
How to Use MKR Connector Carrier: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with MKR Connector Carrier in Cirkit Designer
Design with MKR Connector Carrier in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The MKR Connector Carrier (Manufacturer Part ID: 28-18) is a versatile carrier board designed by Arduino to expand the connectivity and functionality of MKR series microcontrollers. It simplifies the integration of sensors, actuators, and other modules by providing a variety of Grove connectors and additional interfaces. This carrier board is ideal for rapid prototyping, IoT applications, and educational projects, enabling users to quickly connect and test components without the need for complex wiring.
Explore Projects Built with MKR Connector Carrier
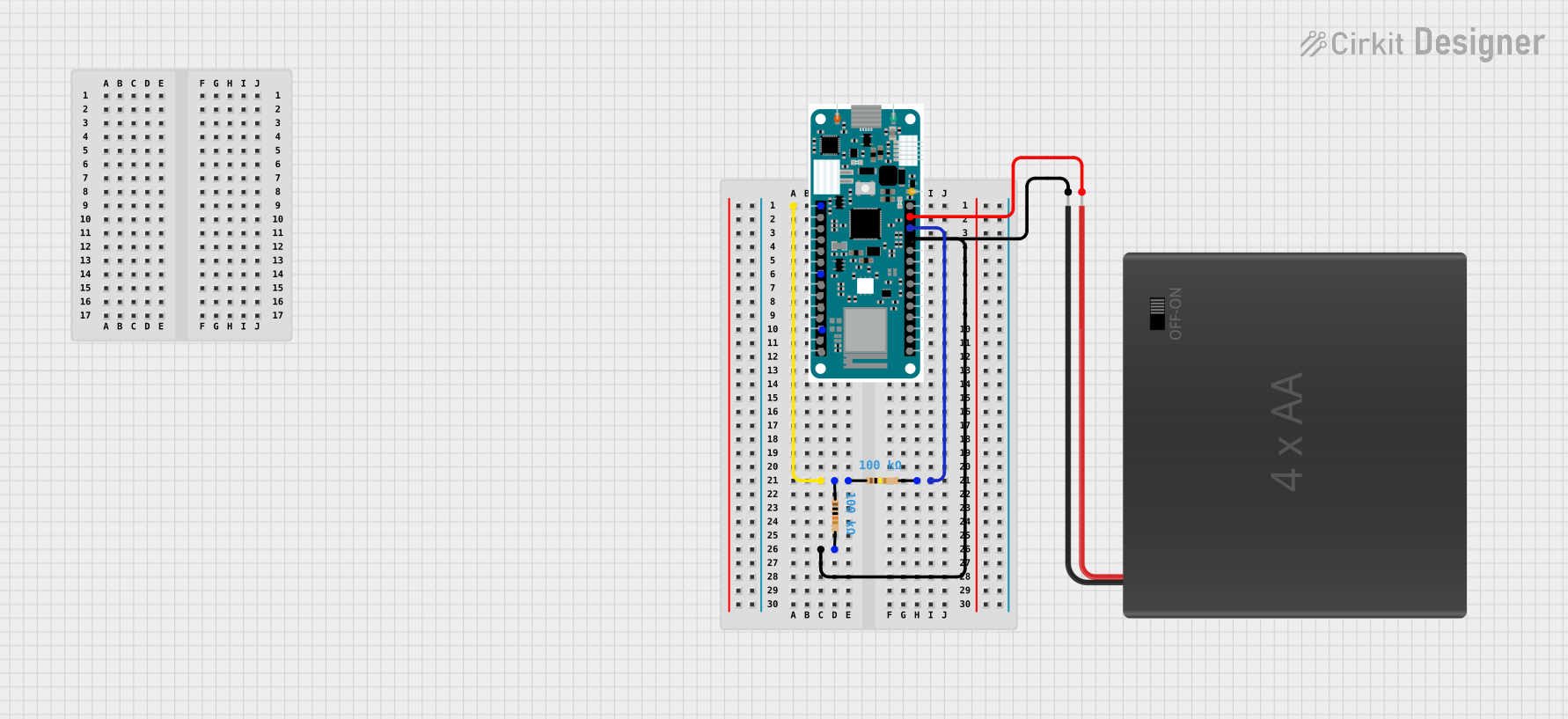
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer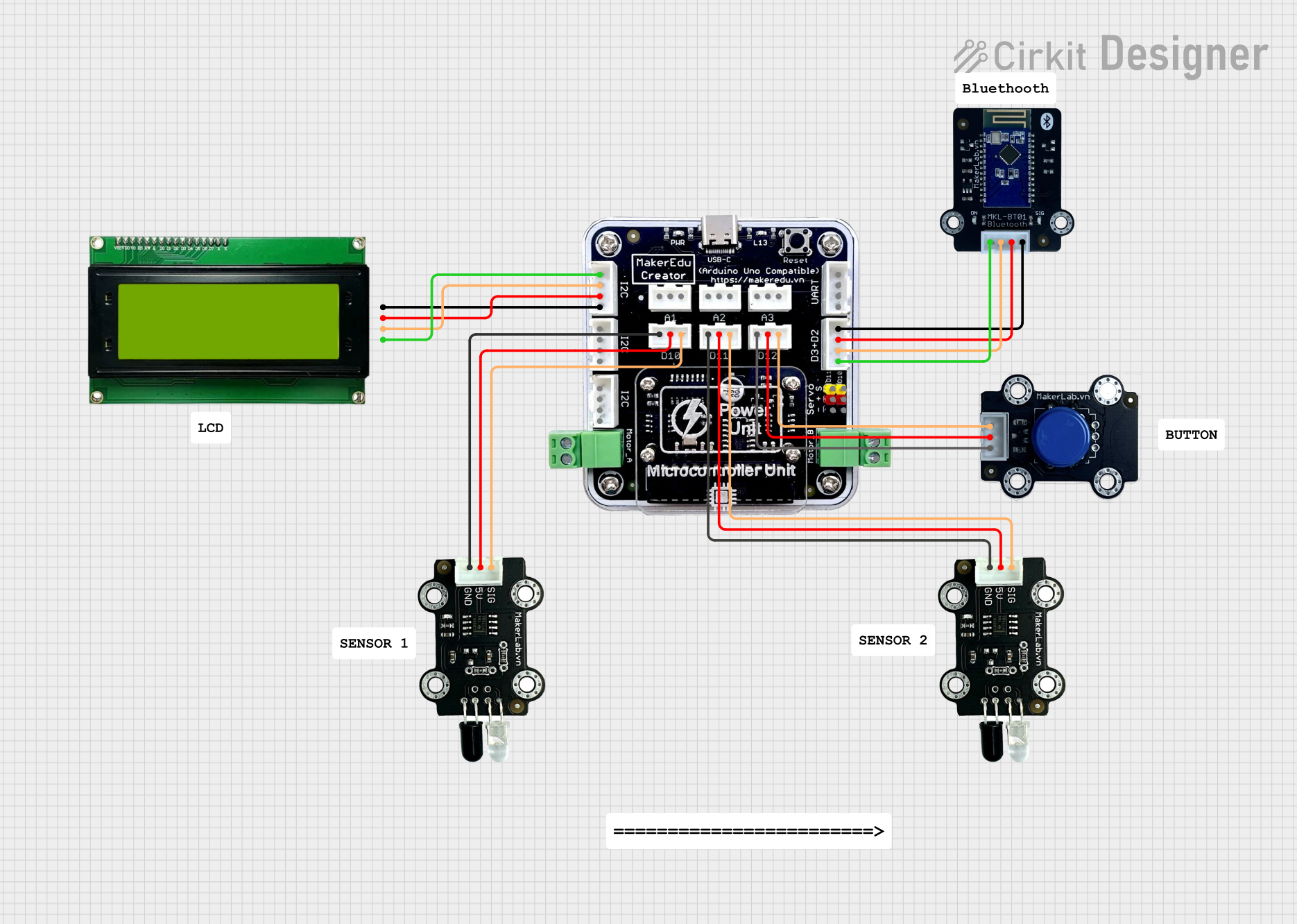
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer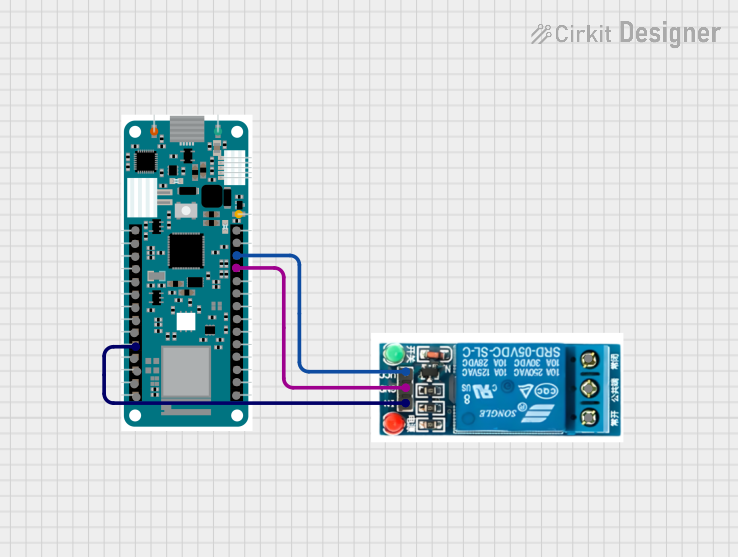
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with MKR Connector Carrier

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- IoT projects requiring multiple sensor connections
- Rapid prototyping with MKR series boards
- Educational projects for learning about sensors and actuators
- Smart home automation systems
- Environmental monitoring and data logging
Technical Specifications
The MKR Connector Carrier is designed to work seamlessly with MKR series microcontrollers, offering a range of connectivity options. Below are the key technical details:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Arduino |
| Part ID | 28-18 |
| Compatible Boards | MKR series microcontrollers |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V |
| Dimensions | 85mm x 55mm |
| Weight | 25g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The MKR Connector Carrier features multiple Grove connectors and pin headers for easy interfacing. Below is a detailed description of the available connectors:
Grove Connectors
| Connector Type | Description | Pinout (Signal) |
