
How to Use Sabertooth 2*32: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
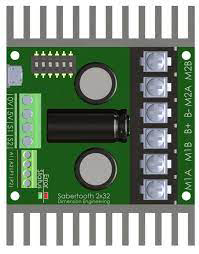
 Design with Sabertooth 2*32 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Sabertooth 2*32 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Sabertooth 2*32 is a dual-channel motor driver designed to control two DC motors with a maximum continuous current of 32A per channel. Manufactured by Dimension Engineering, this motor driver is highly versatile and suitable for a wide range of applications, including robotics, automation systems, and remote-controlled vehicles. It supports multiple control modes such as analog, R/C, serial, and packetized serial, making it adaptable to various control systems.
Explore Projects Built with Sabertooth 2*32
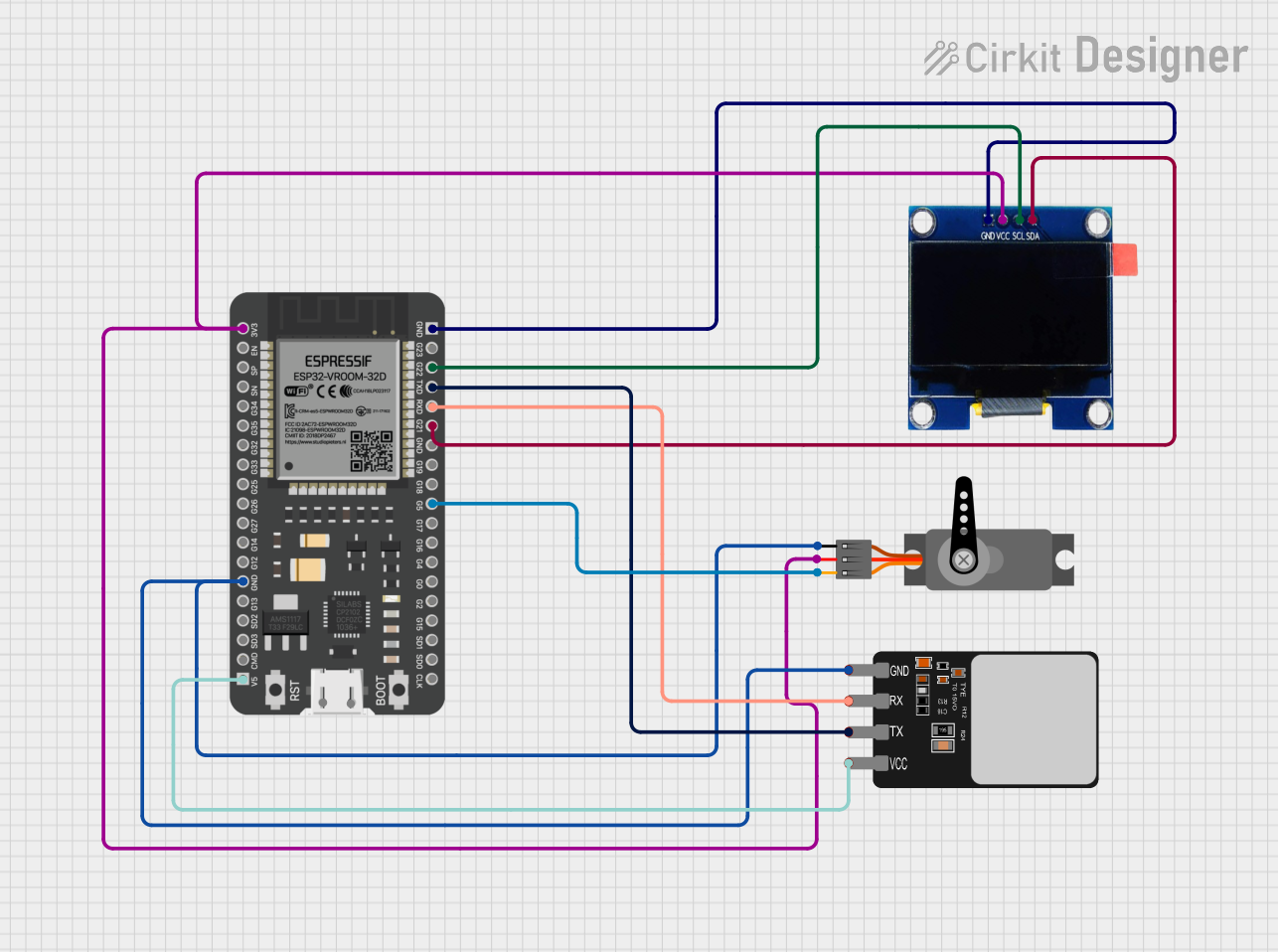
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer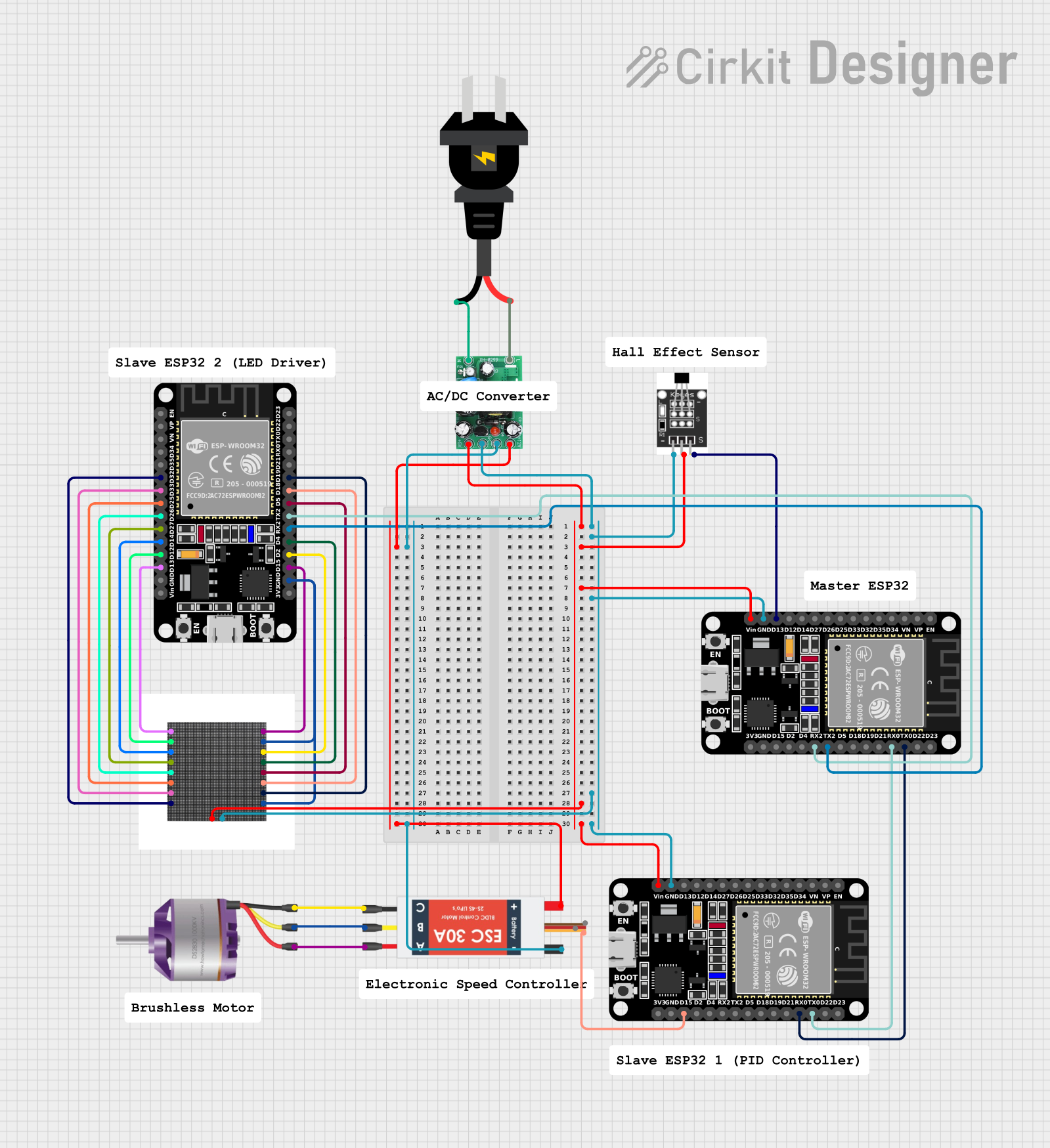
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer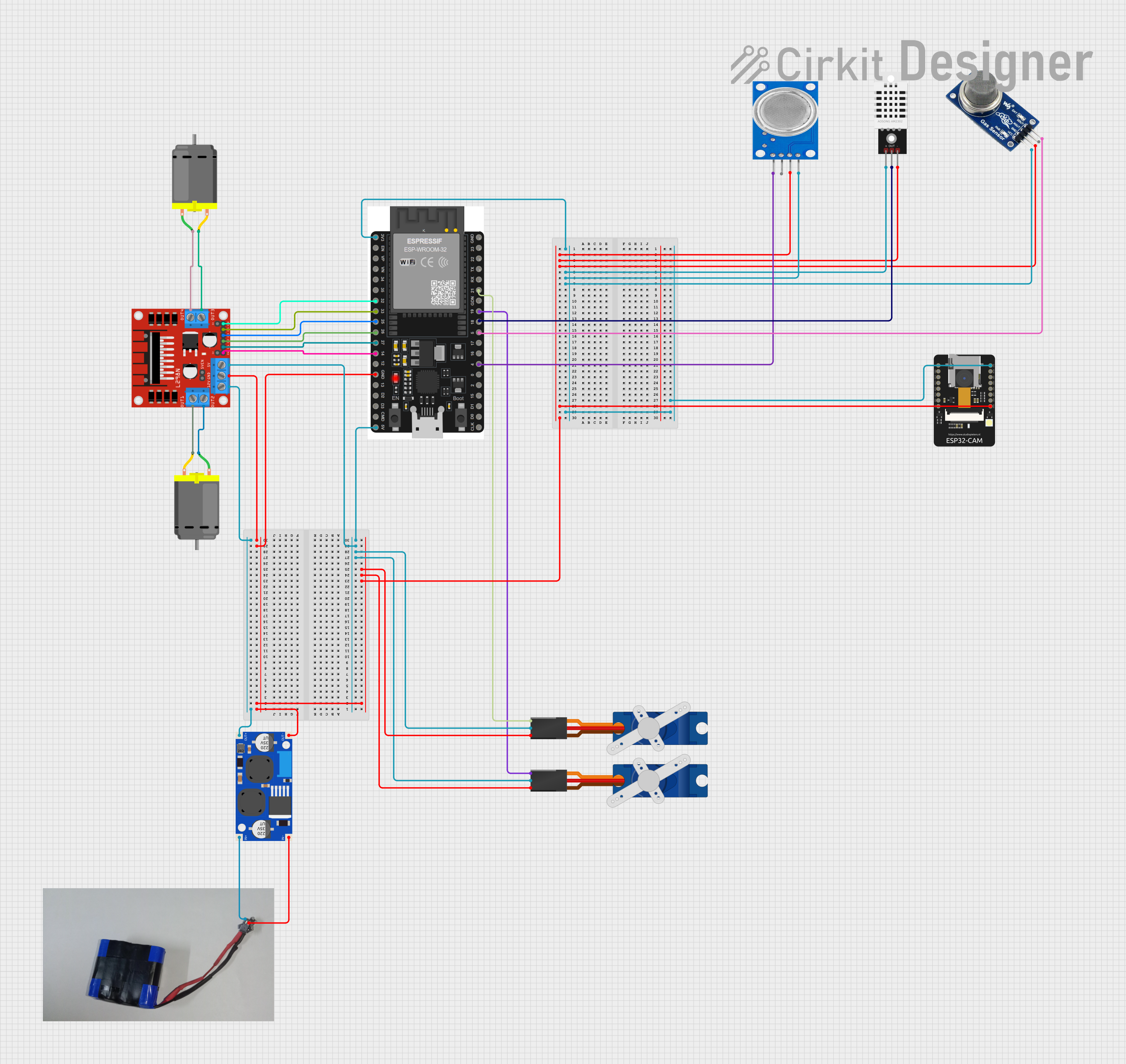
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer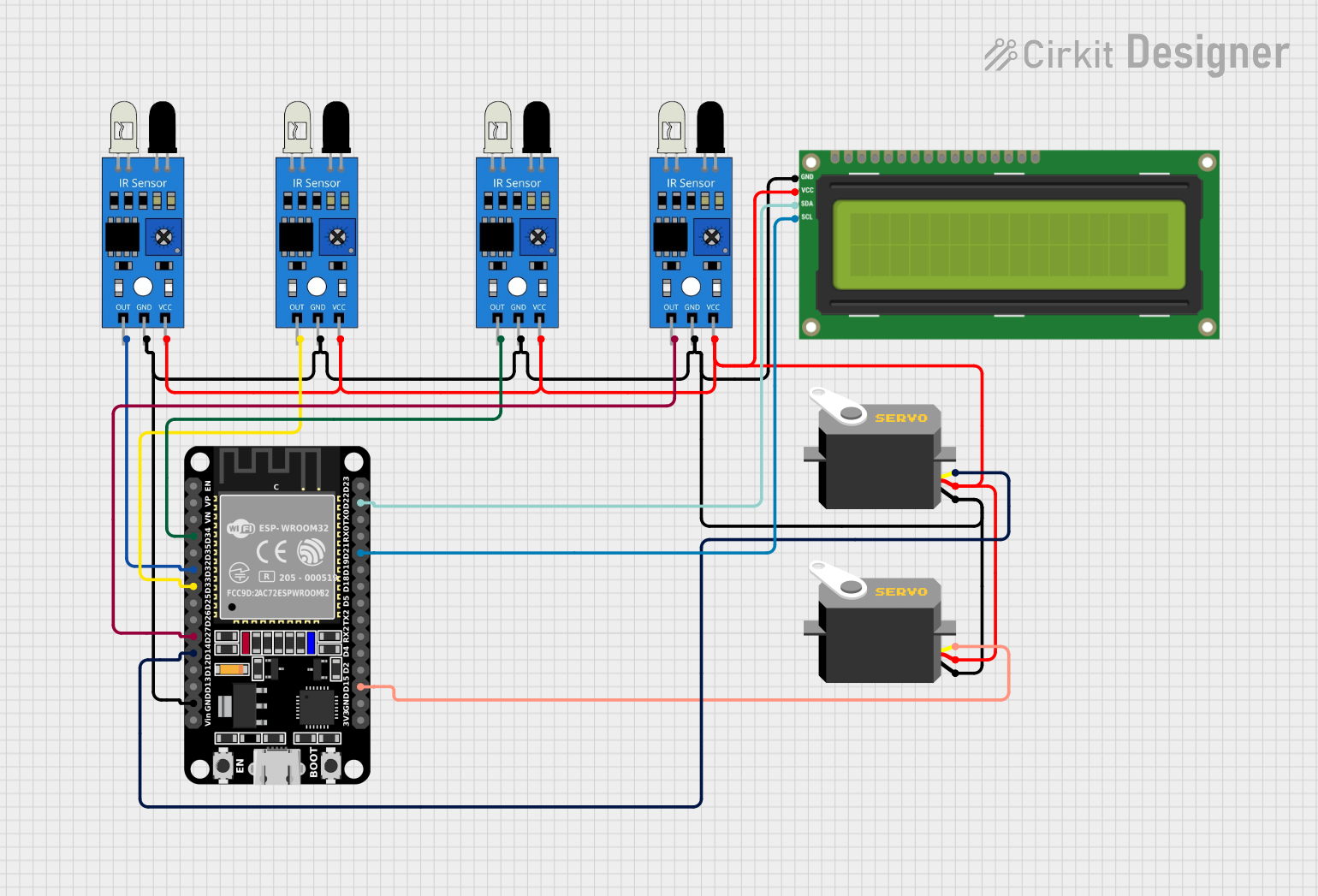
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Sabertooth 2*32

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Robotics (e.g., mobile robots, robotic arms)
