
How to Use Soil moisture: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Soil moisture in Cirkit Designer
Design with Soil moisture in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Soil Moisture Sensor by DFROBOT is a reliable and easy-to-use device designed to measure the volumetric water content in soil. This sensor provides an analog or digital output that reflects the soil's moisture level, making it an essential tool for applications such as automated irrigation systems, agricultural monitoring, and gardening projects. Its compact design and compatibility with microcontrollers like Arduino make it a popular choice for both hobbyists and professionals.
Explore Projects Built with Soil moisture
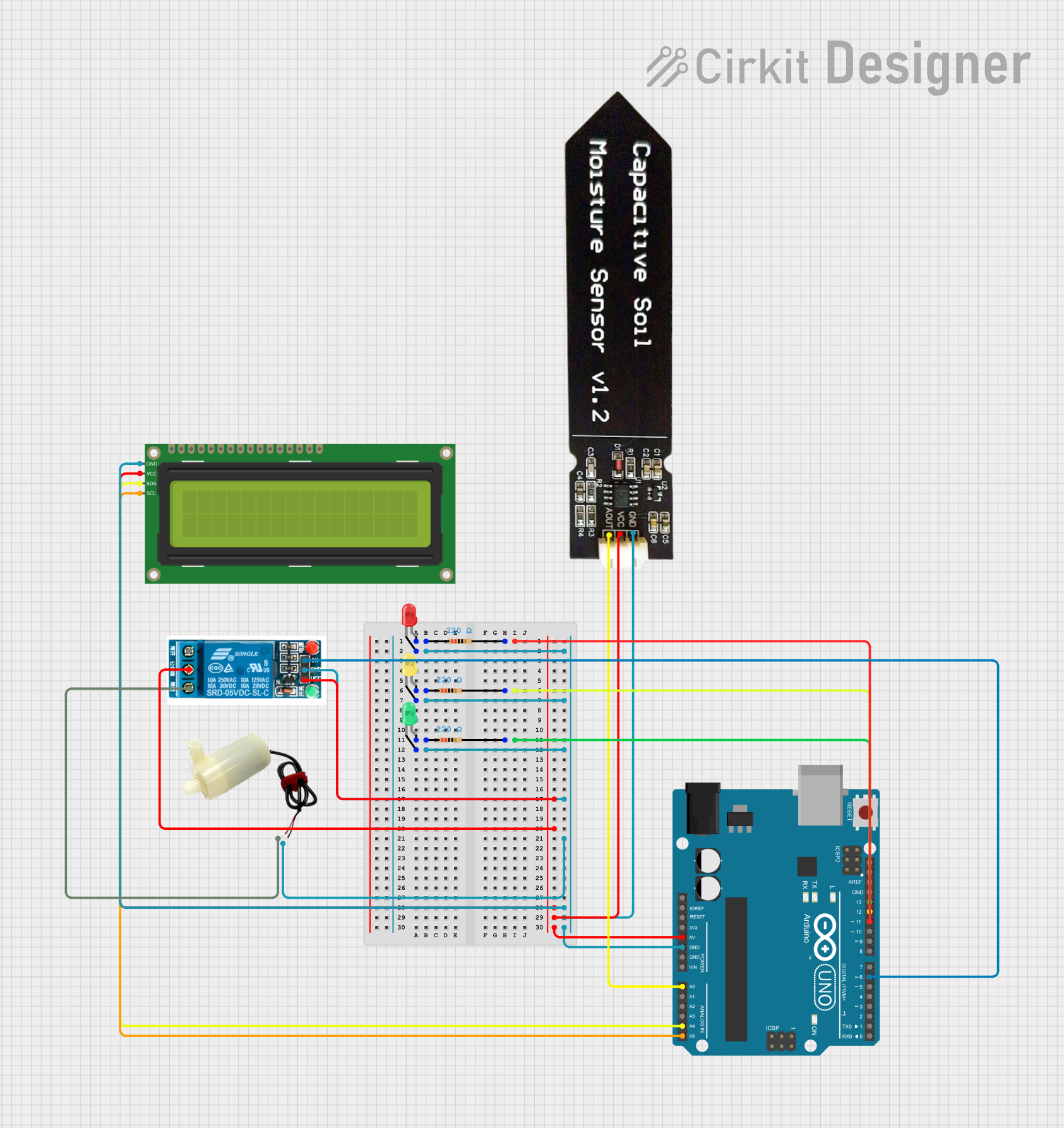
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer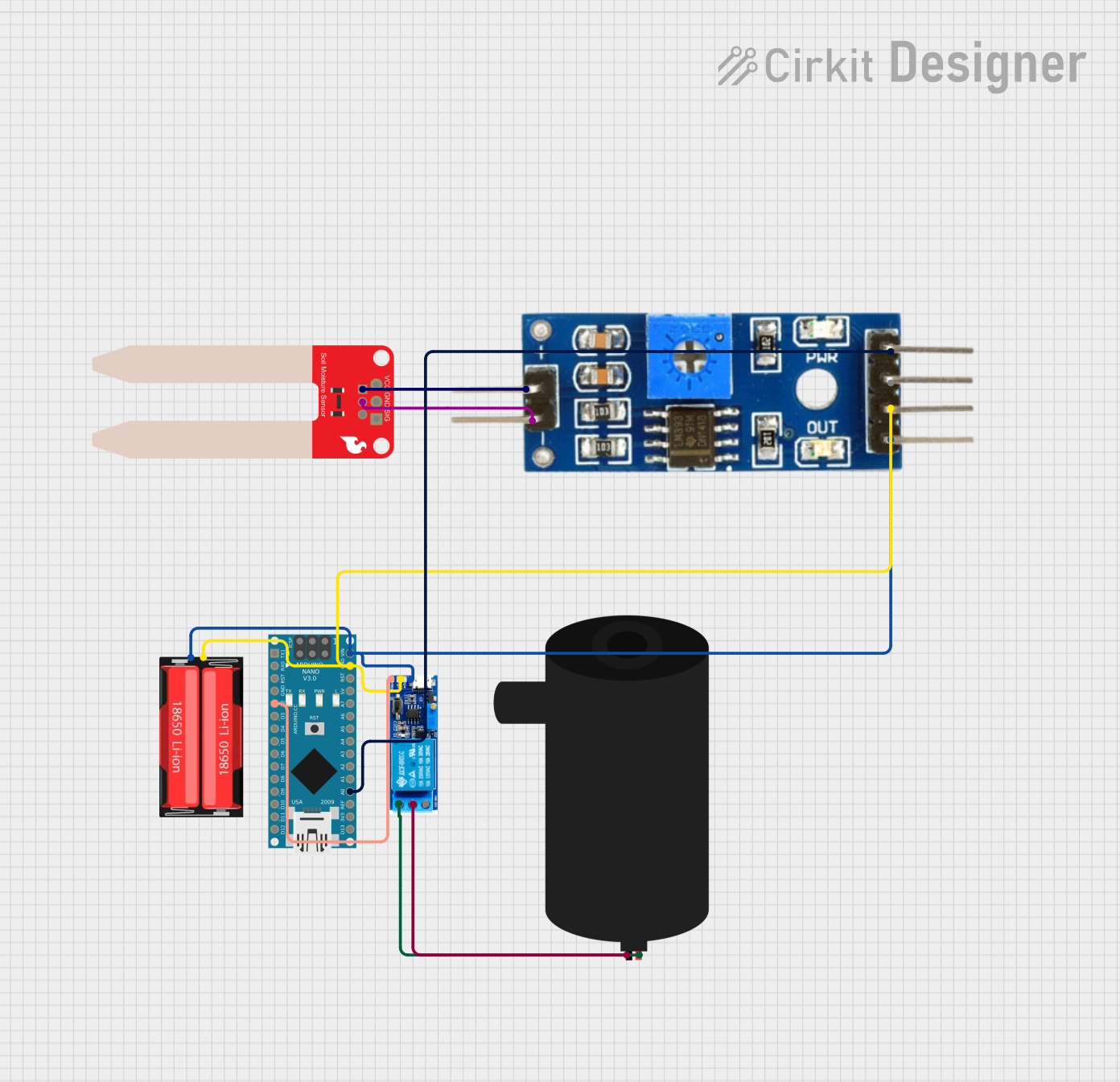
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer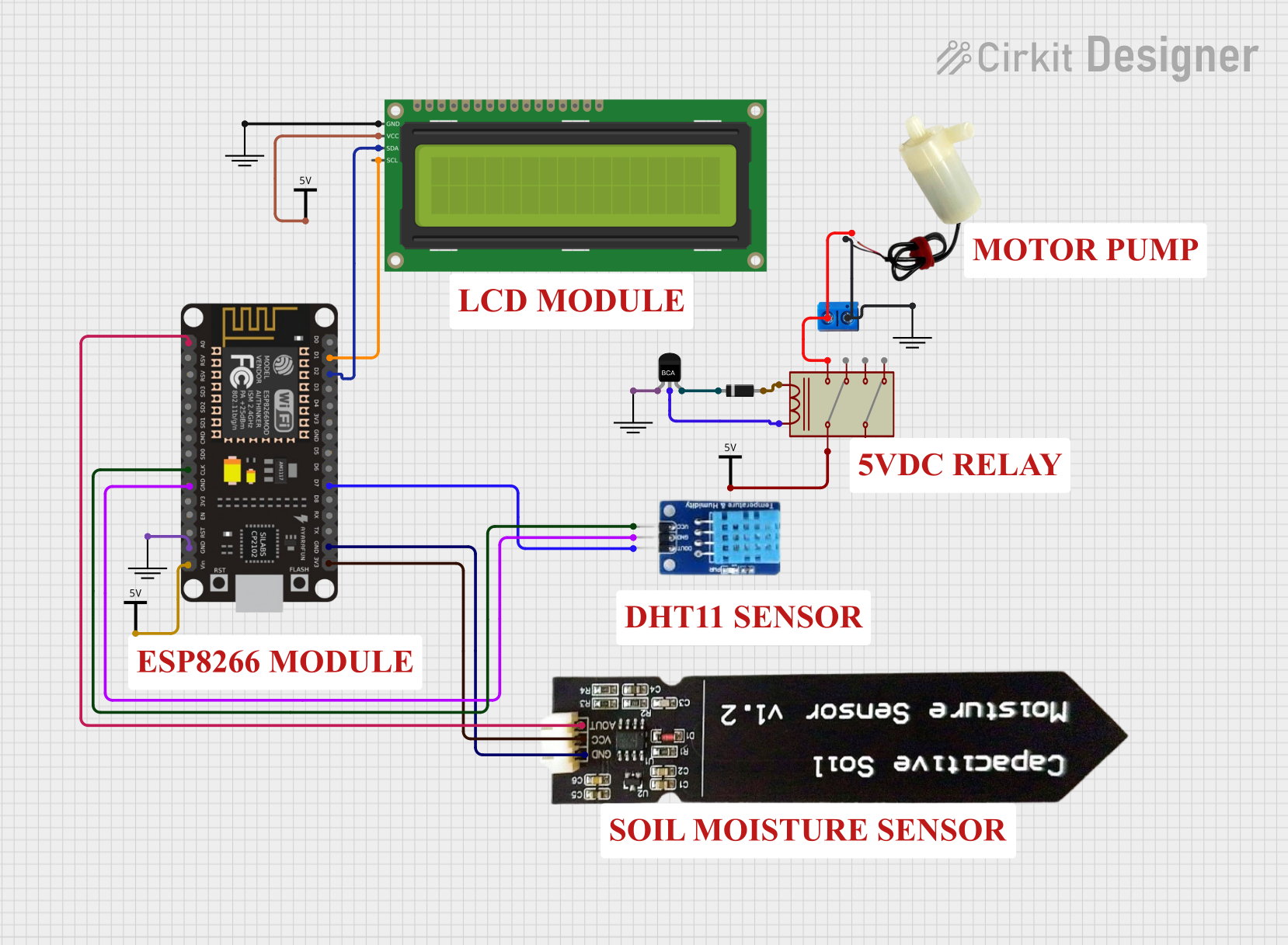
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer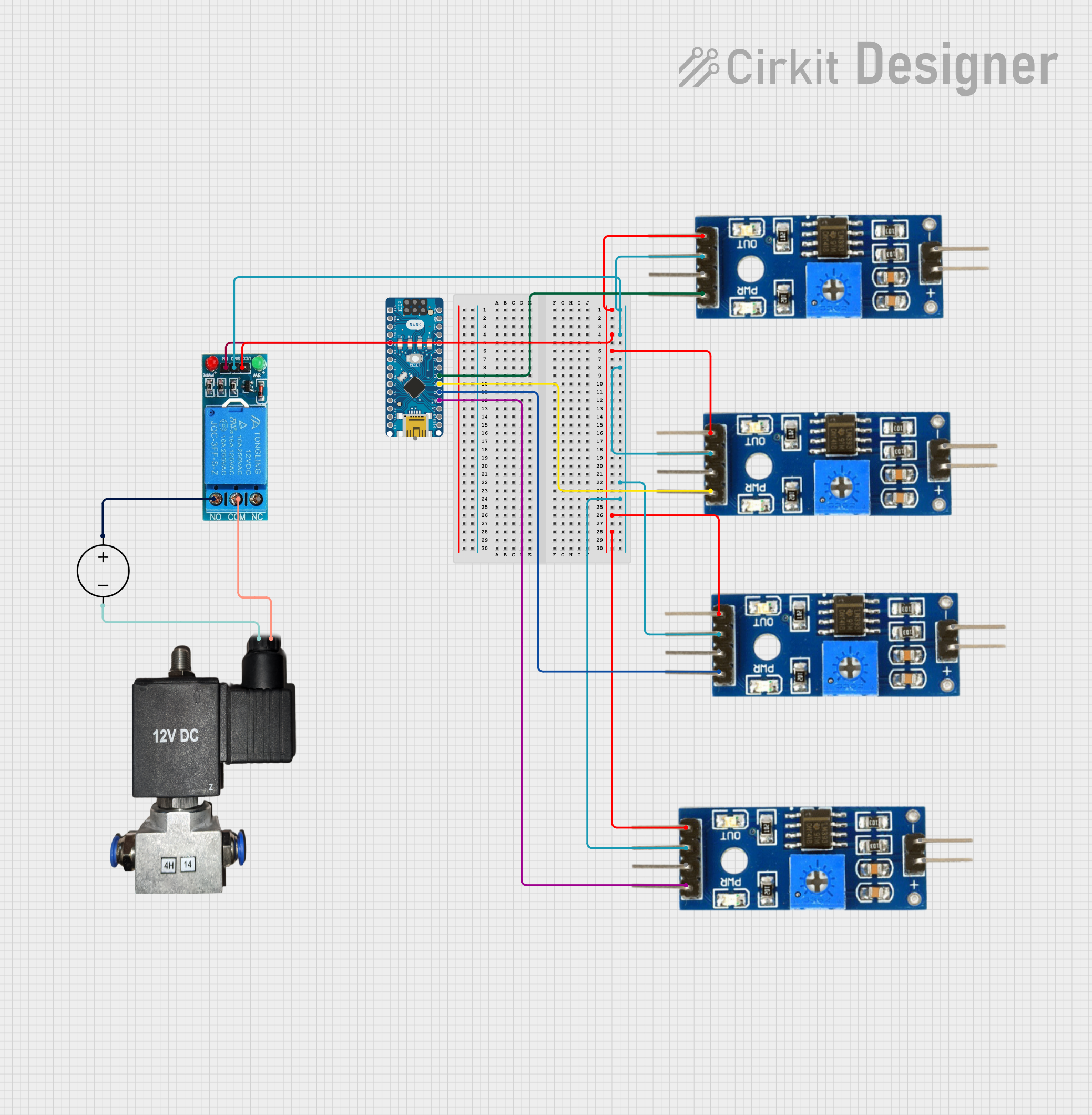
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Soil moisture