|---|---|---|
| Analog | For analog sensors | VCC, GND, Signal |
| Digital | For digital sensors or actuators | VCC, GND, Signal |
| I2C | For I2C-compatible devices | VCC, GND, SDA, SCL |
| UART | For serial communication modules | VCC, GND, TX, RX |
Additional Interfaces
| Interface | Description | Pinout |
|---|---|---|
| Power Input | External power supply (optional) | VIN, GND |
| MKR Header | Connects to MKR microcontroller | Matches MKR pinout |
Usage Instructions
The MKR Connector Carrier is designed for plug-and-play operation with MKR series boards. Follow the steps below to use the carrier board effectively:
Step 1: Connect the MKR Board
- Align the MKR microcontroller with the MKR header on the carrier board.
- Gently press the MKR board into place, ensuring all pins are securely connected.
Step 2: Attach Sensors or Modules
- Identify the type of sensor or module you want to connect (e.g., analog, digital, I2C, UART).
- Use the appropriate Grove connector on the carrier board to connect the sensor/module.
- Ensure the connector is firmly seated to avoid loose connections.
Step 3: Power the System
- Power the MKR board via USB or an external power supply connected to the VIN and GND pins.
- Verify that the power LED on the MKR board and carrier board is lit.
Step 4: Write and Upload Code
- Open the Arduino IDE and select the appropriate MKR board from the "Tools" menu.
- Write or load a sketch that interacts with the connected sensors or modules.
- Upload the code to the MKR board via USB.
Example Code: Reading an Analog Sensor
The following example demonstrates how to read data from an analog sensor connected to the Grove Analog connector:
// Example: Reading an analog sensor connected to the MKR Connector Carrier
const int analogPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the sensor
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
while (!Serial); // Wait for the serial monitor to open
Serial.println("Analog Sensor Reading Example");
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(analogPin); // Read the analog value
