
How to Use Terminal Block GRAY: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
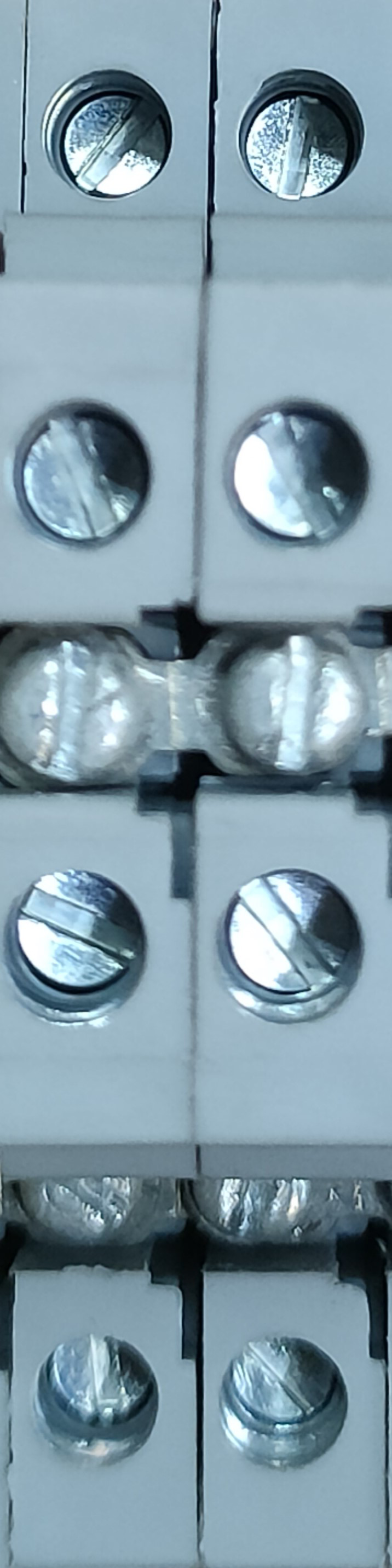

 Design with Terminal Block GRAY in Cirkit Designer
Design with Terminal Block GRAY in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A terminal block is a modular, insulated block designed to secure two or more wires together. The GRAY terminal block is a specific variant, often used to indicate a particular type, rating, or application. These components are essential for connecting and organizing electrical circuits in a safe and efficient manner. Their modular design allows for easy installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting in electrical systems.
Explore Projects Built with Terminal Block GRAY
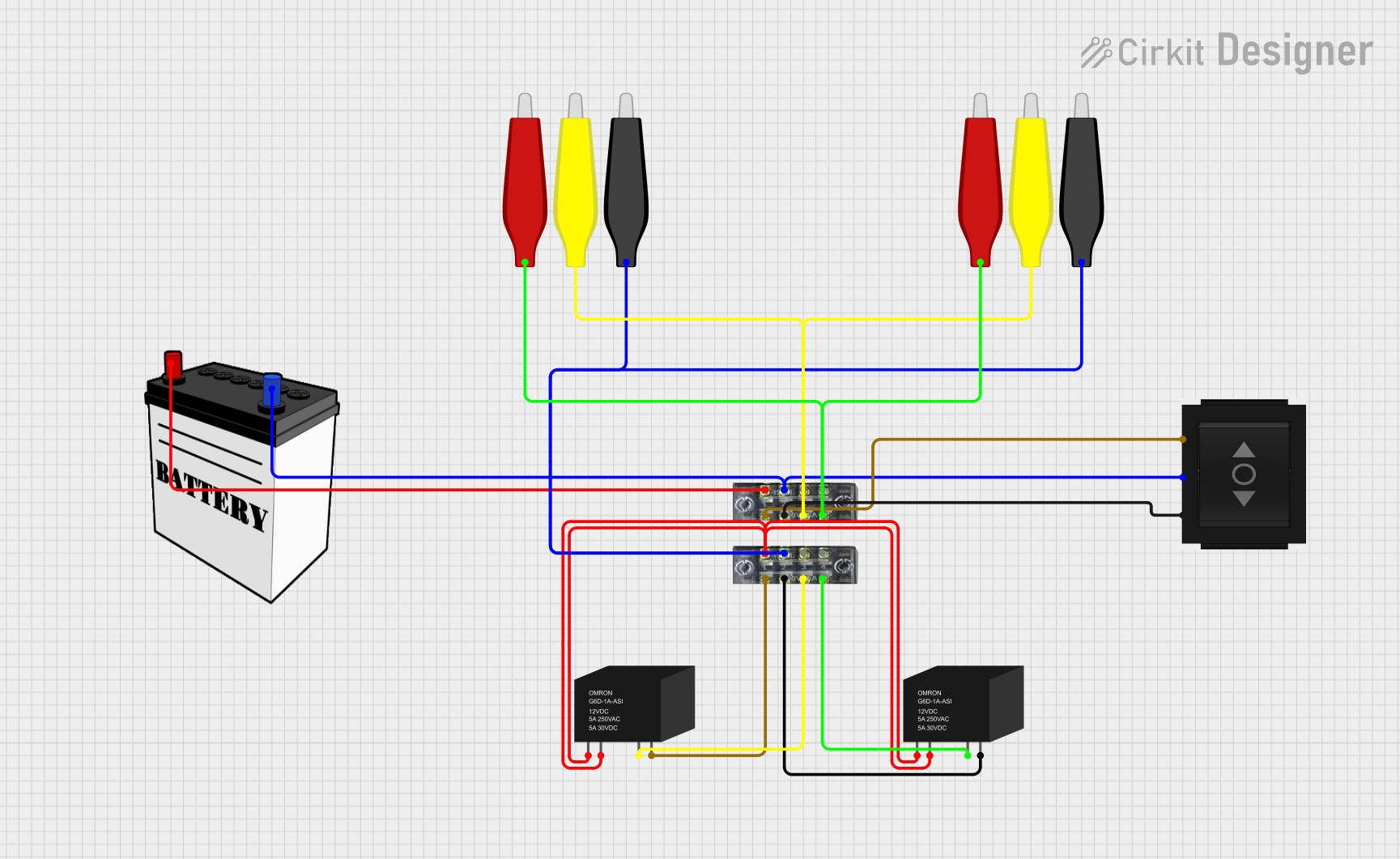
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer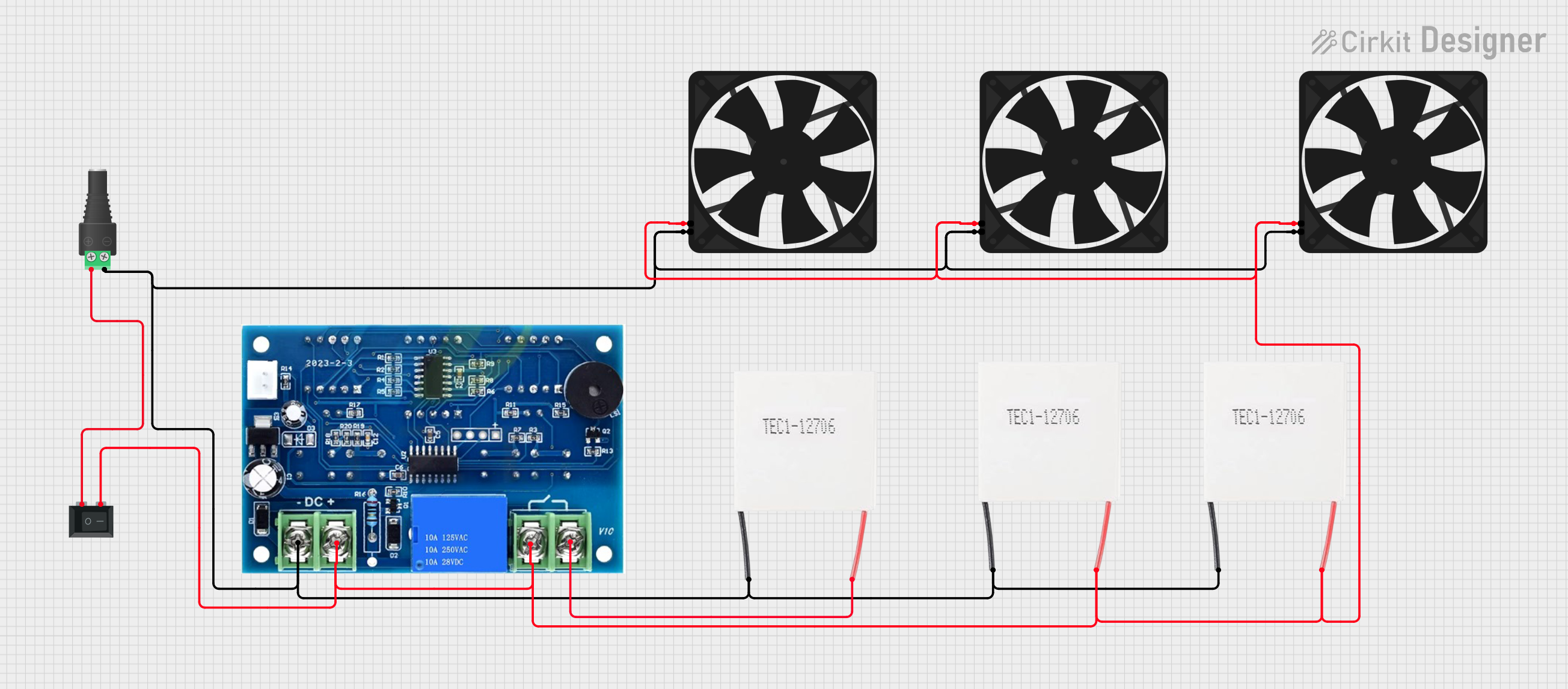
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer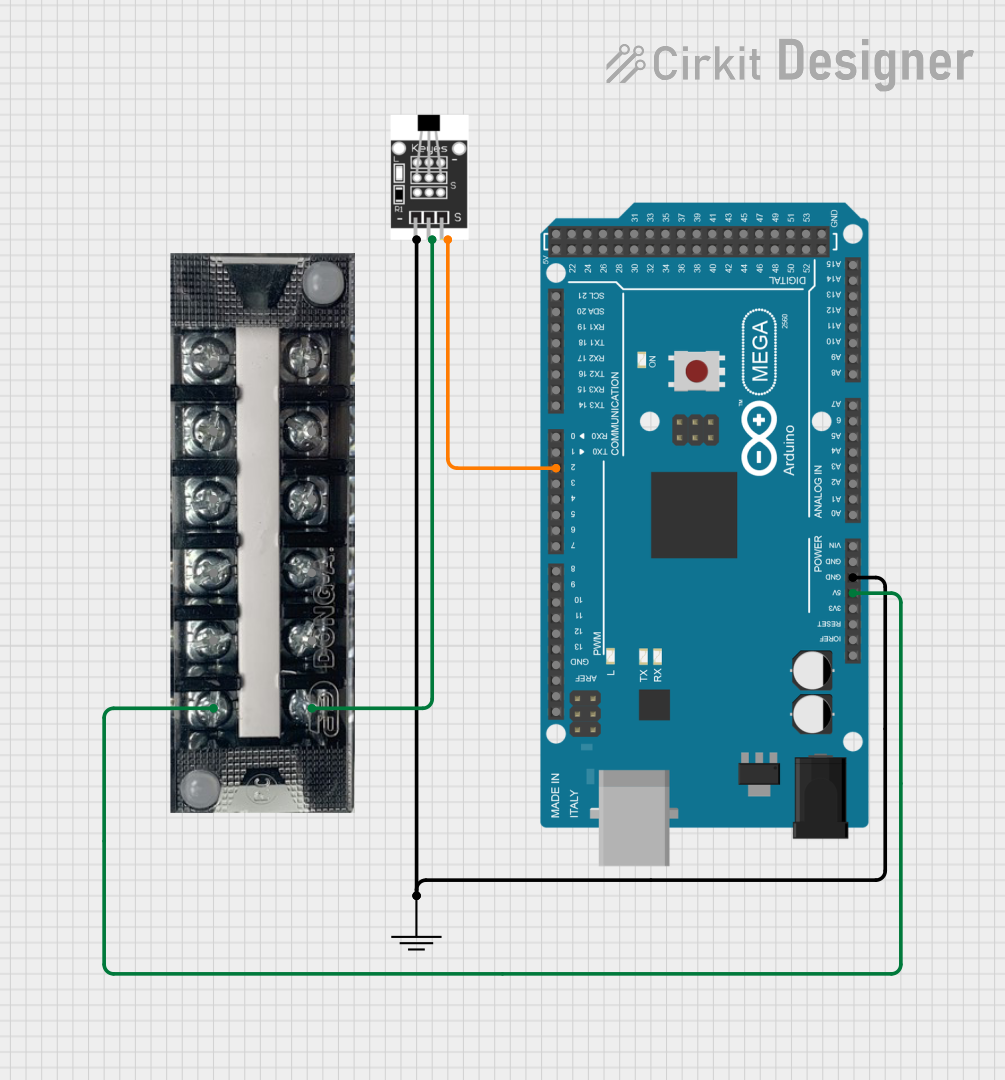
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer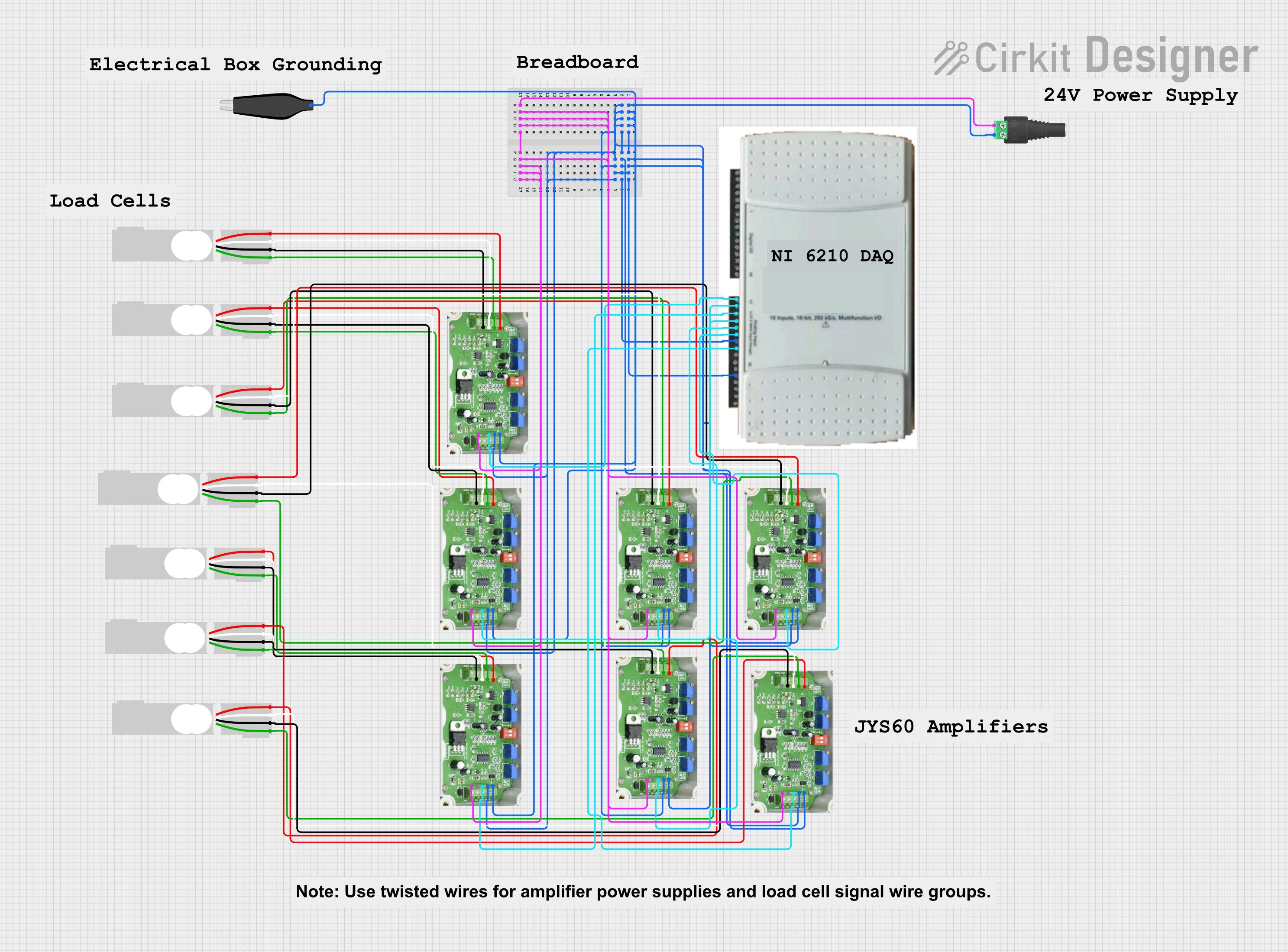
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Terminal Block GRAY

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Industrial control panels and automation systems
- Electrical distribution boards
