
How to Use Alternative Current (AC): Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Alternative Current (AC) in Cirkit Designer
Design with Alternative Current (AC) in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
Alternative Current (AC) is a type of electrical current in which the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction. Unlike Direct Current (DC), where the electric charge flows in a single direction, AC is characterized by its oscillating nature. This makes it highly efficient for transmitting power over long distances, which is why it is commonly used in power supplies and household electrical outlets.
Explore Projects Built with Alternative Current (AC)
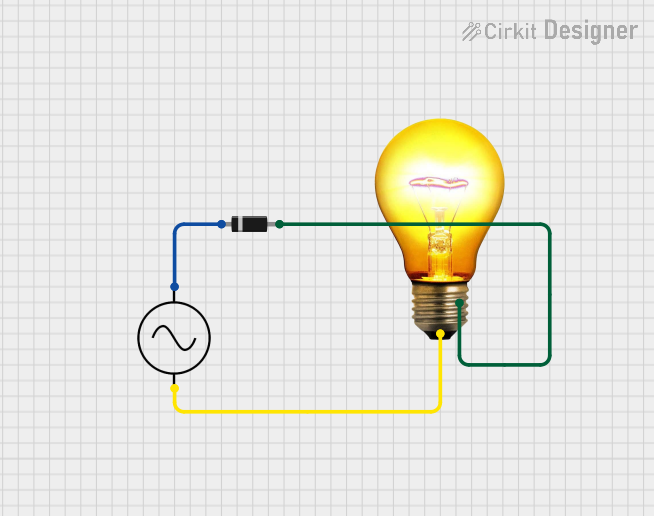
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer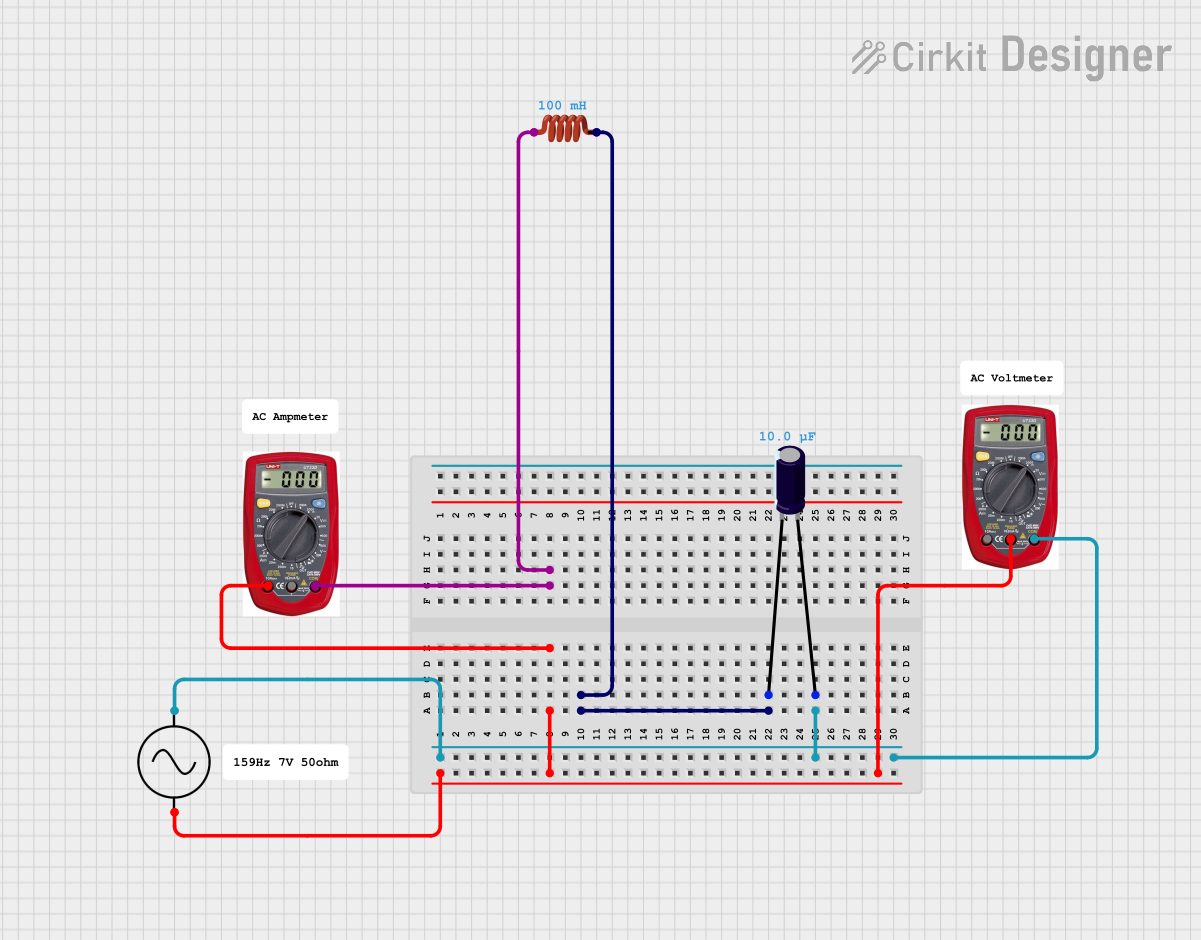
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer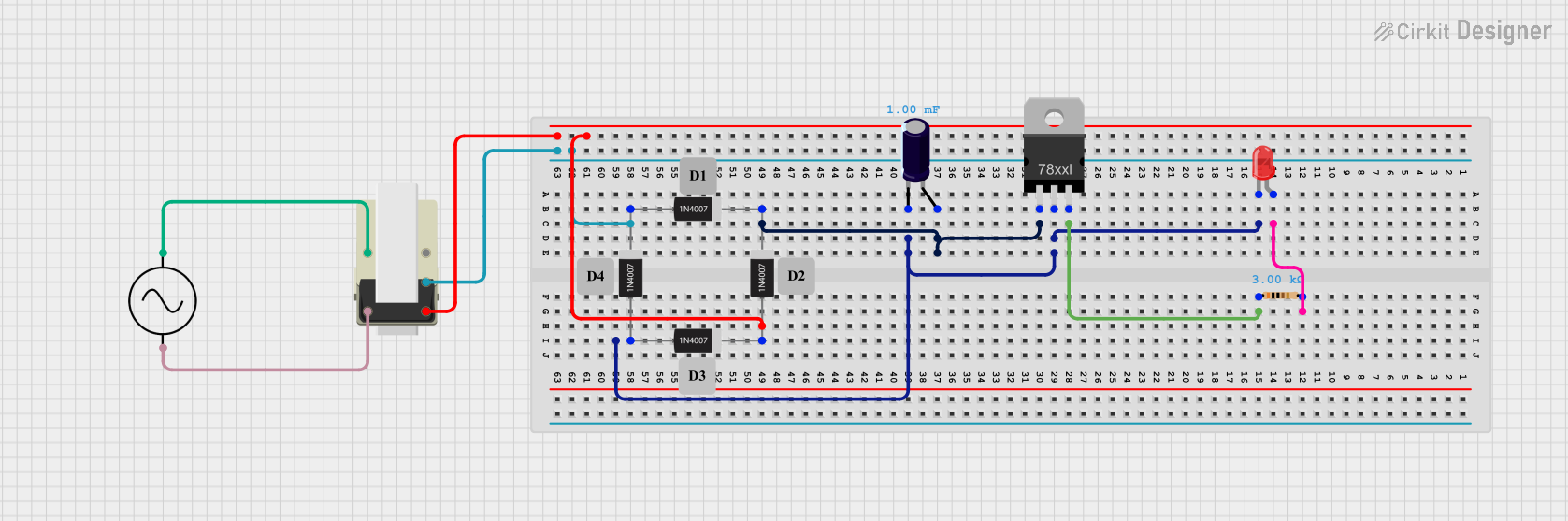
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer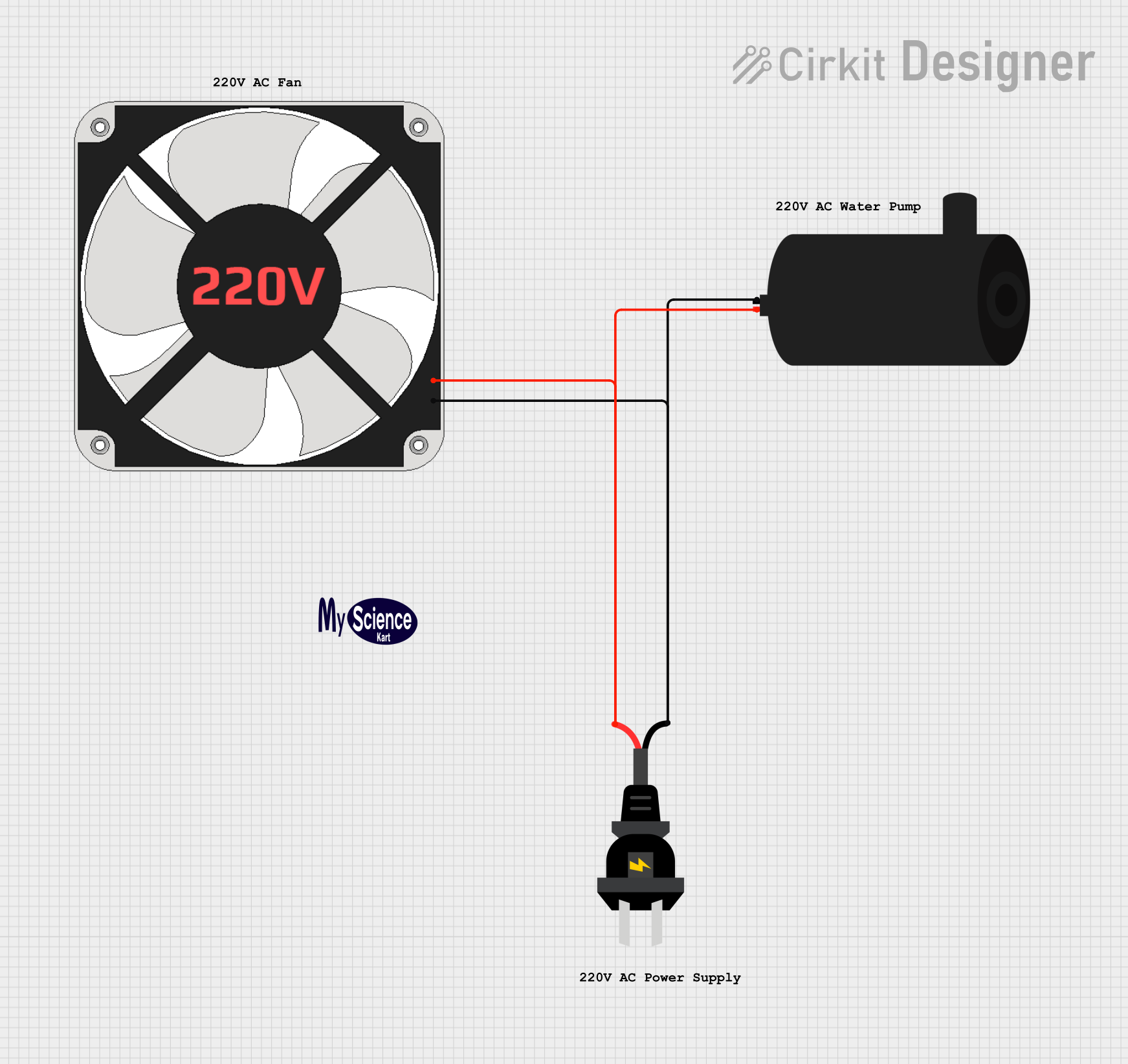
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Alternative Current (AC)

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Household Electrical Outlets: AC is the standard form of electricity supplied to homes and businesses.
- Power Supplies: AC is used to power various electronic devices and appliances.
- Transformers: AC is essential for the operation of transformers, which are used to step up or step down voltage levels.
- Motors: Many types of electric motors operate on AC, including those used in household appliances and industrial machinery.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Voltage Range | 110V - 240V |