Serial.print("Sensor Value: ");
Serial.println(sensorValue); // Print the value to the serial monitor
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms before the next reading
}
Best Practices
- Always check the voltage and current requirements of connected sensors or modules to ensure compatibility.
- Use short and secure connections to minimize signal interference.
- Avoid connecting multiple high-power devices to prevent overloading the MKR board.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Power to the Carrier Board
- Ensure the MKR board is properly seated in the MKR header.
- Verify the power source (USB or external) is functioning correctly.
Sensor/Module Not Responding
- Double-check the connection type (analog, digital, I2C, UART) and use the correct Grove connector.
- Verify the sensor/module is compatible with 3.3V logic levels.
Incorrect Sensor Readings
- Ensure the sensor is properly connected and powered.
- Check for loose connections or damaged cables.
Code Upload Fails
- Confirm the correct MKR board is selected in the Arduino IDE.
- Ensure the USB cable is properly connected and functional.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the MKR Connector Carrier with non-MKR boards?
A: The carrier is specifically designed for MKR series boards. Using it with other boards may require additional adapters or modifications.
Q: What is the maximum current the carrier board can handle?
A: The carrier board is designed to handle the current limits of the MKR series boards, typically up to 500mA. Check the specific MKR board's datasheet for details.
Q: Can I connect multiple I2C devices to the carrier board?
A: Yes, the I2C Grove connector supports multiple devices as long as each device has a unique I2C address.
Q: Is the carrier board compatible with 5V sensors?
A: No, the carrier board operates at 3.3V. Using 5V sensors may damage the board or connected MKR microcontroller.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the MKR Connector Carrier to expand the capabilities of your MKR series microcontroller projects.