- Wiring harnesses in machinery
- Audio and communication systems
- Renewable energy systems (e.g., solar panel connections)
- Prototyping and testing circuits
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Material: Insulated thermoplastic housing (typically flame-retardant)
- Color: Gray (may indicate specific voltage or current rating)
- Voltage Rating: Up to 600V (varies by model)
- Current Rating: Typically 10A to 50A (check specific model)
- Wire Size Compatibility: 22 AWG to 6 AWG (varies by model)
- Mounting Type: DIN rail or panel mount
- Connection Type: Screw clamp or spring clamp
- Operating Temperature: -40°C to +105°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Terminal blocks do not have traditional "pins" like ICs or connectors. Instead, they feature connection points for wires. Below is a general description of the connection points:
| Connection Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Input Terminal | Secures the incoming wire; typically marked with a "+" or input label. |
| Output Terminal | Secures the outgoing wire; typically marked with a "-" or output label. |
| Ground Terminal | (Optional) Provides a connection point for grounding wires. |
| Mounting Slot | Used to secure the terminal block to a DIN rail or panel. |
| Test Point | (Optional) Allows for testing or measuring voltage/current without disconnecting wires. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Terminal Block GRAY in a Circuit
Prepare the Wires:
- Strip the insulation from the ends of the wires to expose approximately 5-10mm of conductor.
- Ensure the wire size matches the terminal block's specifications.
Insert the Wires:
- Loosen the screw or spring clamp on the terminal block.
- Insert the stripped end of the wire into the appropriate terminal (input or output).
Secure the Connection:
- Tighten the screw or engage the spring clamp to secure the wire.
- Ensure the connection is firm but avoid overtightening, which could damage the wire or terminal.
Mount the Terminal Block:
- Attach the terminal block to a DIN rail or panel using the provided mounting slots.
Test the Connection:
- Use a multimeter to verify continuity and ensure proper connections.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always ensure the terminal block's voltage and current ratings match your circuit requirements.
- Use ferrules on stranded wires to improve connection reliability and prevent fraying.
- Avoid overtightening screws, as this can damage the wire or terminal block.
- Ensure proper insulation and spacing between adjacent terminal blocks to prevent short circuits.
