
How to Use ACS712: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with ACS712 in Cirkit Designer
Design with ACS712 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ACS712 Hall Effect Current Sensor, manufactured by Allegro MicroSystems, is a linear current sensor designed to measure both AC and DC currents. It utilizes the Hall effect principle to provide an analog voltage output proportional to the current flowing through the sensor. The ACS712 is widely used in applications requiring current monitoring, such as motor control, power management, overcurrent protection, and energy metering. Its compact design, high accuracy, and electrical isolation make it a versatile choice for a variety of projects.
Explore Projects Built with ACS712
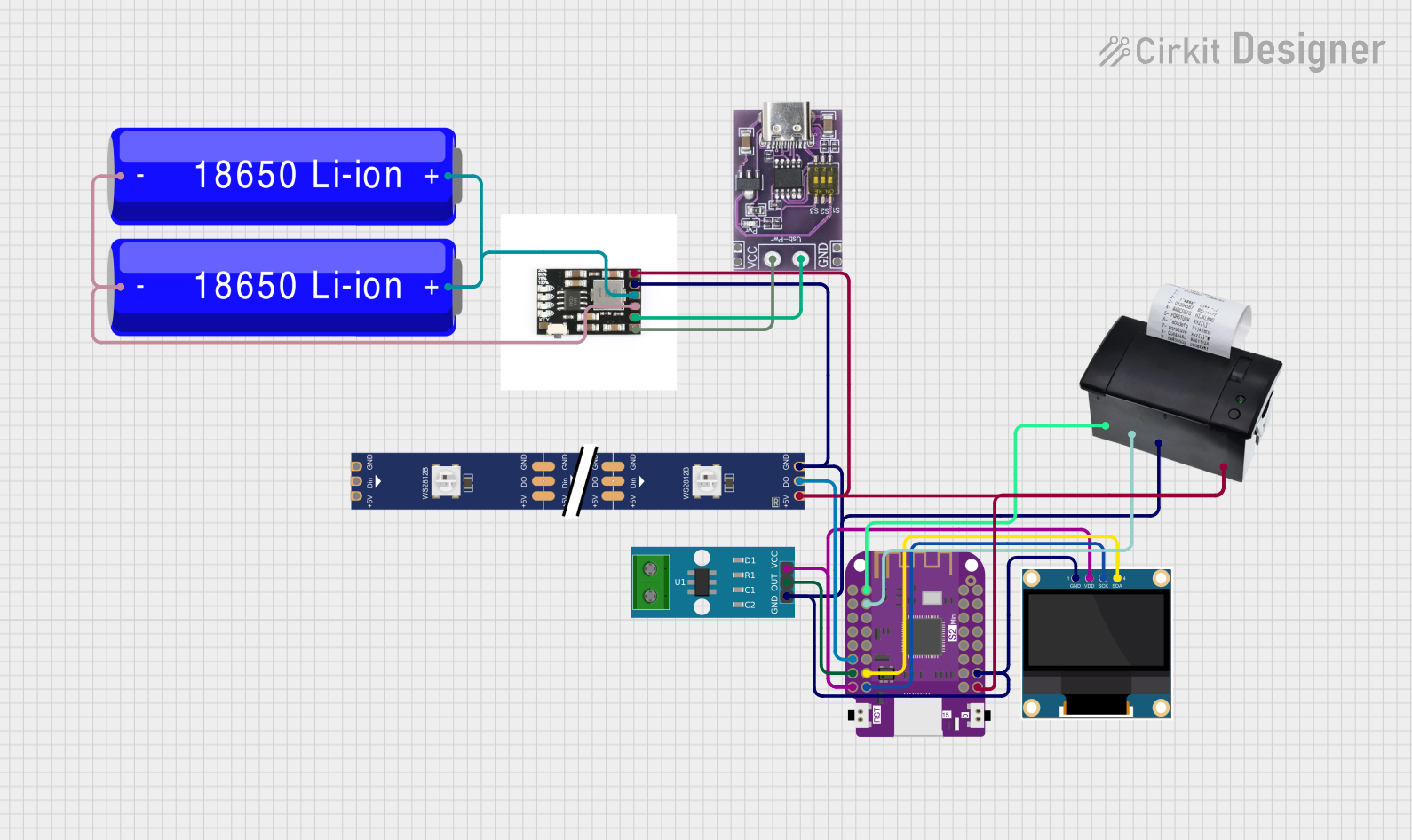
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer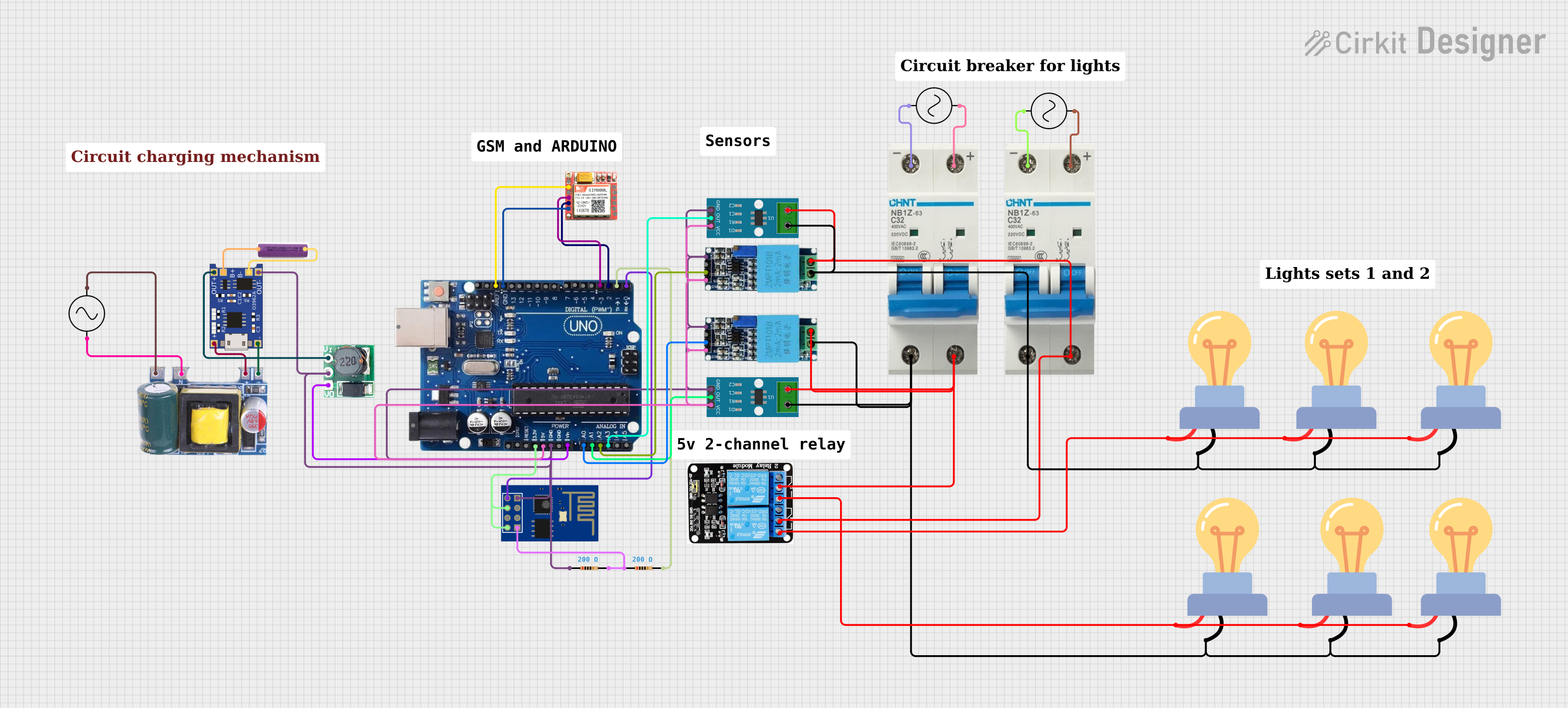
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer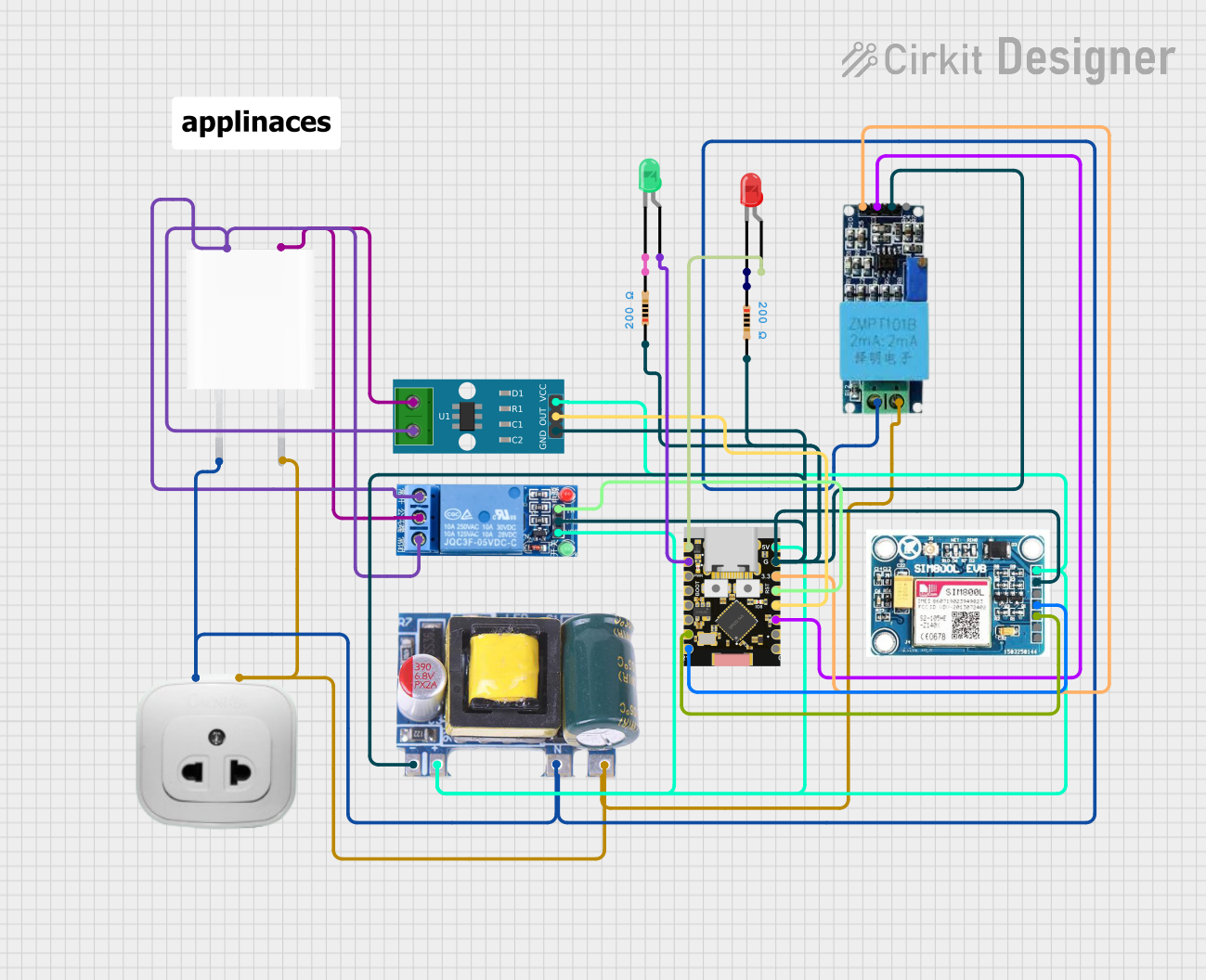
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer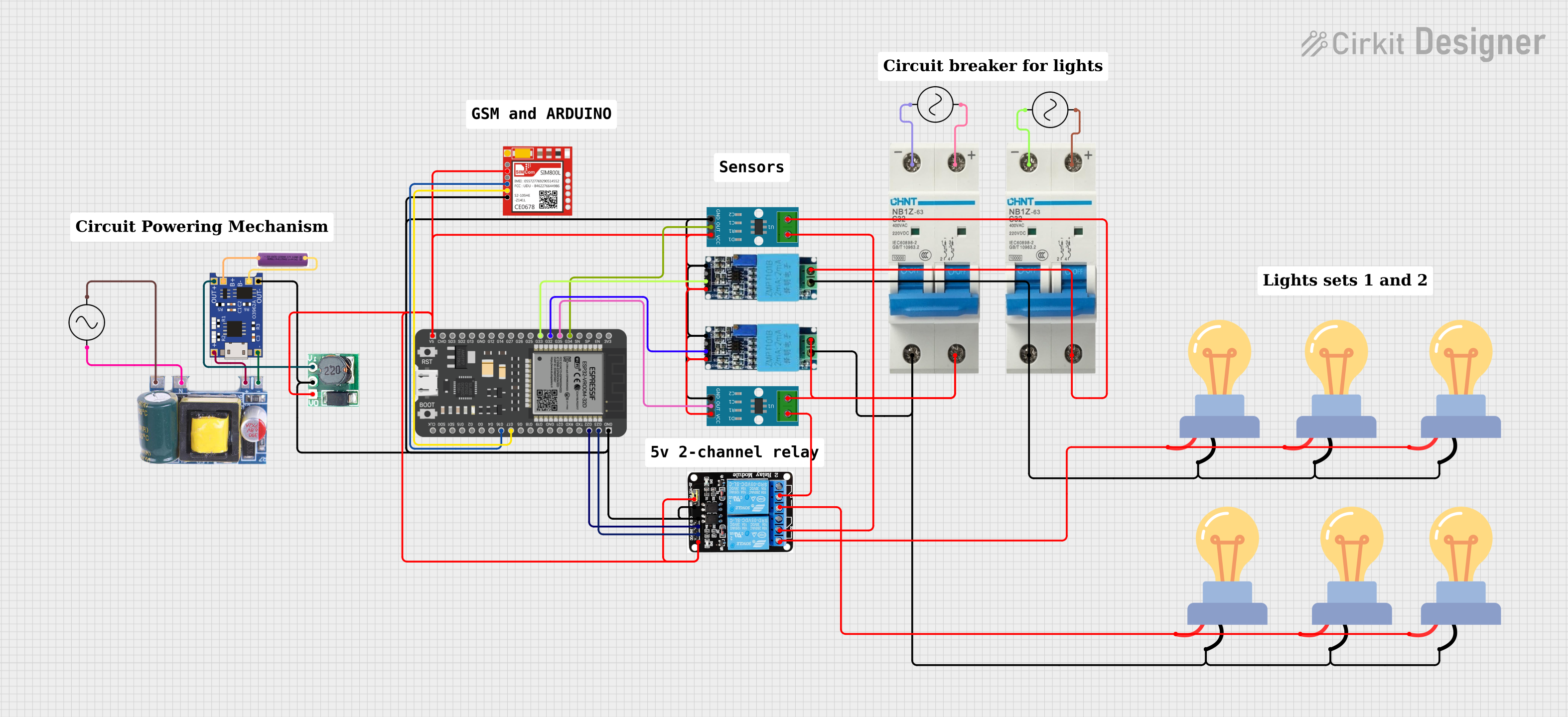
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ACS712

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
The following are the key technical details of the ACS712 Hall Effect Current Sensor:
