
How to Use PCB: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with PCB in Cirkit Designer
Design with PCB in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a flat board made of insulating material that holds and connects electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks, or signal traces. PCBs are the backbone of most electronic devices, providing mechanical support and electrical connections for components such as resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits, and more.
Explore Projects Built with PCB
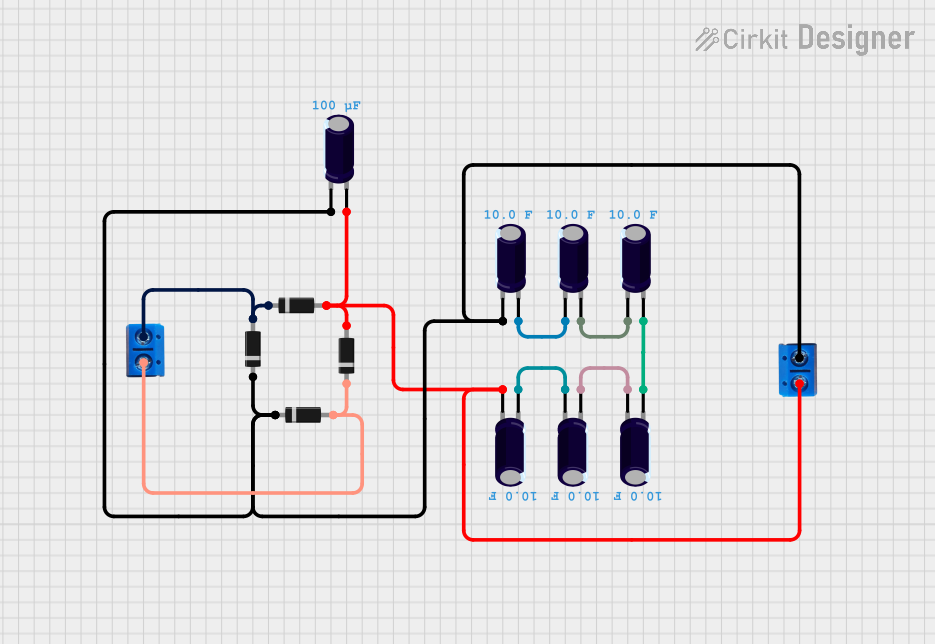
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer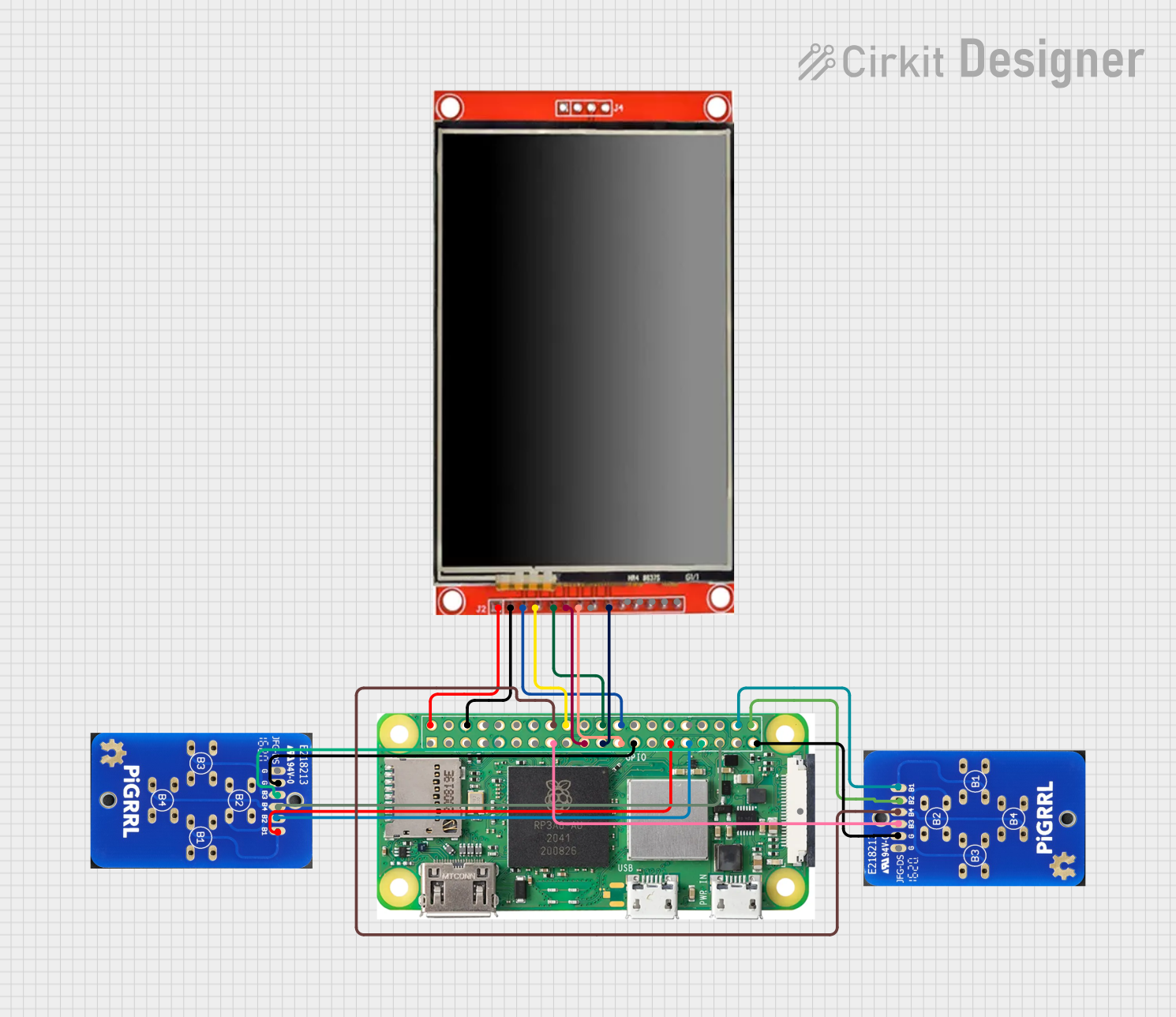
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer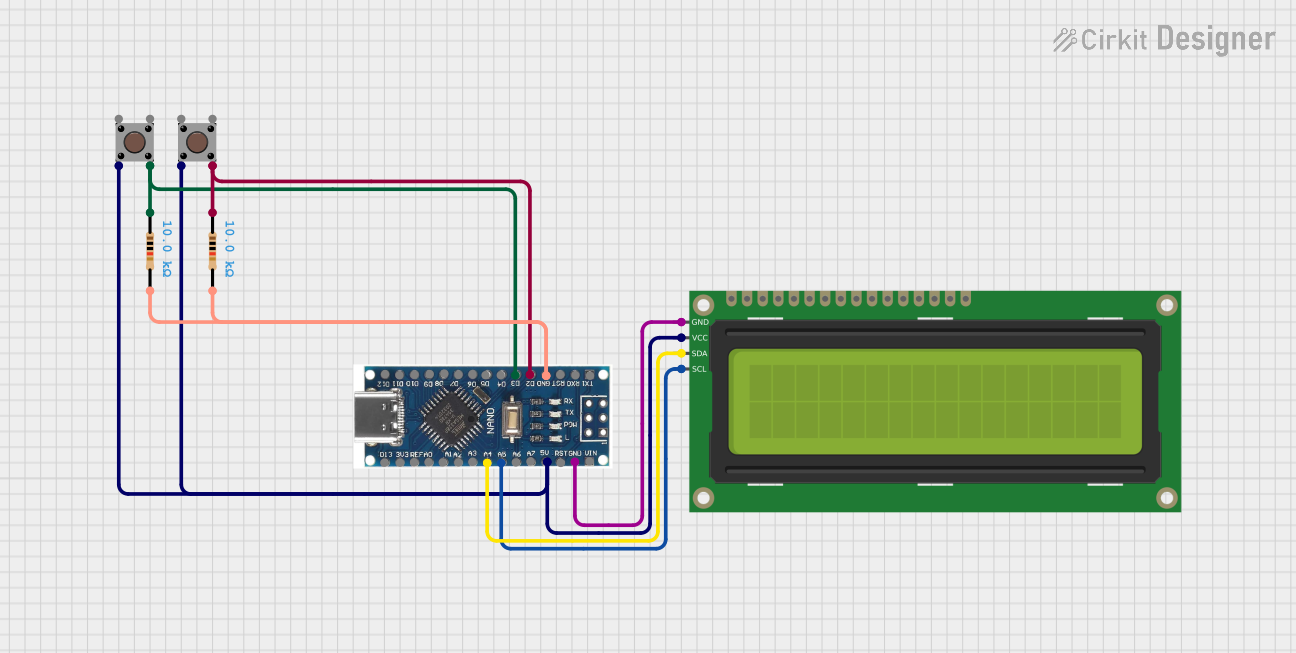
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with PCB

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, laptops, televisions, and gaming consoles.
