
How to Use TDs sensor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with TDs sensor in Cirkit Designer
Design with TDs sensor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) sensor is an electronic device used to measure the concentration of dissolved solids in a liquid. These dissolved solids include minerals, salts, and organic compounds, which affect the conductivity of the liquid. The sensor provides a TDS value in parts per million (ppm), which is a key indicator of water quality.
Explore Projects Built with TDs sensor
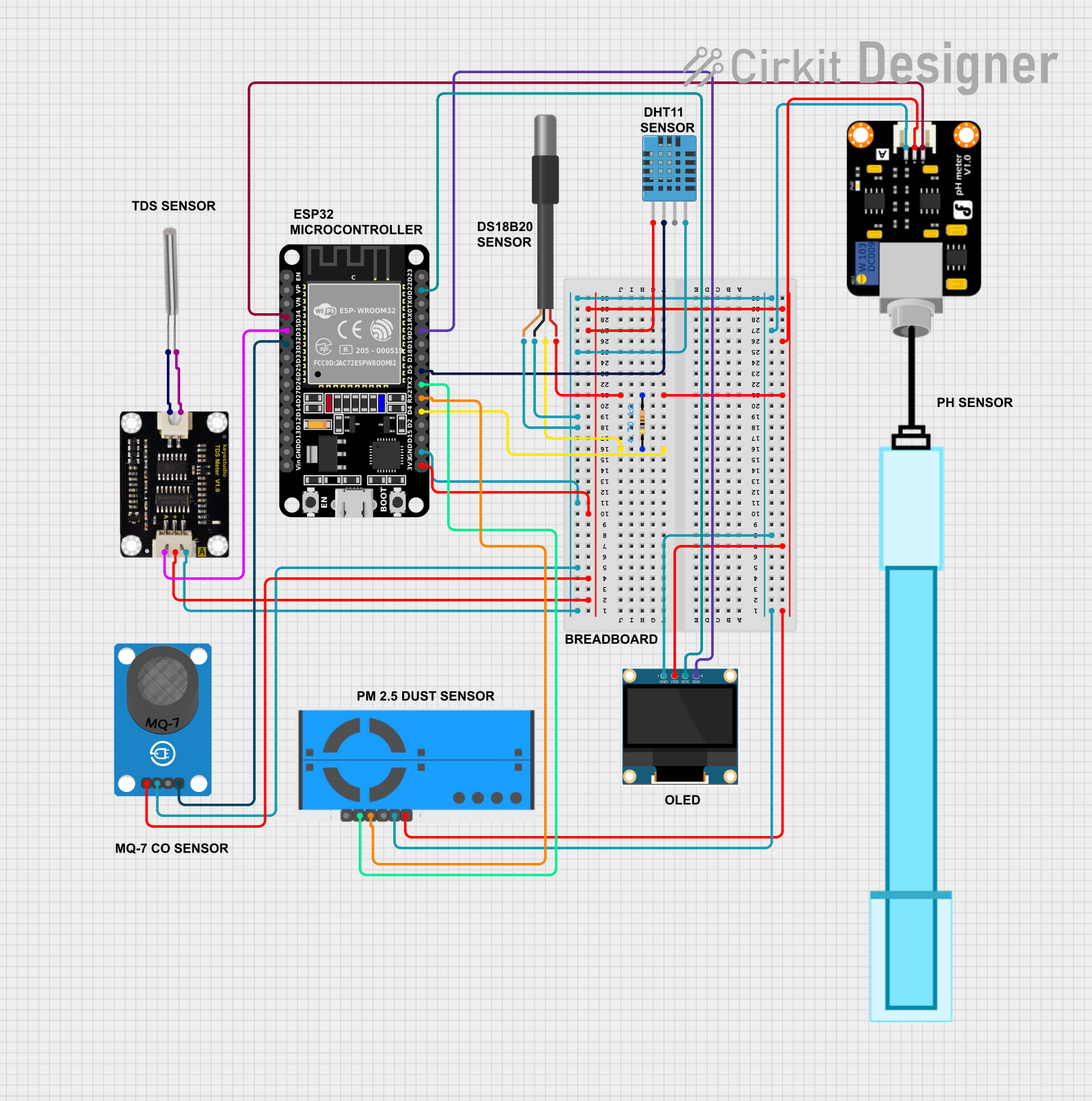
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer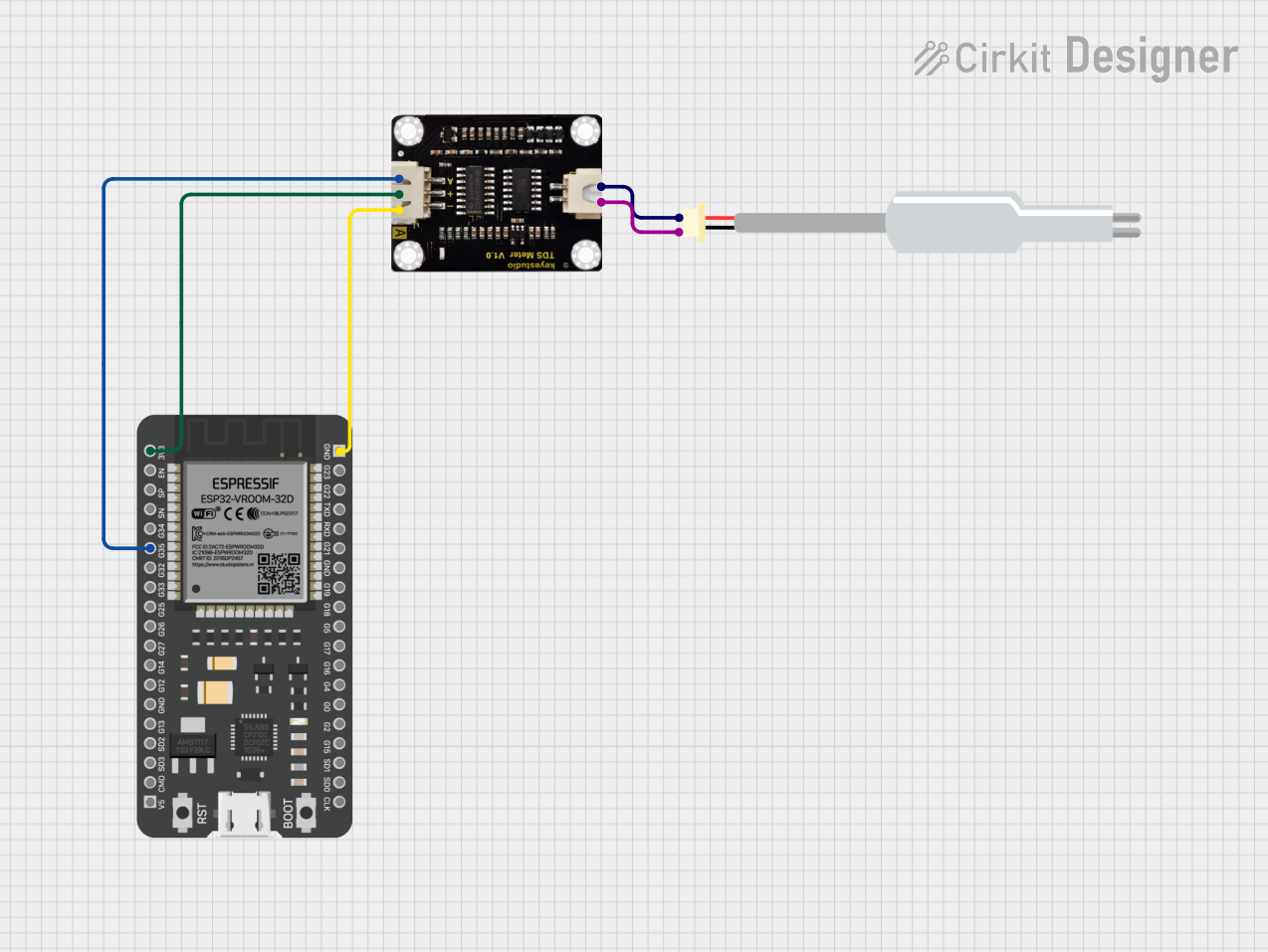
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer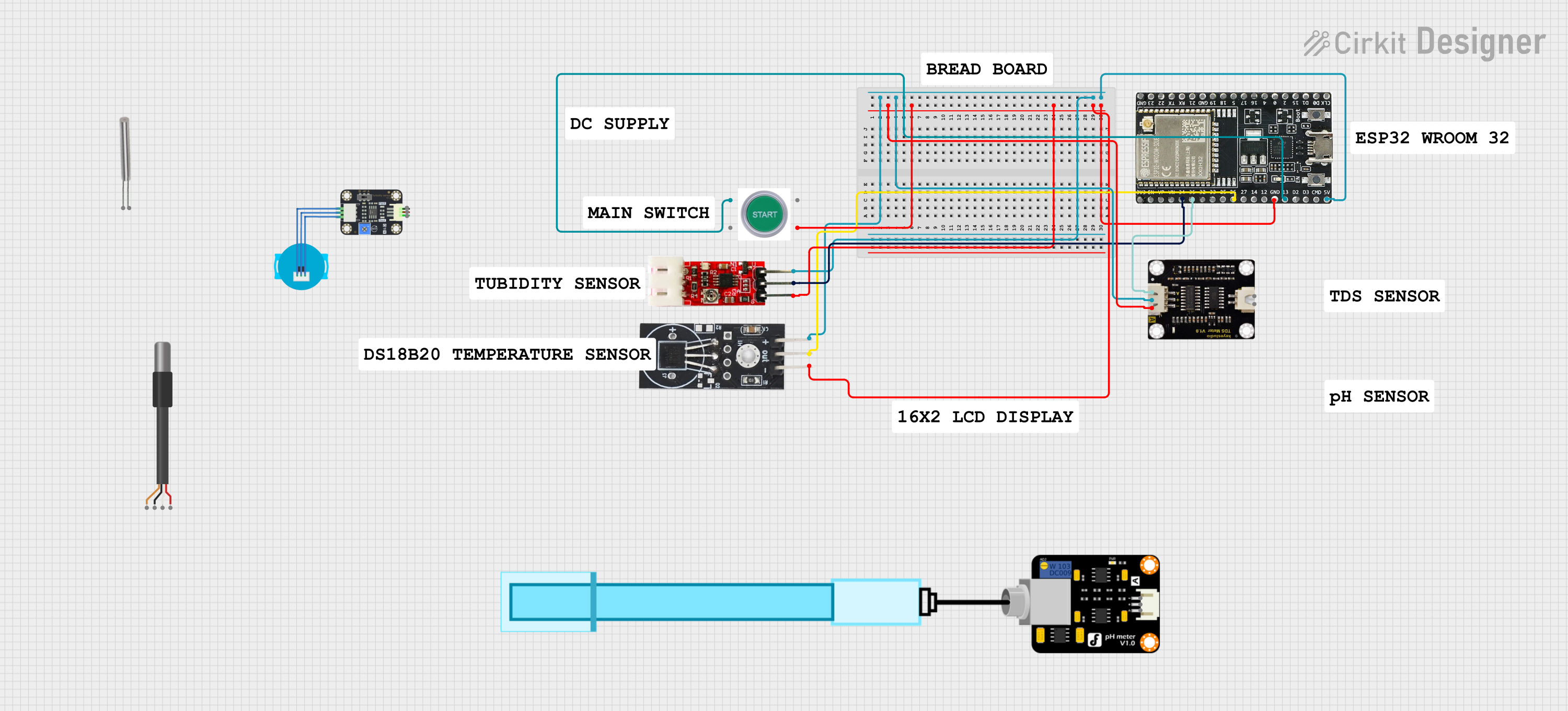
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer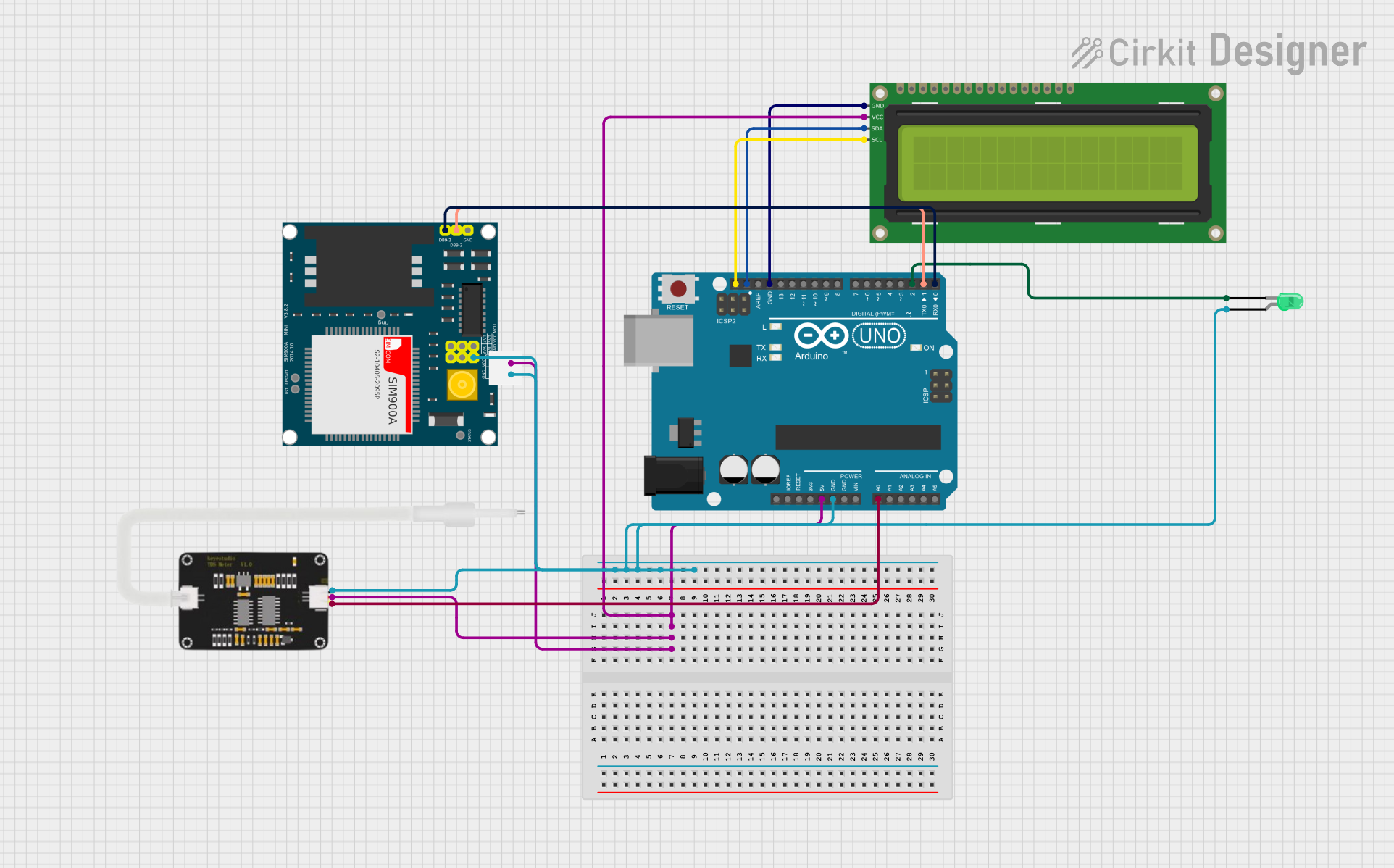
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TDs sensor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Water quality monitoring in aquariums, hydroponics, and swimming pools