- Manufacturer Part ID: ACS712
- Supply Voltage (Vcc): 4.5V to 5.5V
- Current Measurement Range:
- ACS712-05B: ±5A
- ACS712-20A: ±20A
- ACS712-30A: ±30A
- Sensitivity:
- ACS712-05B: 185 mV/A
- ACS712-20A: 100 mV/A
- ACS712-30A: 66 mV/A
- Output Voltage: Analog, centered at Vcc/2 (2.5V for 5V supply)
- Bandwidth: 80 kHz
- Response Time: 5 µs
- Isolation Voltage: 2.1 kV RMS
- Operating Temperature Range: -40°C to 85°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ACS712 is typically available in an 8-pin SOIC package. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | IP+ | Positive current input terminal (connect to the load or current source). |
| 2 | IP- | Negative current input terminal (connect to the return path of the load). |
| 3 | NC | Not connected (leave unconnected). |
| 4 | GND | Ground (connect to the system ground). |
| 5 | VIOUT | Analog output voltage proportional to the measured current. |
| 6 | NC | Not connected (leave unconnected). |
| 7 | Vcc | Supply voltage (4.5V to 5.5V, typically 5V). |
| 8 | NC | Not connected (leave unconnected). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the ACS712 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the Vcc pin to a 5V power supply and the GND pin to the system ground.
