
How to Use BMS: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with BMS in Cirkit Designer
Design with BMS in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Battery Management System (BMS) is an electronic system designed to monitor and manage rechargeable batteries. It ensures the safe operation of the battery by monitoring its state, calculating secondary data (e.g., state of charge, state of health), and controlling its environment. The BMS plays a critical role in optimizing battery performance, extending its lifespan, and preventing hazardous conditions such as overcharging, over-discharging, or overheating.
Explore Projects Built with BMS
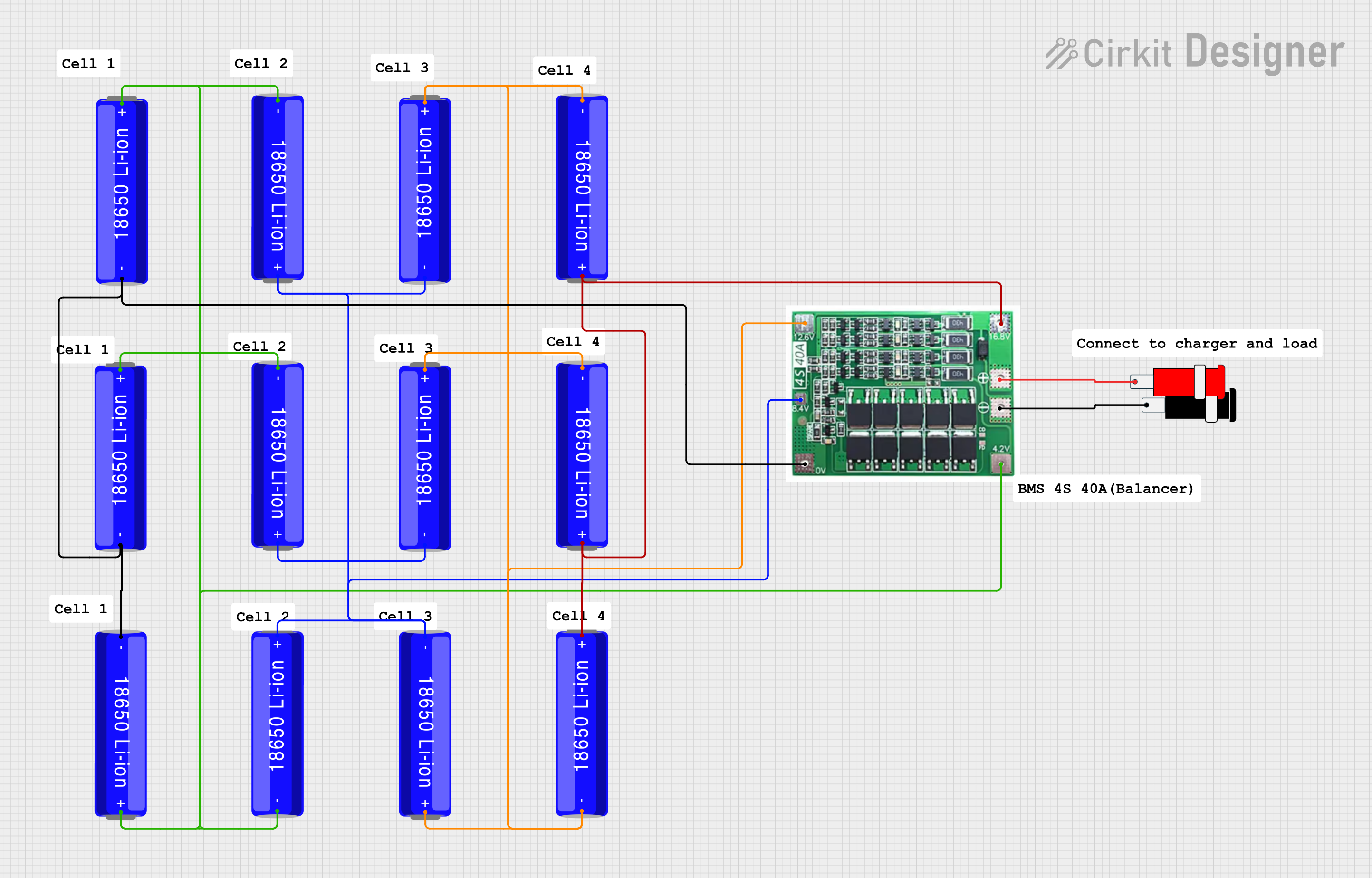
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer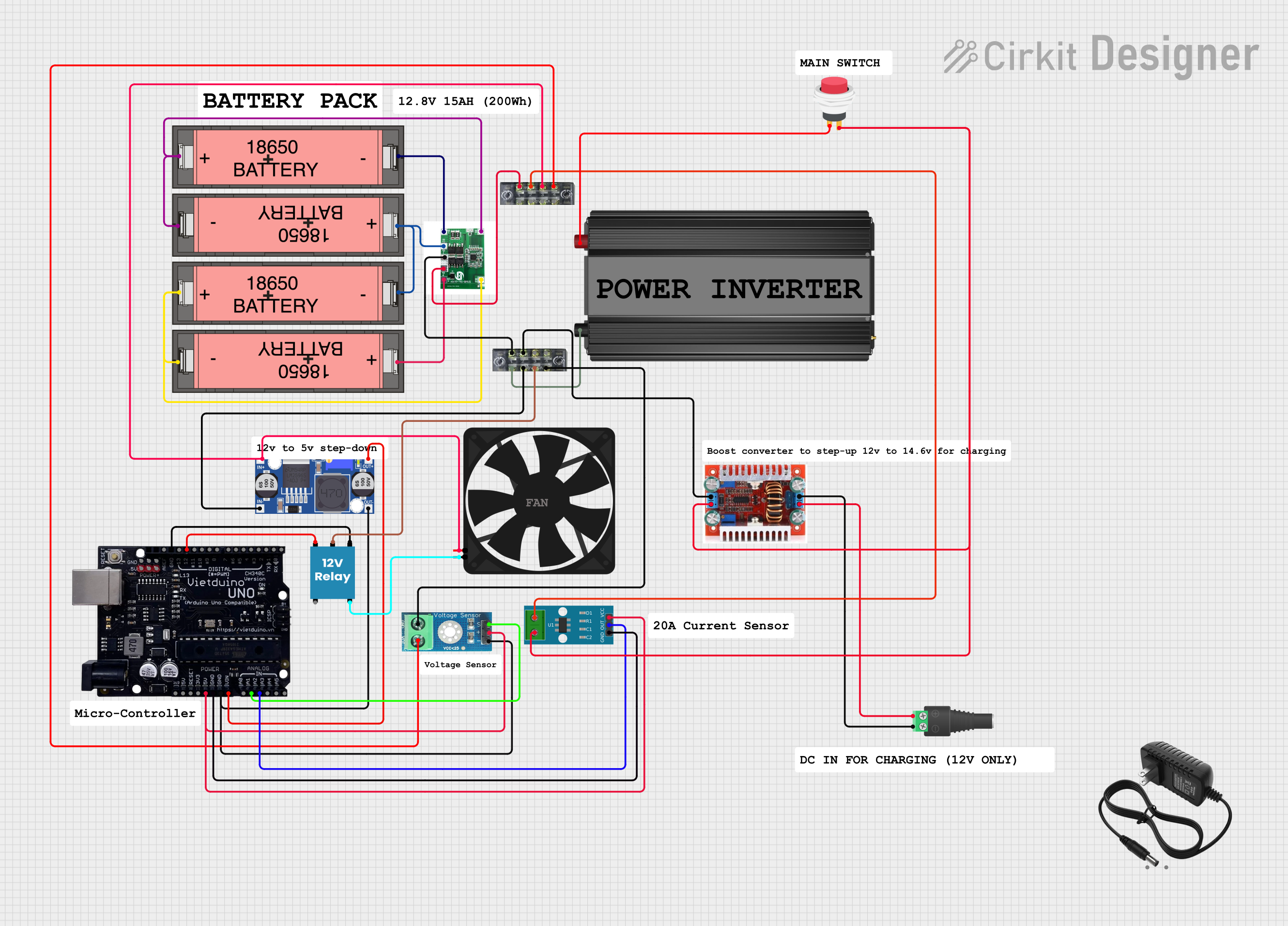
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer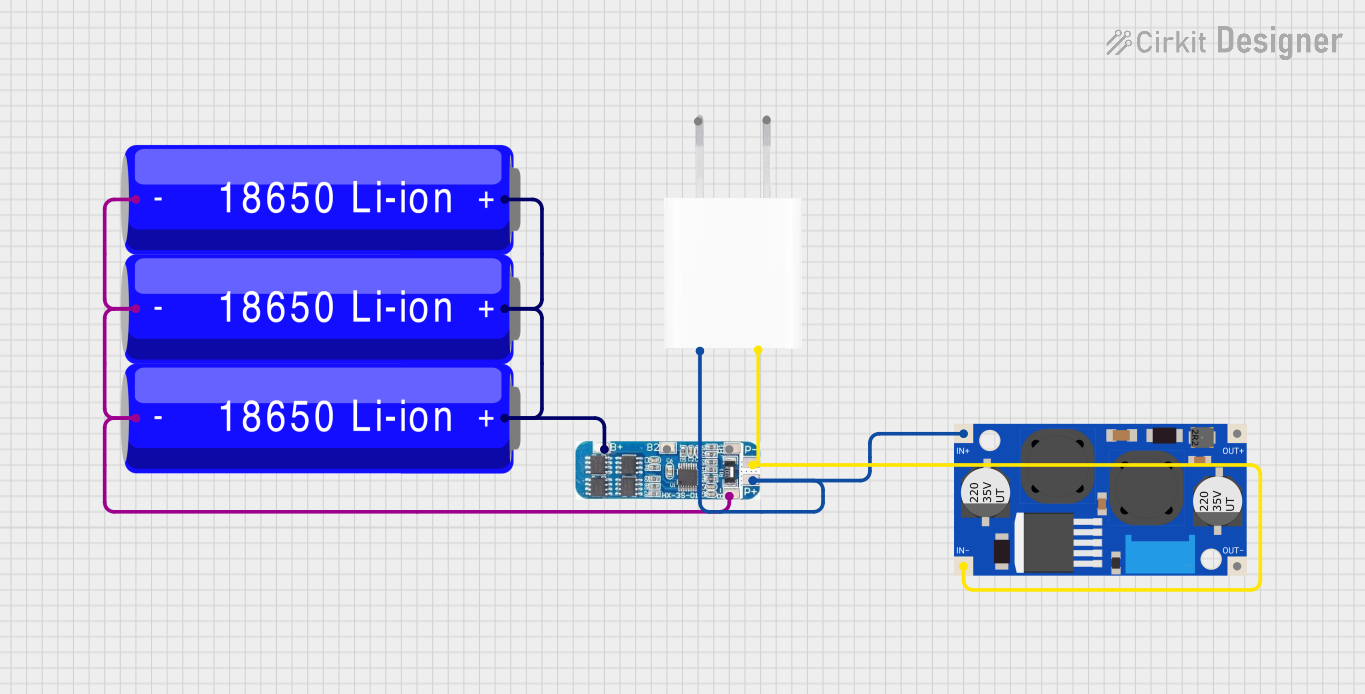