- Drinking water purification systems
- Industrial water treatment processes
- Environmental water testing for rivers, lakes, and reservoirs
- Agricultural irrigation systems to ensure proper nutrient levels
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details and pin configuration for a typical TDS sensor module:
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V - 5.0V |
| Operating Current | 3-6 mA |
| Measurement Range | 0 - 1000 ppm |
| Accuracy | ±10% (25°C calibration) |
| Output Signal | Analog voltage (0-2.3V typical) |
| Temperature Compensation | Supported (via external probe) |
| Operating Temperature | 0°C - 60°C |
Pin Configuration
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply input (3.3V - 5.0V) |
| GND | Ground connection |
| AOUT | Analog output signal proportional to TDS value |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the TDS Sensor in a Circuit
Connect the Sensor Module:
- Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5V power source. - Connect the
GNDpin to the ground of your circuit. - Connect the
AOUTpin to an analog input pin of your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino).
- Connect the
Calibrate the Sensor:
- Immerse the TDS probe in a standard solution with a known TDS value (e.g., 342 ppm).
- Adjust the potentiometer on the sensor module to match the expected output voltage.
Measure TDS:
- Place the probe in the liquid to be tested, ensuring it is fully submerged.
- Read the analog voltage from the
AOUTpin and convert it to a TDS value using the formula provided in the sensor's datasheet.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Temperature Compensation: TDS readings are temperature-dependent. Use a temperature sensor for compensation if precise measurements are required.
- Probe Maintenance: Clean the probe regularly to prevent fouling, which can affect accuracy.
- Avoid Air Bubbles: Ensure no air bubbles are trapped around the probe during measurement.
- Do Not Immerse the Module: Only the probe is waterproof; the module should remain dry.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use a TDS sensor with an Arduino UNO:
// Define the analog pin connected to the TDS sensor
const int tdsPin = A0;
// Calibration factor for converting voltage to TDS (adjust as needed)
const float calibrationFactor = 0.5;
// Variable to store the analog reading
int analogValue = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
pinMode(tdsPin, INPUT); // Set the TDS pin as input
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the TDS sensor
analogValue = analogRead(tdsPin);
// Convert the analog value to voltage (assuming 5V reference)
float voltage = analogValue * (5.0 / 1023.0);
// Calculate the TDS value in ppm
float tdsValue = voltage / calibrationFactor;
// Print the TDS value to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("TDS Value: ");
Serial.print(tdsValue);
Serial.println(" ppm");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Inaccurate Readings:
- Cause: The sensor is not calibrated.
- Solution: Calibrate the sensor using a standard solution with a known TDS value.
No Output or Fluctuating Values:
- Cause: Poor connections or loose wires.
- Solution: Check all connections and ensure the probe is securely connected to the module.
Sensor Not Responding:
- Cause: The probe is damaged or the module is faulty.
- Solution: Inspect the probe for physical damage and replace it if necessary. Test the module with a multimeter.
Readings Drift Over Time:
- Cause: Probe fouling or contamination.
- Solution: Clean the probe with distilled water and a soft cloth.
FAQs
Q: Can the TDS sensor measure salinity?
A: While the TDS sensor measures dissolved solids, it is not specifically designed for salinity measurement. However, it can provide an approximate salinity value in ppm.
Q: Is the TDS sensor waterproof?
A: Only the probe is waterproof. The module must be kept dry to avoid damage.
Q: How often should I calibrate the sensor?
A: Calibration frequency depends on usage. For critical applications, calibrate before each use. For general use, calibrate monthly or as needed.
Q: Can I use the TDS sensor with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, the sensor operates at 3.3V and 5V, making it compatible with most microcontrollers.