- Current Path: Connect the current-carrying conductor to the IP+ and IP- pins. Ensure the current flows in the correct direction as indicated on the sensor.
- Output Signal: The VIOUT pin provides an analog voltage proportional to the current. At 0A, the output voltage is approximately 2.5V (for a 5V supply). The voltage increases or decreases linearly with the current.
- Load Resistor: If required, connect a pull-down resistor to stabilize the output signal.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Isolation: The ACS712 provides electrical isolation between the current-carrying conductor and the output signal, making it safe for high-voltage applications.
- Filtering: To reduce noise, connect a capacitor (e.g., 0.1 µF) between the VIOUT pin and GND.
- Calibration: For accurate measurements, calibrate the sensor by measuring the output voltage at 0A and adjusting for any offset.
- Current Range: Choose the appropriate ACS712 variant (05B, 20A, or 30A) based on the maximum current in your application.
- Heat Dissipation: Avoid exceeding the maximum current rating to prevent overheating.
Example: Using ACS712 with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to interface the ACS712 with an Arduino UNO to measure current:
// Include necessary libraries (if any)
// Define the analog pin connected to the ACS712 VIOUT pin
const int sensorPin = A0;
// Define the sensitivity of the ACS712 (e.g., 185 mV/A for ACS712-05B)
const float sensitivity = 0.185; // Sensitivity in V/A
// Define the supply voltage (Vcc) and the zero-current voltage (Vcc/2)
const float Vcc = 5.0; // Supply voltage in volts
const float zeroCurrentVoltage = Vcc / 2; // Zero-current output voltage
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the sensor
int sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
// Convert the analog value to voltage
float sensorVoltage = (sensorValue / 1023.0) * Vcc;
// Calculate the current in amperes
float current = (sensorVoltage - zeroCurrentVoltage) / sensitivity;
// Print the current to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Current: ");
Serial.print(current);
Serial.println(" A");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output or Incorrect Readings:
- Ensure the Vcc and GND pins are properly connected to a 5V power supply and ground.
- Verify that the current-carrying conductor is connected to the IP+ and IP- pins.
High Noise in Output Signal:
- Add a capacitor (e.g., 0.1 µF) between the VIOUT pin and GND to filter out noise.
- Use shielded cables for the current-carrying conductor to reduce electromagnetic interference.
Output Voltage Does Not Return to 2.5V at 0A:
- Calibrate the sensor by measuring the output voltage at 0A and adjusting for any offset in your calculations.
Overheating:
- Ensure the current flowing through the sensor does not exceed its maximum rating.
- Use proper heat dissipation techniques if the sensor is operating near its maximum current limit.
FAQs
Q1: Can the ACS712 measure both AC and DC currents?
A1: Yes, the ACS712 can measure both AC and DC currents. The output voltage varies linearly with the current in both cases.
Q2: How do I choose the right ACS712 variant for my application?
A2: Select the variant based on the maximum current you need to measure:
- ACS712-05B: ±5A
- ACS712-20A: ±20A
- ACS712-30A: ±30A
Q3: What is the accuracy of the ACS712?
A3: The ACS712 has a typical accuracy of ±1.5% at 25°C. However, accuracy may vary with temperature and other factors.
Q4: Can I use the ACS712 with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A4: Yes, but you need to ensure the output voltage range of the ACS712 is compatible with the ADC input range of your microcontroller.