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with BMS

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs)
- Renewable energy storage systems (e.g., solar and wind energy)
- Consumer electronics (e.g., laptops, smartphones, power banks)
- Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS)
- Industrial and medical equipment requiring reliable battery management
Technical Specifications
The technical specifications of a BMS can vary depending on the application and battery type. Below are general specifications for a typical BMS:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Supported Battery Types | Lithium-ion, LiFePO4, Lead-acid, NiMH |
| Input Voltage Range | 3.7V to 60V (varies by model) |
| Maximum Current | 10A to 200A (varies by model) |
| Overcharge Protection | Configurable (e.g., 4.2V per Li-ion cell) |
| Over-discharge Protection | Configurable (e.g., 2.5V per Li-ion cell) |
| Balancing Method | Passive or Active |
| Communication Protocols | I2C, UART, CAN, SMBus |
| Operating Temperature Range | -20°C to 60°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Below is a typical pin configuration for a BMS module:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| B+ | Battery positive terminal |
| B- | Battery negative terminal |
| P+ | Load/charger positive terminal |
| P- | Load/charger negative terminal |
| C+ | Charger positive terminal (if separate from P+) |
| C- | Charger negative terminal (if separate from P-) |
| Balance Pins | Connect to individual battery cells for voltage balancing |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the BMS in a Circuit
Connect the Battery Pack:
- Connect the B+ and B- terminals of the BMS to the positive and negative terminals of the battery pack, respectively.
