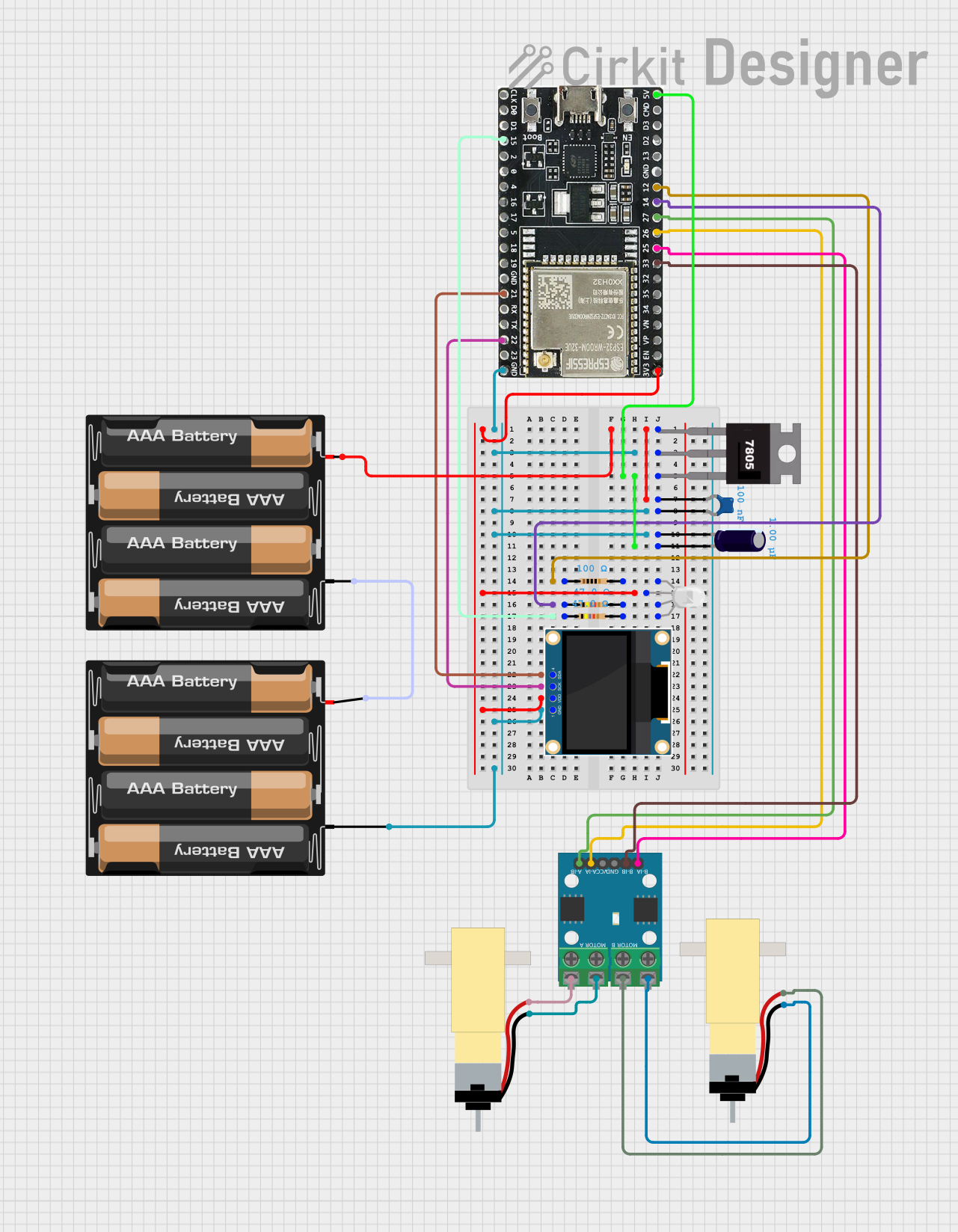
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer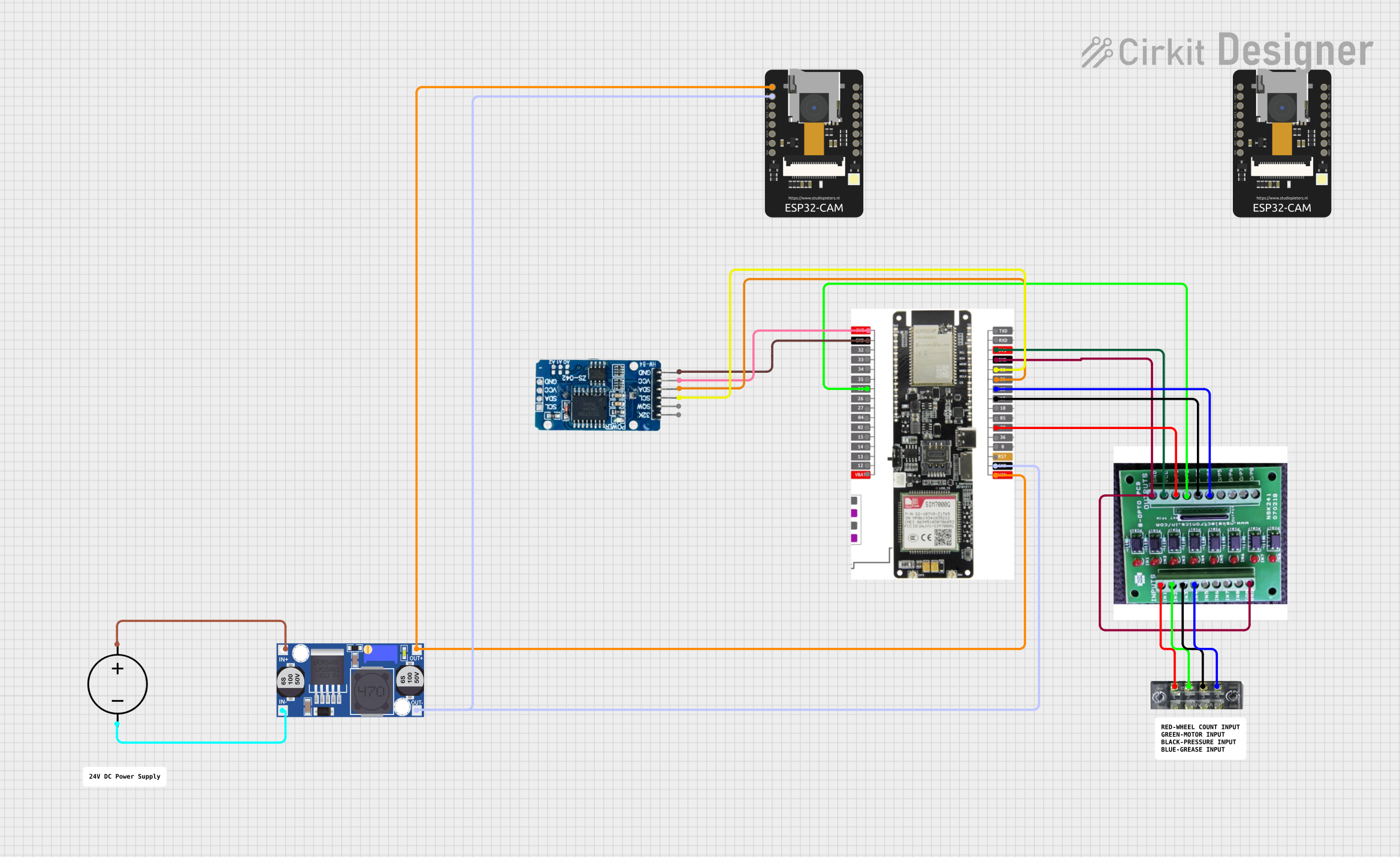
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with opt_8ch

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Telecommunications: Efficiently multiplexing and demultiplexing optical signals in long-distance communication systems.
- Data Centers: Optimizing fiber usage for high-speed data transmission between servers.
- FTTH Networks: Delivering multiple services (e.g., internet, TV, and phone) over a single optical fiber.
- Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Systems: Supporting Dense WDM (DWDM) or Coarse WDM (CWDM) technologies.