- Automated guided vehicles (AGVs)
- Remote-controlled cars, boats, and drones
- Conveyor systems and industrial automation
- Electric wheelchairs and mobility devices
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the Sabertooth 2*32 motor driver:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 6V to 30V |
| Continuous Current (per channel) | 32A |
| Peak Current (per channel) | 64A (for a few seconds) |
| Control Modes | Analog, R/C, Serial, Packetized Serial |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | 3.25" x 2.75" x 1.5" (82.5mm x 70mm x 38mm) |
| Weight | 150g |
| Communication Protocols | TTL Serial, USB (via adapter) |
| Safety Features | Overcurrent, overvoltage, thermal protection |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Sabertooth 2*32 has a set of input and output pins for motor control and communication. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| M1A, M1B | Motor Output | Connect to the terminals of Motor 1. |
| M2A, M2B | Motor Output | Connect to the terminals of Motor 2. |
| VIN, GND | Power Input | Connect to the power supply (6V to 30V) and ground. |
| S1, S2 | Signal Input | Control inputs for analog, R/C, or serial modes. |
| 0V, 5V | Power Output | Provides 5V regulated output for external devices (e.g., sensors, microcontrollers). |
| TX, RX | Serial I/O | TTL serial communication pins for interfacing with microcontrollers or PCs. |
| USB | Communication | USB port for configuration and control (requires USB-to-serial adapter). |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the Sabertooth 2*32
- Power Supply: Connect a DC power supply (6V to 30V) to the VIN and GND terminals. Ensure the power supply can handle the current requirements of your motors.
- Motor Connections: Connect the terminals of Motor 1 to M1A and M1B, and Motor 2 to M2A and M2B.
- Control Input: Depending on your control mode:
- For analog control, connect a potentiometer or analog signal to S1 and S2.
- For R/C control, connect the R/C receiver outputs to S1 and S2.
- For serial control, connect the TX and RX pins to a microcontroller or PC.
- Configuration: Use the DIP switches on the board to set the operating mode. Refer to the user manual for DIP switch settings.
Example: Using with Arduino UNO
The Sabertooth 2*32 can be controlled via serial communication with an Arduino UNO. Below is an example code snippet to control two motors:
