
How to Use MCB: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with MCB in Cirkit Designer
Design with MCB in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) is an automatically-operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by excess current from an overload or short circuit. MCBs are commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings to ensure the safety and reliability of electrical systems.
Explore Projects Built with MCB

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer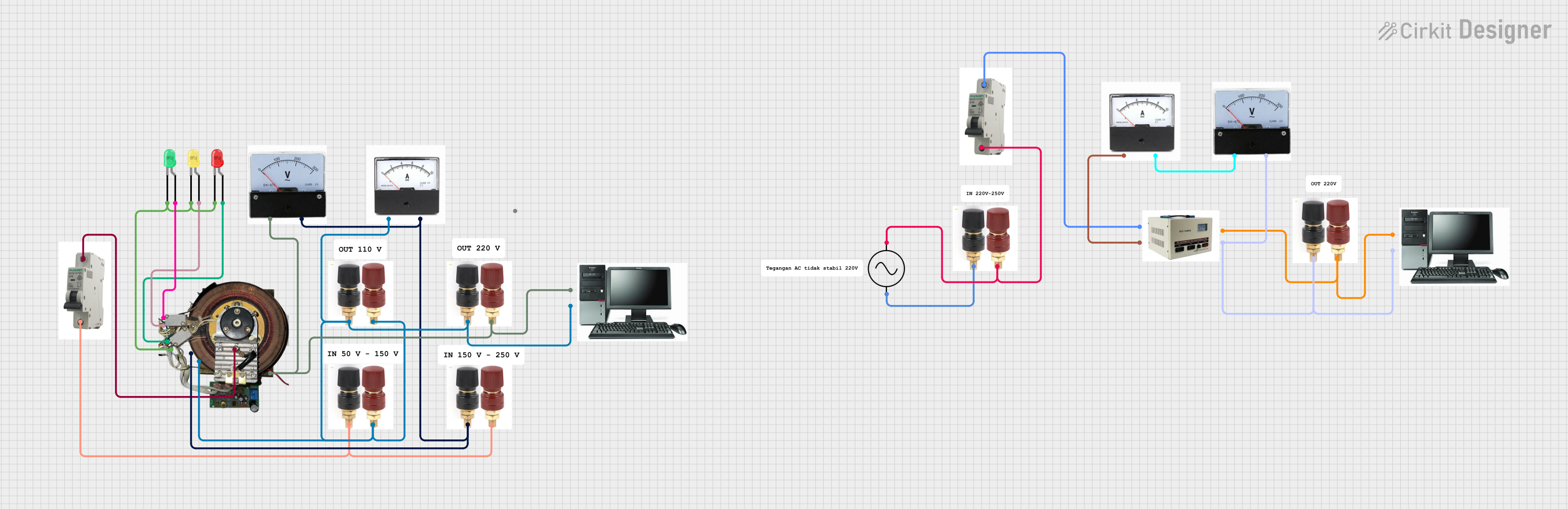
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer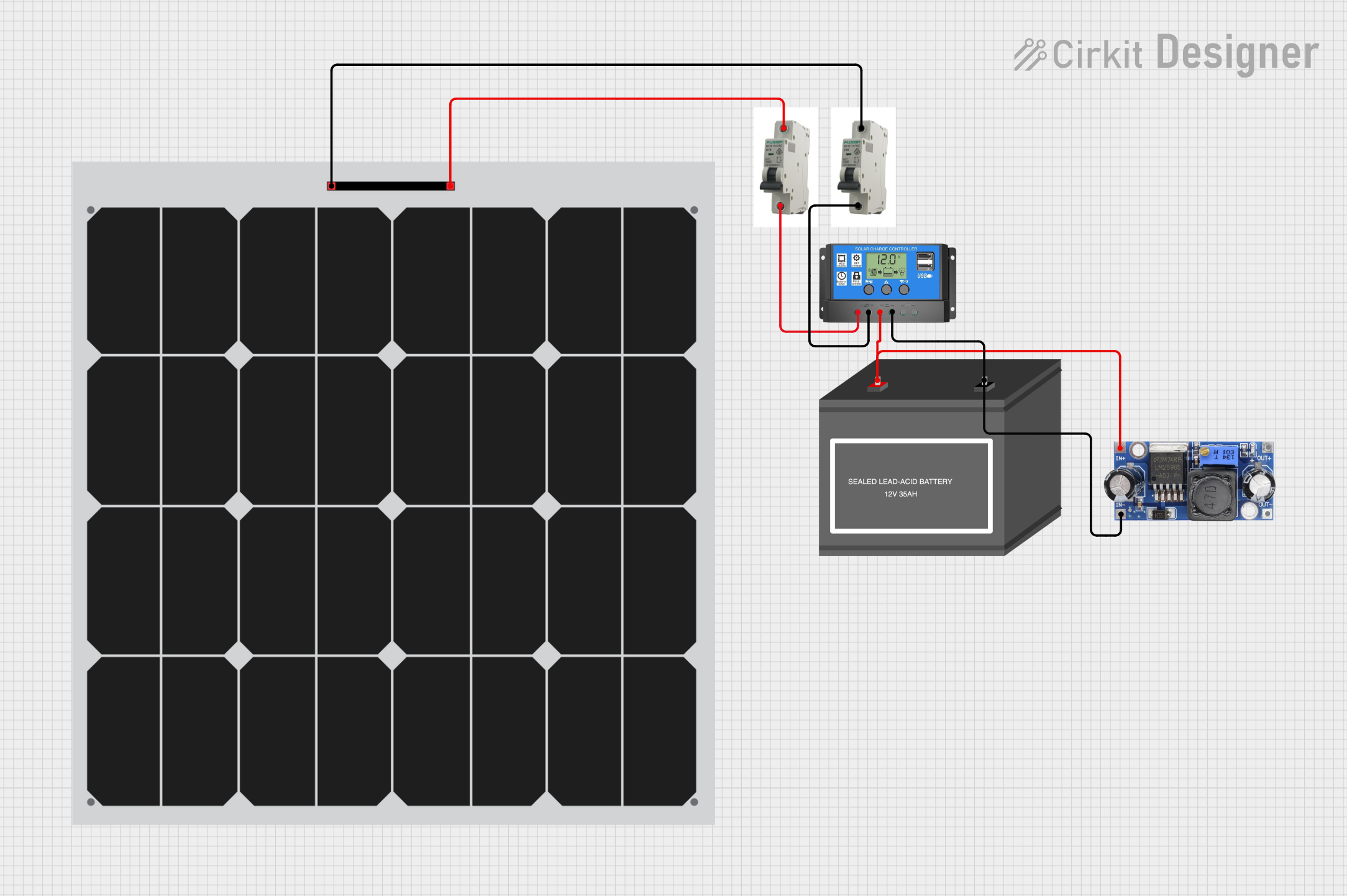
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with MCB

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases:
- Home electrical panels to protect against electrical fires.
- Office buildings for circuit management and safety.
- Industrial environments to safeguard machinery and plant equipment.
- Power distribution in data centers to prevent equipment damage.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details:
- Rated Current (In): The maximum current that the MCB can carry without tripping.
- Rated Voltage (Ue): The maximum voltage at which the MCB can operate safely.
- Breaking Capacity (Icn): The maximum fault current that the MCB can interrupt without damage.
- Tripping Characteristics: The response time of the MCB to different levels of overcurrent, typically labeled as B, C, or D curves.
Pin Configuration and Descriptions:
| Pin Number | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Phase Input | Connect to the live wire |
| 2 | Neutral Input | Connect to the neutral wire |
| 3 | Phase Output | Connect to the load's live wire |
| 4 | Neutral Output | Connect to the load's neutral |
Note: MCBs do not have "pins" in the traditional sense like ICs or other electronic components, but they do have terminals for wire connections. The above table is a simplified representation.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the MCB in a Circuit:
- Mounting: Secure the MCB onto a DIN rail within the distribution board.