Technical Specifications
The OPT_8CH is designed to meet the demands of high-speed optical communication systems. Below are its key technical details:
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of Channels | 8 |
| Wavelength Range | 1260 nm - 1620 nm |
| Channel Spacing | 20 nm (CWDM) or 0.8 nm (DWDM) |
| Insertion Loss | ≤ 1.5 dB |
| Return Loss | ≥ 45 dB |
| Polarization Dependent Loss (PDL) | ≤ 0.1 dB |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Storage Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Fiber Type | Single-mode (SMF-28 or equivalent) |
| Connector Type | LC/UPC, SC/APC, or custom |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The OPT_8CH typically uses optical ports rather than electrical pins. Below is a description of its ports:
| Port Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Common Port | The shared optical port for multiplexed or demultiplexed signals. |
| Channel Ports 1-8 | Individual ports for each optical channel (e.g., λ1, λ2, ..., λ8). |
| Monitor Port | Optional port for monitoring signal quality or power levels. |
Usage Instructions
The OPT_8CH is straightforward to use in optical communication systems. Below are the steps and best practices for integrating it into your setup:
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Connect the Common Port: Attach the common port to the main optical fiber that will carry the multiplexed or demultiplexed signals.
- Connect the Channel Ports: Attach the individual channel ports to the corresponding optical transceivers or devices operating at specific wavelengths.
- Monitor Port (Optional): If available, connect the monitor port to an optical power meter or monitoring device to track signal quality.
- Power Considerations: Ensure that the optical power levels are within the component's specified range to avoid damage or signal degradation.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Wavelength Matching: Ensure that the optical transceivers or devices connected to the channel ports operate at the specified wavelengths for each channel.
- Insertion Loss: Account for the insertion loss of the OPT_8CH in your system design to maintain adequate signal strength.
- Fiber Type: Use single-mode fiber (SMF-28 or equivalent) for optimal performance.
- Connector Cleaning: Clean all optical connectors before use to minimize signal loss and maintain high return loss.
- Temperature Range: Operate the component within the specified temperature range to ensure reliability and longevity.
Arduino UNO Integration
While the OPT_8CH is primarily an optical component, it can be indirectly monitored or controlled using an Arduino UNO by interfacing with optical transceivers or power meters. Below is an example code snippet for monitoring optical power using a compatible sensor:
// Example: Reading optical power levels using an analog sensor
// connected to an Arduino UNO. Ensure the sensor is compatible
// with the optical monitor port of the OPT_8CH.
const int sensorPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the optical power sensor
float voltage = 0.0; // Variable to store the sensor voltage
float power_dBm = 0.0; // Variable to store the calculated optical power in dBm
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
pinMode(sensorPin, INPUT); // Set the sensor pin as input
}
void loop() {
voltage = analogRead(sensorPin) * (5.0 / 1023.0); // Convert ADC value to voltage
power_dBm = (voltage - 1.5) * 10.0; // Example conversion formula for sensor
// Adjust the formula based on your sensor's datasheet
Serial.print("Optical Power: ");
Serial.print(power_dBm);
Serial.println(" dBm");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
High Insertion Loss:
- Cause: Dirty or damaged optical connectors.
- Solution: Clean the connectors using an appropriate fiber cleaning kit. Inspect for damage and replace if necessary.
Signal Crosstalk Between Channels:
- Cause: Incorrect wavelength alignment or poor-quality transceivers.
- Solution: Verify that the transceivers match the specified wavelengths for each channel. Use high-quality components.
No Signal Detected:
- Cause: Incorrect port connections or fiber damage.
- Solution: Double-check all connections and ensure the fibers are intact. Use an optical power meter to verify signal presence.
Temperature-Related Performance Issues:
- Cause: Operating outside the specified temperature range.
- Solution: Ensure the component is used within the -40°C to +85°C range. Use temperature-controlled environments if necessary.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Use an optical power meter to verify signal strength at each port.
- Ensure all fibers and connectors are properly aligned and secured.
- Regularly inspect and clean optical connectors to maintain performance.
- If using the monitor port, verify that the monitoring device is calibrated and functioning correctly.
By following these guidelines and best practices, the OPT_8CH can be effectively integrated into your optical communication system, ensuring reliable and efficient data transmission.