- Industrial Equipment: Control systems, robotics, and automation devices.
- Automotive Industry: Engine control units, infotainment systems, and sensors.
- Medical Devices: Diagnostic equipment, monitoring systems, and wearable devices.
- Aerospace and Defense: Navigation systems, communication devices, and avionics.
Technical Specifications
The specifications of a PCB can vary widely depending on its design and application. Below are some general technical details:
Key Technical Details
- Material: FR4 (fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate) is the most common.
- Layers: Single-layer, double-layer, or multi-layer (up to 40+ layers for complex designs).
- Copper Thickness: Typically 1 oz/ft² (35 µm), but can range from 0.5 oz/ft² to 3 oz/ft².
- Board Thickness: Commonly 1.6 mm, but can vary from 0.2 mm to 3.2 mm.
- Solder Mask Color: Green is standard, but other colors like blue, red, and black are available.
- Surface Finish: HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), etc.
- Operating Temperature: Typically -40°C to 85°C, depending on the material.
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
While a PCB itself does not have pins, it features pads, vias, and connectors for interfacing with components and external devices. Below is an example of common PCB features:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Pads | Flat conductive areas where components are soldered. |
| Vias | Holes plated with copper to connect layers of a multi-layer PCB. |
| Traces | Conductive pathways that connect components electrically. |
| Connectors | Interfaces for external connections, such as headers, sockets, or terminals. |
| Ground Plane | A large area of copper used as a common ground reference for the circuit. |
| Silkscreen | Printed labels and markings for component placement and identification. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use a PCB in a Circuit
Design the PCB Layout:
- Use PCB design software (e.g., KiCad, Eagle, or Altium Designer) to create the schematic and layout.
- Define the placement of components, traces, and vias.
- Ensure proper spacing and routing to avoid short circuits or signal interference.
Manufacture the PCB:
- Send the design files (Gerber files) to a PCB manufacturer.
- Specify the material, layer count, copper thickness, and surface finish.
Assemble the PCB:
- Solder components onto the PCB using a soldering iron or reflow soldering process.
- Verify the orientation and placement of components.
Test the PCB:
- Power the PCB and check for proper functionality.
- Use tools like a multimeter or oscilloscope to troubleshoot any issues.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Trace Width and Spacing: Ensure traces are wide enough to handle the required current and spaced to prevent short circuits.
- Thermal Management: Use heat sinks, thermal vias, or copper pours to dissipate heat from high-power components.
- Signal Integrity: Minimize noise and interference by using proper grounding and shielding techniques.
- Design for Manufacturability (DFM): Follow guidelines to ensure the PCB can be easily and reliably manufactured.
Example: Connecting a PCB to an Arduino UNO
If your PCB is designed to interface with an Arduino UNO, you can use headers to connect the two. Below is an example Arduino code snippet for controlling an LED on a custom PCB:
// Example Arduino code to control an LED on a custom PCB
const int ledPin = 13; // Pin connected to the LED on the PCB
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Short Circuits:
- Cause: Traces or solder joints are too close, causing unintended connections.
- Solution: Inspect the PCB under a magnifying glass and use a multimeter to locate shorts. Rework the soldering if necessary.
Open Circuits:
- Cause: Broken traces or poor solder joints.
- Solution: Use a continuity test to identify breaks and repair them with solder or jumper wires.
Component Misplacement:
- Cause: Components soldered in the wrong orientation or position.
- Solution: Refer to the silkscreen and schematic to verify placement. Desolder and reposition components if needed.
Overheating:
- Cause: Insufficient thermal management or excessive current through traces.
- Solution: Redesign the PCB with wider traces or add thermal vias and heat sinks.
FAQs
Q: Can I reuse a PCB after desoldering components?
- A: Yes, but repeated heating can damage the pads and traces. Handle with care.
Q: What software should I use for PCB design?
- A: Popular options include KiCad (free), Eagle, and Altium Designer.
Q: How do I choose the right PCB material?
- A: For general use, FR4 is sufficient. For high-frequency or high-temperature applications, consider specialized materials like Rogers or polyimide.
Q: What is the difference between single-layer and multi-layer PCBs?
- A: Single-layer PCBs have components and traces on one side, while multi-layer PCBs have multiple layers of traces separated by insulating material, allowing for more complex designs.
By following this documentation, you can effectively design, assemble, and troubleshoot PCBs for a wide range of applications.