
How to Use relay: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with relay in Cirkit Designer
Design with relay in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A relay is an electromechanical switch that uses an electromagnetic coil to open or close a circuit. It allows a low-power signal to control a higher power circuit, providing isolation and control in various applications. Relays are widely used in automation, home appliances, automotive systems, and industrial control systems. They are essential for applications where electrical isolation or the ability to control high-power devices with low-power signals is required.
Common applications of relays include:
- Switching high-power devices such as motors, lights, and heaters.
- Providing electrical isolation between control and load circuits.
- Implementing logic control in automation systems.
- Protecting circuits by acting as a safety switch.
Explore Projects Built with relay
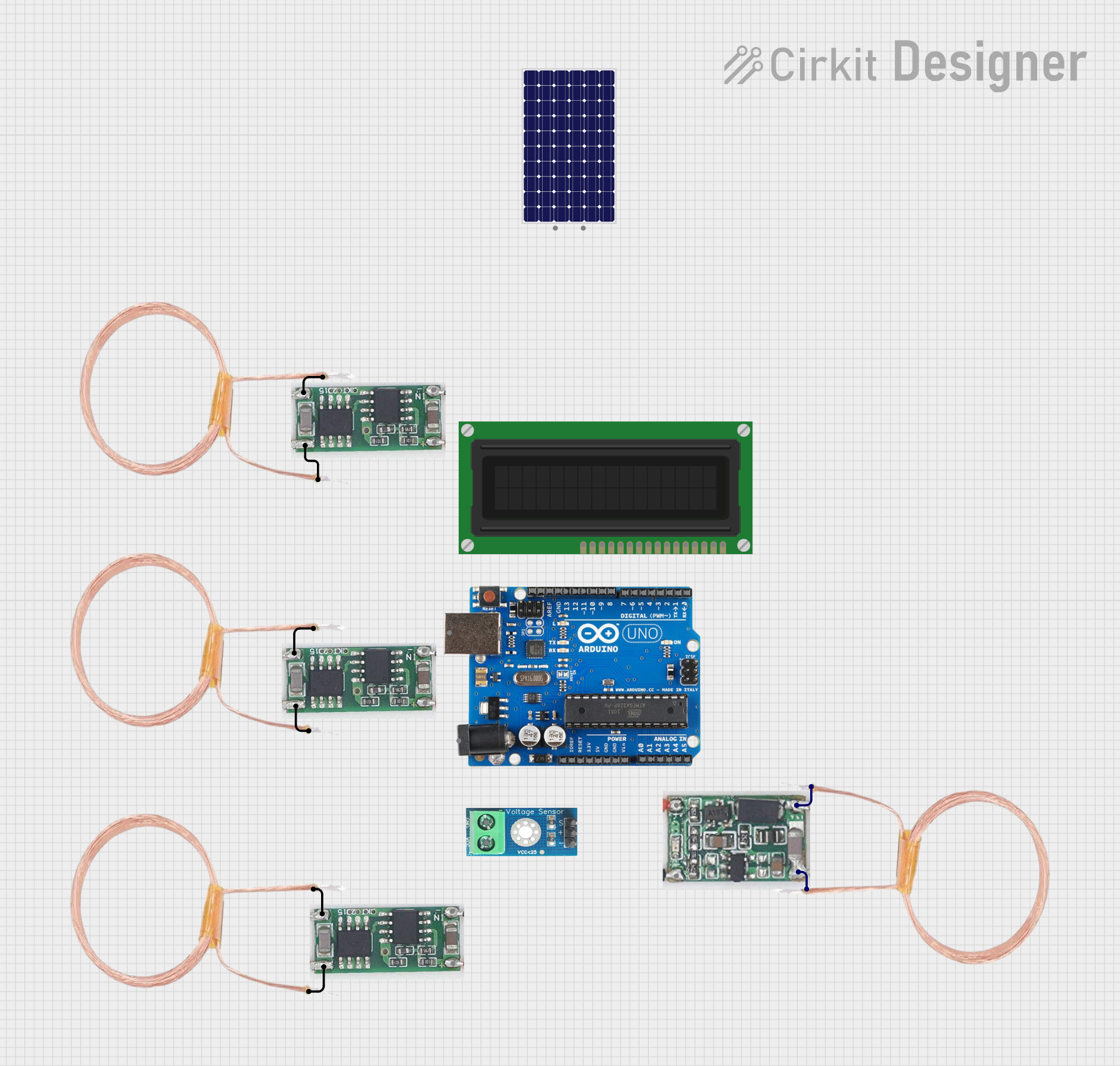
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer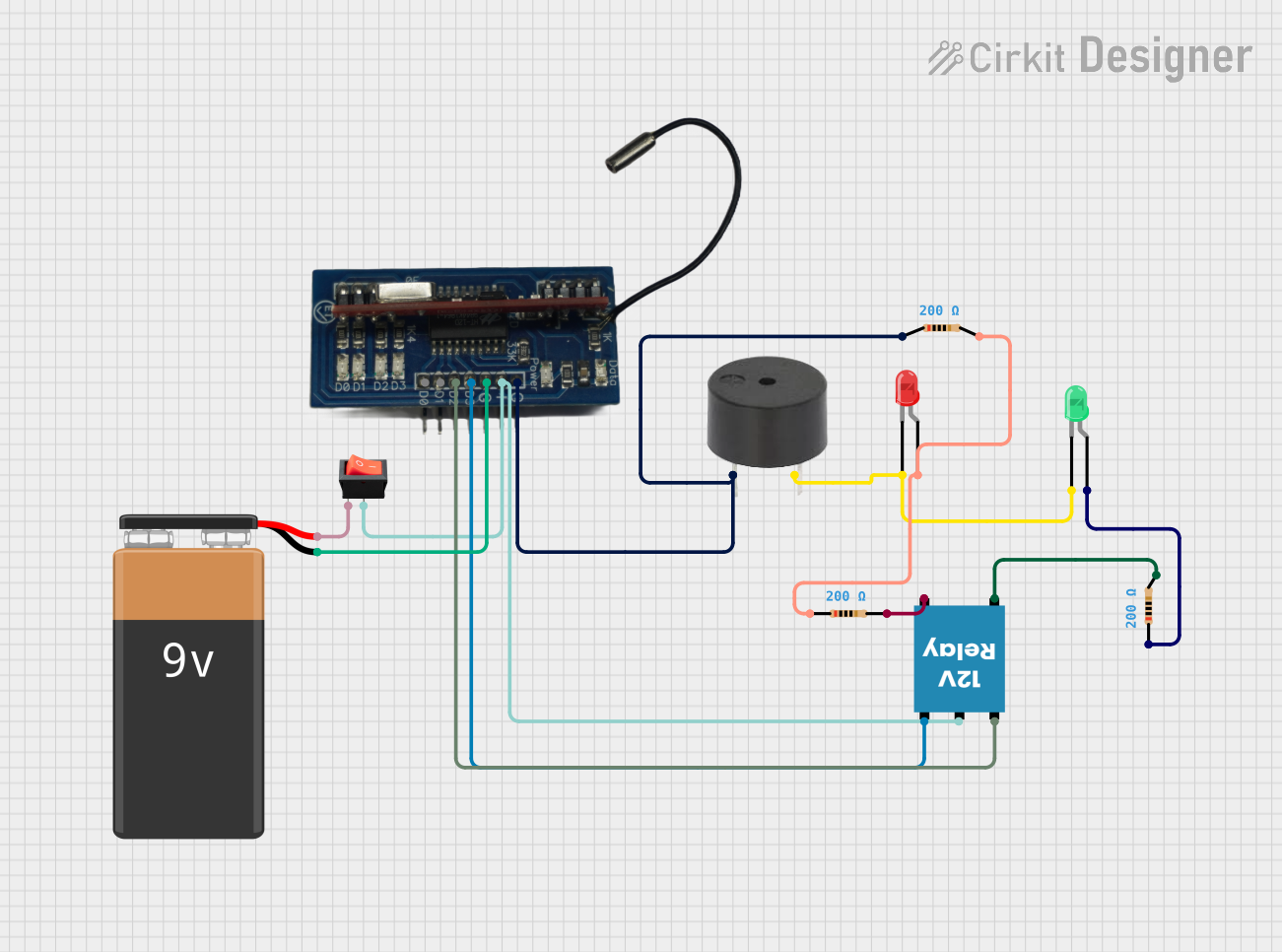
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer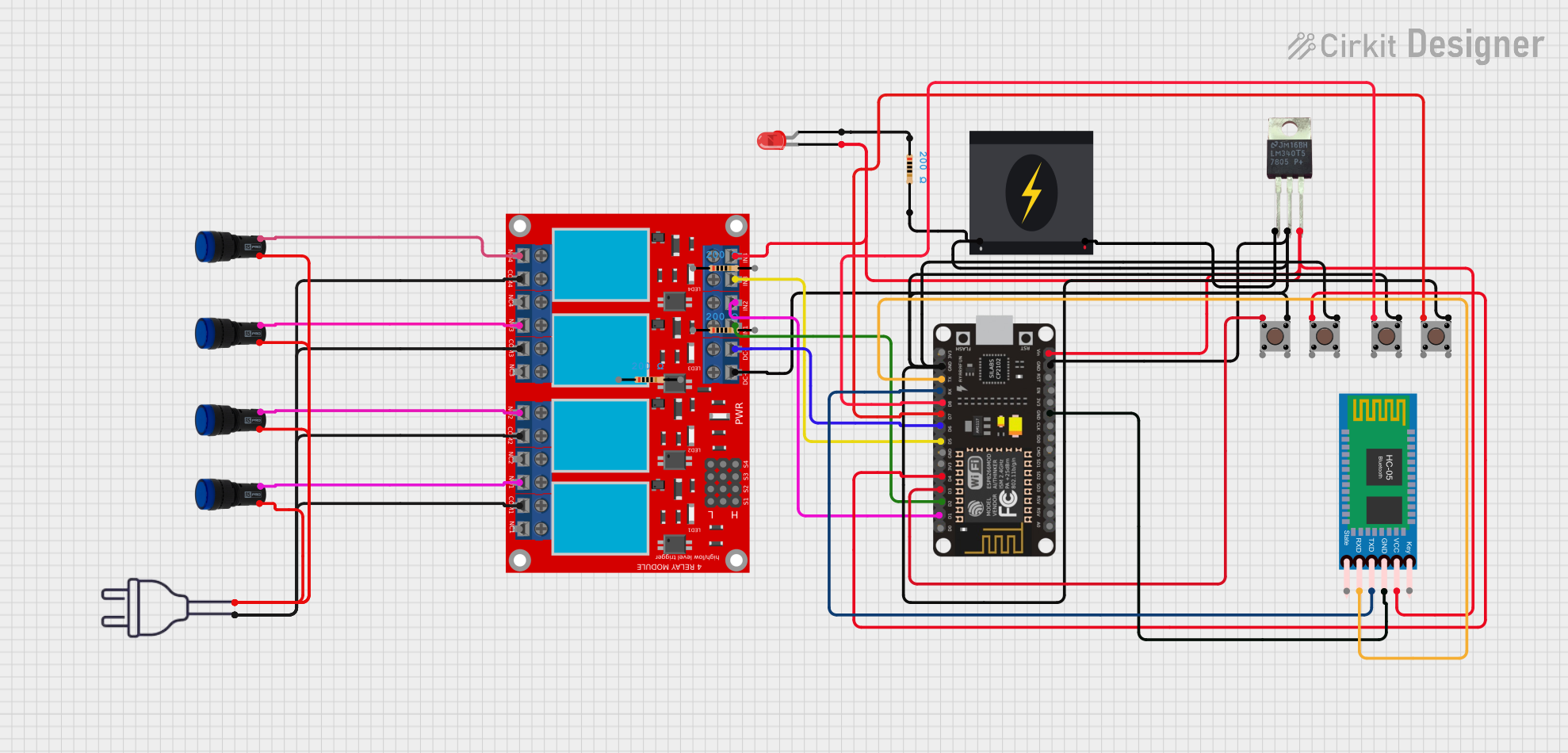
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with relay

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a standard single-pole single-throw (SPST) relay. Specifications may vary depending on the specific relay model.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Coil Voltage | 5V, 12V, or 24V DC (common values) |
| Coil Resistance | 70Ω to 400Ω (varies by model) |
| Switching Voltage (Load) | Up to 250V AC or 30V DC |
| Switching Current (Load) | Up to 10A |
| Contact Configuration | SPST, SPDT, DPDT, etc. |
| Isolation Voltage | 1000V or higher |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to 85°C |
| Mechanical Life | 10 million operations (typical) |
| Electrical Life | 100,000 operations (typical) |
Pin Configuration
The pin configuration of a typical 5-pin SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw) relay is as follows:
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Coil (+) | Positive terminal of the electromagnetic coil. |
| 2 | Coil (-) | Negative terminal of the electromagnetic coil. |
| 3 | Common (COM) | Common terminal connected to the moving contact. |
| 4 | Normally Open (NO) | Contact that remains open until the relay is activated. |
| 5 | Normally Closed (NC) | Contact that remains closed until the relay is activated. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use a Relay in a Circuit
- Power the Coil: Connect the relay's coil terminals (pins 1 and 2) to a DC power source. Ensure the voltage matches the relay's rated coil voltage (e.g., 5V, 12V).