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Automated irrigation systems for gardens and farms
- Soil moisture monitoring in greenhouses
- Smart gardening projects
- Environmental monitoring systems
- Educational projects involving soil and plant science
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the DFROBOT Soil Moisture Sensor:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V - 5V |
| Output Type | Analog and Digital |
| Analog Output Range | 0V (dry) to 5V (wet) |
| Digital Output | High (wet) or Low (dry) |
| Current Consumption | < 20mA |
| Dimensions | 60mm x 20mm |
| Interface Type | 3-pin (VCC, GND, Signal) |
| Operating Temperature | -10°C to 60°C |
| Sensor Type | Resistive |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The sensor has a 3-pin interface, as described in the table below:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply pin (3.3V - 5V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | Signal | Outputs analog or digital signal based on moisture |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Sensor in a Circuit
Connect the Sensor to a Microcontroller:
- Connect the VCC pin to the 3.3V or 5V power supply of your microcontroller.
- Connect the GND pin to the ground (GND) of your microcontroller.
- Connect the Signal pin to an analog input pin (e.g., A0) or a digital input pin, depending on your application.
Insert the Sensor into the Soil:
- Place the sensor's probes into the soil at the desired depth. Ensure the probes are fully in contact with the soil for accurate readings.
Read the Output:
- For analog output, read the voltage from the Signal pin using an analog input pin on your microcontroller.
- For digital output, adjust the onboard potentiometer to set the moisture threshold. The Signal pin will output HIGH or LOW based on the soil's moisture level.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid prolonged exposure of the sensor to water or highly humid environments to prevent corrosion.
- Use the sensor in non-corrosive soil for extended lifespan.
- Calibrate the sensor for your specific soil type to improve accuracy.
