
How to Use 5V UPS: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
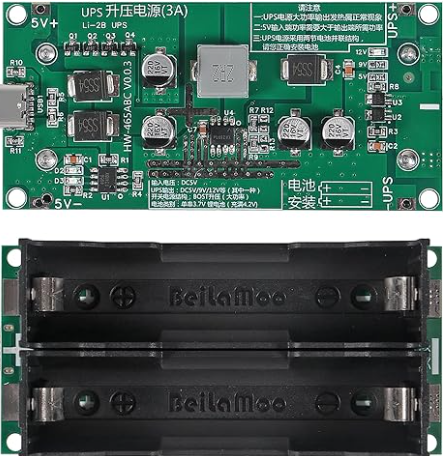

 Design with 5V UPS in Cirkit Designer
Design with 5V UPS in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A 5V Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is a compact power management device designed to provide a stable 5V output to electronic devices during power outages or fluctuations. It ensures uninterrupted operation by seamlessly switching to a rechargeable battery when the primary power source is unavailable. This makes it an essential component for critical systems, IoT devices, Raspberry Pi boards, and other low-power electronics that require reliable power delivery.
Explore Projects Built with 5V UPS
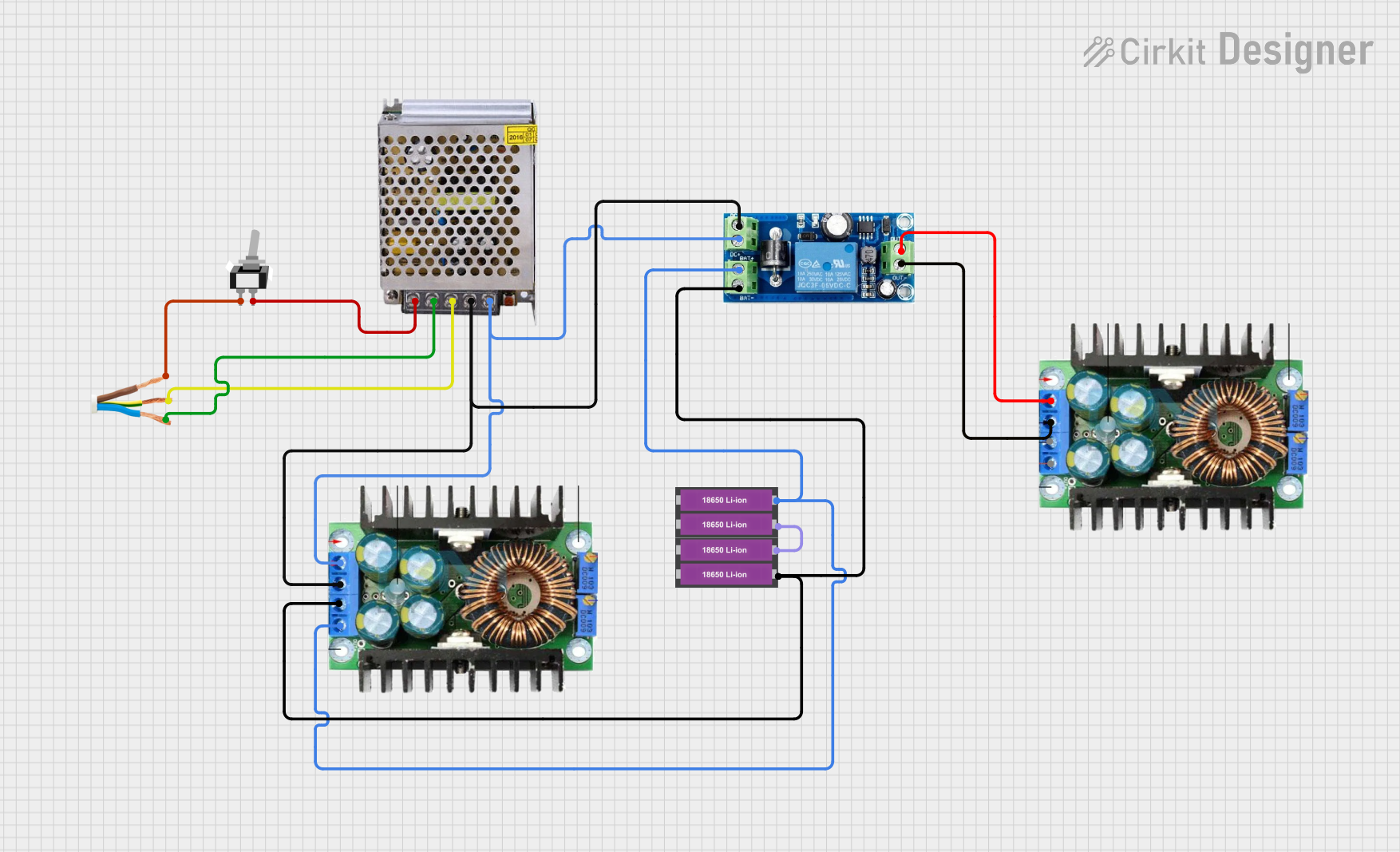
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer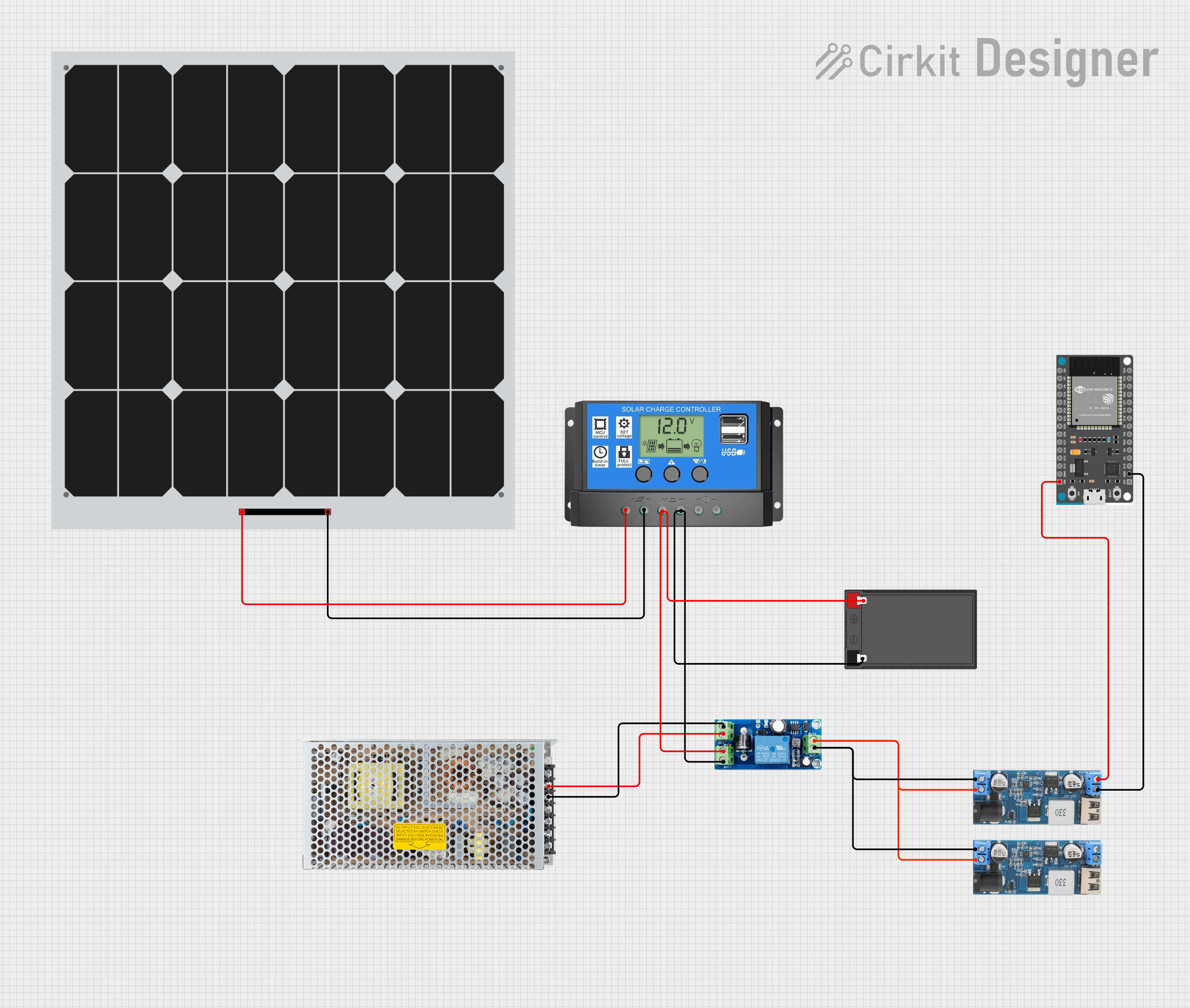
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer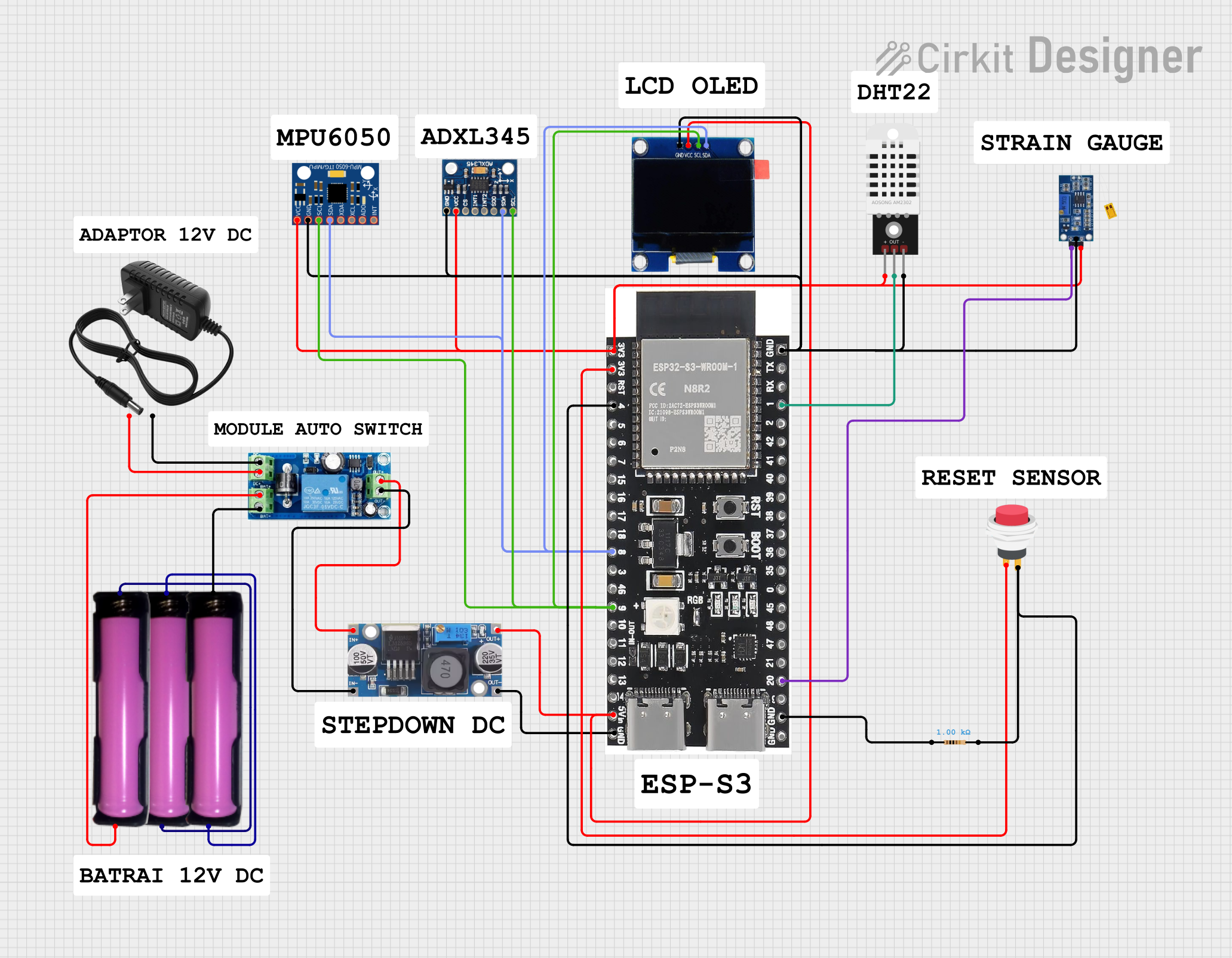
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 5V UPS

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Backup power for Raspberry Pi, Arduino, and other microcontroller-based systems.
- IoT devices deployed in remote or unstable power environments.
- Network equipment such as routers and modems.
- Portable electronics requiring stable 5V power.
- Data logging systems to prevent data loss during power interruptions.