- Control the Load: Connect the load (e.g., motor, light) to the relay's NO or NC terminal and the COM terminal.
- Use the NO terminal if you want the load to turn on when the relay is activated.
- Use the NC terminal if you want the load to turn off when the relay is activated.
- Provide Isolation: Use an optocoupler or transistor to drive the relay coil if the control signal is from a microcontroller or low-power source.
- Add Protection: Place a flyback diode across the coil terminals to protect the circuit from voltage spikes when the relay is deactivated.
Example: Connecting a Relay to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control a relay using an Arduino UNO:
Circuit Connections:
- Connect the relay's coil (+) pin to a digital pin on the Arduino (e.g., pin 7) through a transistor.
- Connect the relay's coil (-) pin to the Arduino's GND.
- Connect the load (e.g., a light bulb) to the relay's NO and COM terminals.
- Add a flyback diode across the relay coil to prevent voltage spikes.
Arduino Code:
// Define the relay pin
const int relayPin = 7;
void setup() {
// Set the relay pin as an output
pinMode(relayPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Turn the relay ON
digitalWrite(relayPin, HIGH);
delay(1000); // Keep the relay ON for 1 second
// Turn the relay OFF
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW);
delay(1000); // Keep the relay OFF for 1 second
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Check Voltage and Current Ratings: Ensure the relay's voltage and current ratings match your application.
- Use a Flyback Diode: Always use a flyback diode across the coil to protect the circuit from voltage spikes.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the relay's maximum switching current or voltage.
- Provide Proper Isolation: Use optocouplers or transistors to isolate the control circuit from the load circuit.
- Test Before Deployment: Test the relay in your circuit to ensure proper operation under load conditions.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Relay Not Activating:
- Cause: Insufficient voltage or current to the coil.
- Solution: Verify the power supply voltage and current match the relay's specifications.
Load Not Switching:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring of the load to the relay terminals.
- Solution: Double-check the connections to the NO, NC, and COM terminals.
Voltage Spikes Damaging Components:
- Cause: Absence of a flyback diode across the coil.
- Solution: Add a flyback diode (e.g., 1N4007) across the coil terminals.
Relay Buzzing or Chattering:
- Cause: Insufficient or unstable power supply to the coil.
- Solution: Use a stable power source and ensure proper connections.
Relay Overheating:
- Cause: Exceeding the relay's current or voltage ratings.
- Solution: Use a relay with appropriate ratings for your application.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use a relay to control an AC load?
A1: Yes, relays are commonly used to control AC loads. Ensure the relay's switching voltage and current ratings are suitable for the AC load.
Q2: What is the purpose of the flyback diode?
A2: The flyback diode protects the circuit from voltage spikes generated when the relay coil is de-energized.
Q3: Can I directly connect a relay to an Arduino pin?
A3: No, most relays require more current than an Arduino pin can supply. Use a transistor or relay driver module to control the relay.
Q4: How do I know if my relay is SPST or SPDT?
A4: Check the relay's datasheet or inspect the pin configuration. SPST relays have 4 pins, while SPDT relays typically have 5 pins.
Q5: Can a relay switch both AC and DC loads?
A5: Yes, but ensure the relay's specifications support the type of load (AC or DC) and its voltage/current requirements.