- If using the sensor outdoors, consider waterproofing the connections to protect them from environmental damage.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
The following code demonstrates how to use the DFROBOT Soil Moisture Sensor with an Arduino UNO to read analog values and display them in the Serial Monitor:
// Define the analog pin connected to the sensor's Signal pin
const int sensorPin = A0;
void setup() {
// Initialize the Serial Monitor for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the sensor
int sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
// Map the sensor value to a percentage (0% = dry, 100% = wet)
int moisturePercent = map(sensorValue, 0, 1023, 0, 100);
// Print the moisture percentage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Soil Moisture: ");
Serial.print(moisturePercent);
Serial.println("%");
// Wait for 1 second before taking the next reading
delay(1000);
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output or Incorrect Readings:
- Ensure the sensor is properly connected to the microcontroller.
- Verify that the power supply voltage is within the specified range (3.3V - 5V).
- Check for loose or corroded connections.
Sensor Corrosion:
- Avoid leaving the sensor in wet soil for extended periods.
- Use a protective coating (e.g., nail polish) on the sensor's probes to reduce corrosion.
Unstable Readings:
- Ensure the sensor is fully inserted into the soil and in good contact with it.
- Avoid using the sensor in highly saline or conductive soils, as this may affect accuracy.
FAQs
Q: Can this sensor be used with a Raspberry Pi?
A: Yes, the sensor can be used with a Raspberry Pi. However, since the Raspberry Pi does not have built-in analog input pins, you will need an external ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) to read the analog output.
Q: How do I calibrate the sensor for my soil type?
A: To calibrate, take readings from the sensor in completely dry soil and fully saturated soil. Use these values to map the sensor's output to a percentage scale in your code.
Q: Is the sensor waterproof?
A: The sensor's probes are water-resistant, but the PCB and connections are not. Use waterproofing measures if deploying the sensor outdoors.