- For high-vibration environments, consider using spring clamp terminal blocks for better reliability.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
While terminal blocks are not directly connected to an Arduino UNO, they can be used to organize and secure connections between the Arduino and external components. Below is an example of using a terminal block to connect an LED to an Arduino:
// Example: Controlling an LED via a terminal block connection
// Connect the LED's positive leg to a terminal block, which is wired to pin 13 on the Arduino.
// The negative leg of the LED is connected to another terminal block, wired to GND.
int ledPin = 13; // Pin connected to the LED via the terminal block
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Loose Connections:
- Issue: Wires are not securely held in the terminal block.
- Solution: Ensure screws are tightened properly or spring clamps are fully engaged.
Overheating:
- Issue: Terminal block becomes hot during operation.
- Solution: Verify that the current does not exceed the terminal block's rating. Use a larger terminal block if necessary.
Wire Fraying:
- Issue: Stranded wires fray when inserted into the terminal block.
- Solution: Use ferrules on stranded wires to prevent fraying and improve connection quality.
Short Circuits:
- Issue: Adjacent wires or terminals cause a short circuit.
- Solution: Ensure proper insulation and spacing between wires. Use terminal blocks with barriers if needed.
Difficulty Mounting:
- Issue: Terminal block does not fit securely on the DIN rail or panel.
- Solution: Check the mounting slots and ensure compatibility with the rail or panel type.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a GRAY terminal block for high-current applications?
- A: Yes, but ensure the terminal block's current rating matches your application. For high-current circuits, choose a model rated for at least 20% more than the expected current.
Q: How do I identify the voltage rating of a GRAY terminal block?
- A: Check the manufacturer's datasheet or markings on the terminal block for voltage and current ratings.
Q: Can I use a GRAY terminal block outdoors?
- A: Only if it is rated for outdoor use. Look for IP-rated terminal blocks for protection against moisture and dust.
Q: What is the advantage of using a GRAY terminal block over other colors?
- A: The gray color may indicate a specific standard or rating, making it easier to organize and identify circuits in complex systems. Always refer to the manufacturer's documentation for details.