- If the BMS supports balancing, connect the balance pins to the corresponding battery cells.
Connect the Load and Charger:
- Connect the P+ and P- terminals to the load (e.g., motor, inverter).
- Connect the charger to the C+ and C- terminals (if separate from P+ and P-).
Power On:
- Ensure all connections are secure and within the BMS's voltage and current limits.
- Power on the system and monitor the BMS's status indicators (e.g., LEDs or communication output).
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Battery Compatibility: Ensure the BMS is compatible with the battery chemistry and configuration (e.g., number of cells in series/parallel).
- Heat Management: Avoid overheating by ensuring proper ventilation or using a heatsink if necessary.
- Balancing: Use the BMS's balancing feature to maintain equal voltage across all cells, which improves battery performance and lifespan.
- Firmware Updates: If the BMS supports firmware updates, keep it updated to ensure optimal performance and safety.
- Arduino Integration: Many BMS modules support communication protocols like I2C or UART, making them compatible with microcontrollers like Arduino.
Example Arduino Code for Monitoring a BMS
Below is an example of how to use an Arduino UNO to communicate with a BMS via I2C:
#include <Wire.h> // Include the Wire library for I2C communication
#define BMS_I2C_ADDRESS 0x08 // Replace with your BMS's I2C address
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I2C communication
Serial.println("BMS Monitoring Started");
}
void loop() {
Wire.beginTransmission(BMS_I2C_ADDRESS); // Start communication with BMS
Wire.write(0x01); // Request data (e.g., voltage, current, etc.)
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(10); // Short delay before reading data
Wire.requestFrom(BMS_I2C_ADDRESS, 4); // Request 4 bytes of data
if (Wire.available() == 4) {
int voltage = Wire.read() << 8 | Wire.read(); // Read 2 bytes for voltage
int current = Wire.read() << 8 | Wire.read(); // Read 2 bytes for current
// Print the received data
Serial.print("Voltage: ");
Serial.print(voltage);
Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Current: ");
Serial.print(current);
Serial.println(" mA");
} else {
Serial.println("Error: No data received from BMS");
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
BMS Not Powering On:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient input voltage.
- Solution: Double-check all connections and ensure the battery voltage is within the BMS's input range.
Overcharge/Over-discharge Protection Triggered:
- Cause: Battery voltage exceeds or drops below the protection thresholds.
- Solution: Verify the battery's state and adjust the BMS's protection settings if configurable.
Uneven Cell Voltages:
- Cause: Balancing feature not functioning or improperly connected.
- Solution: Ensure balance pins are correctly connected and the BMS supports active/passive balancing.
Communication Issues with Arduino:
- Cause: Incorrect I2C address or wiring.
- Solution: Verify the BMS's I2C address and ensure proper SDA/SCL connections.
FAQs
Can I use a BMS with different battery chemistries?
- Yes, but ensure the BMS is specifically designed to support the chemistry (e.g., Li-ion, LiFePO4).
What happens if I exceed the BMS's current rating?
- The BMS will likely trigger overcurrent protection, shutting down the output to prevent damage.
Do I need a BMS for a single-cell battery?
- While not always necessary, a BMS can still provide overcharge, over-discharge, and short-circuit protection for single-cell batteries.
Can I bypass the BMS for higher current loads?
- Bypassing the BMS is not recommended as it compromises safety and may damage the battery.