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the 5V UPS:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 5V DC ± 5% |
| Output Voltage | 5V DC ± 2% |
| Maximum Output Current | 2A |
| Battery Type | Lithium-ion or Lithium-polymer |
| Battery Capacity | Typically 1000mAh to 5000mAh |
| Charging Current | 1A (typical) |
| Switching Time | < 10ms |
| Operating Temperature | -10°C to 60°C |
| Dimensions | Varies by model (e.g., 50x30x10mm) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 5V UPS typically includes the following pins or connectors:
| Pin/Connector | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage pin for connecting a 5V DC power source. |
| VOUT | Output voltage pin providing a stable 5V DC supply to the load. |
| GND | Ground pin shared by the input, output, and battery. |
| BAT+ | Positive terminal for connecting the rechargeable battery (if external). |
| BAT- | Negative terminal for connecting the rechargeable battery (if external). |
| CHG_IND | Charging indicator pin (optional) - active when the battery is charging. |
| PWR_GOOD | Power status indicator pin (optional) - signals when the output is stable. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 5V UPS in a Circuit
Connect the Input Power Source:
Attach a 5V DC power source to theVINandGNDpins. Ensure the input voltage is within the specified range to avoid damage.Connect the Load:
Connect the device or circuit requiring backup power to theVOUTandGNDpins. Verify that the load does not exceed the maximum output current (2A).Attach the Battery:
If the UPS requires an external battery, connect the positive and negative terminals of the battery to theBAT+andBAT-pins, respectively. Use a compatible lithium-ion or lithium-polymer battery.Monitor Indicators (Optional):
- Use the
CHG_INDpin to monitor the charging status of the battery. - Use the
PWR_GOODpin to check if the output voltage is stable.
- Use the
Test the UPS Functionality:
Disconnect the input power source to simulate a power outage. Verify that the UPS seamlessly switches to battery power and maintains a stable 5V output.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Battery Selection: Use a battery with sufficient capacity to meet the runtime requirements of your application. Ensure the battery voltage matches the UPS specifications.
- Heat Management: Avoid placing the UPS in enclosed spaces without ventilation, as heat may build up during operation or charging.
- Load Limitations: Do not exceed the maximum output current (2A) to prevent damage to the UPS or connected devices.
- Regular Maintenance: Periodically check the battery health and replace it if the capacity significantly degrades.
Example: Using a 5V UPS with an Arduino UNO
The following example demonstrates how to connect a 5V UPS to an Arduino UNO for uninterrupted operation:
Circuit Connections
- Connect the
VOUTpin of the UPS to the 5V pin of the Arduino UNO. - Connect the
GNDpin of the UPS to the GND pin of the Arduino UNO. - Optionally, monitor the
PWR_GOODpin to detect power stability.
Sample Code
// Example code to monitor the PWR_GOOD pin of a 5V UPS
const int powerGoodPin = 2; // Connect PWR_GOOD pin to Arduino digital pin 2
const int ledPin = 13; // Built-in LED on Arduino UNO
void setup() {
pinMode(powerGoodPin, INPUT); // Set PWR_GOOD pin as input
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set LED pin as output
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn off LED initially
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int powerStatus = digitalRead(powerGoodPin); // Read PWR_GOOD pin status
if (powerStatus == HIGH) {
// Power is stable, turn off LED
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
Serial.println("Power is stable.");
} else {
// Power is unstable, turn on LED
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
Serial.println("Power is unstable! Running on battery.");
}
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before checking again
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
UPS Not Switching to Battery Power
- Cause: Battery is not connected or is discharged.
- Solution: Verify the battery connections and ensure the battery is charged.
Output Voltage Drops Below 5V
- Cause: Load exceeds the maximum output current or battery is low.
- Solution: Reduce the load or replace/charge the battery.
Battery Overheating During Charging
- Cause: Faulty battery or inadequate ventilation.
- Solution: Replace the battery and ensure proper ventilation.
CHG_IND or PWR_GOOD Pins Not Responding
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or damaged pins.
- Solution: Check the connections and test the pins with a multimeter.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use the 5V UPS with a 3.3V device?
A1: No, the 5V UPS is designed to provide a stable 5V output. Use a voltage regulator or level shifter for 3.3V devices.
Q2: How long will the UPS run on battery power?
A2: The runtime depends on the battery capacity and the power consumption of the connected load. For example, a 2000mAh battery powering a 500mA load will last approximately 4 hours.
Q3: Can I charge the battery while the UPS is powering a device?
A3: Yes, most 5V UPS modules support simultaneous charging and powering of the load.
Q4: Is the UPS compatible with solar panels?
A4: Yes, as long as the solar panel provides a stable 5V output within the input voltage range of the UPS.