- Wiring: Connect the incoming live (hot) wire to the MCB's phase input terminal and the neutral wire to the neutral input terminal.
- Load Connection: Connect the load's live wire to the phase output terminal and the neutral wire to the neutral output terminal.
- Testing: Once installed, switch on the MCB and test the connected circuit for proper operation.
Important Considerations and Best Practices:
- Rating Selection: Choose an MCB with a suitable current rating for the circuit it will protect.
- Tripping Curve: Select the appropriate tripping curve (B, C, or D) based on the application's surge tolerance.
- Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect the MCB for any signs of damage or wear.
- Professional Installation: Always have a qualified electrician install and service MCBs.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face:
- MCB Tripping Frequently: This could be due to overloads, short circuits, or a faulty MCB.
- No Power to Circuit: Ensure the MCB is switched on and that there are no tripped MCBs upstream.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting:
- Check Load: Reduce the load on the circuit to below the MCB's rated current.
- Inspect Wiring: Look for any signs of damaged wiring or loose connections.
- Reset MCB: If the MCB has tripped, reset it by switching it to the OFF position and then back to ON.
- Replace MCB: If the MCB continues to trip without an apparent overload or short circuit, it may need to be replaced.
FAQs:
Q: Can I replace an MCB with a higher-rated one to stop it from tripping? A: No, replacing an MCB with a higher-rated one can be dangerous and may lead to cable overheating and fire.
Q: How do I know if an MCB is faulty? A: If an MCB trips frequently without a clear cause or does not stay in the ON position, it may be faulty.
Q: Are MCBs polarized? A: Yes, MCBs are polarized. The live wire must be connected to the phase input terminal.
Note: MCBs are not typically used with Arduino UNO or similar microcontroller boards, as they operate at much lower currents and voltages. Therefore, no Arduino-related code is provided in this documentation.