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define TX and RX pins for SoftwareSerial
SoftwareSerial SabertoothSerial(10, 11); // TX = Pin 10, RX = Pin 11
void setup() {
SabertoothSerial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
// Send commands to control motor speed
// Motor 1 forward at 50% speed
SabertoothSerial.write(64 + 50); // 64 is the base command for motor 1 forward
delay(1000); // Run motor for 1 second
// Motor 2 reverse at 75% speed
SabertoothSerial.write(192 + 75); // 192 is the base command for motor 2 reverse
delay(1000); // Run motor for 1 second
}
Important Considerations
- Power Supply: Ensure the power supply voltage and current ratings match the requirements of your motors and the Sabertooth 2*32.
- Heat Dissipation: The motor driver may heat up during operation. Use proper ventilation or a heatsink if necessary.
- Wiring: Use thick wires for motor and power connections to handle high currents without overheating.
- Configuration: Always configure the DIP switches correctly before powering the device.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motors not running:
- Check the power supply voltage and connections.
- Verify the DIP switch settings for the selected control mode.
- Ensure the control signals (e.g., serial commands) are being sent correctly.
Overheating:
- Ensure the motor driver is not exceeding its current or voltage limits.
- Improve ventilation or add a heatsink to the device.
Erratic motor behavior:
- Check for loose or faulty wiring.
- Verify that the control signals are clean and within the expected range.
No response to serial commands:
- Ensure the baud rate matches the Sabertooth 2*32 settings.
- Check the TX and RX connections between the microcontroller and the motor driver.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the Sabertooth 2*32 with a 24V battery?
A: Yes, the Sabertooth 2*32 supports input voltages up to 30V, so a 24V battery is within the acceptable range.
Q: How do I reset the Sabertooth 2*32 to factory settings?
A: You can reset the device by setting all DIP switches to the default position and cycling the power.
Q: Can I control brushless motors with the Sabertooth 2*32?
A: No, the Sabertooth 2*32 is designed for brushed DC motors only.
Q: Is it possible to control the Sabertooth 2*32 via USB?
A: Yes, but you will need a USB-to-serial adapter to connect it to a PC.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the Sabertooth 2*32 into your projects and troubleshoot common issues.