| Frequency | 50Hz or 60Hz |
| Phase | Single-phase or Three-phase |
| Power Rating | Varies based on application |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Since AC is typically delivered through power outlets and not through pins like other electronic components, the following table describes the standard wiring configuration for a typical household AC outlet.
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Live (L) | Carries the current to the load |
| Neutral (N) | Returns the current to the source |
| Ground (G) | Safety ground to prevent electric shock |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Safety First: Always ensure that the power is turned off before working with AC circuits to avoid electric shock.
- Wiring: Connect the Live (L) wire to the load (e.g., an appliance or device). Connect the Neutral (N) wire to the return path. The Ground (G) wire should be connected to a grounding point for safety.
- Power On: Once all connections are securely made, you can turn on the power supply.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Insulation: Use proper insulation for all wires to prevent short circuits and electric shocks.
- Grounding: Always ensure that the ground wire is properly connected to avoid potential hazards.
- Voltage Rating: Make sure that the devices connected to the AC supply are rated for the voltage being supplied.
- Circuit Breakers: Use circuit breakers to protect against overcurrent conditions.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
No Power to Device:
- Solution: Check if the power supply is turned on and if the circuit breaker is not tripped. Verify all connections.
Electric Shock:
- Solution: Ensure that the ground wire is properly connected and that all wires are insulated. Always turn off the power before working on the circuit.
Overheating:
- Solution: Check if the device is drawing more current than it is rated for. Use a device with a proper power rating.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use AC for all electronic devices?
- A1: No, some electronic devices require DC power. Use an AC to DC converter if needed.
Q2: What is the difference between single-phase and three-phase AC?
- A2: Single-phase AC has one alternating voltage cycle, while three-phase AC has three cycles, each 120 degrees out of phase with the others. Three-phase is more efficient for heavy loads.
Q3: How do I measure AC voltage?
- A3: Use a multimeter set to the AC voltage mode to measure the voltage across the Live (L) and Neutral (N) terminals.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
While AC is not directly used with microcontrollers like the Arduino UNO, you can use an AC voltage sensor to measure AC voltage. Below is an example code to read AC voltage using an AC voltage sensor.
// Example code to read AC voltage using an AC voltage sensor with Arduino UNO
const int sensorPin = A0; // Pin connected to the sensor output
float voltage = 0.0; // Variable to store the voltage value
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin); // Read the sensor value
voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0); // Convert the sensor value to voltage
// Print the voltage value to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("AC Voltage: ");
Serial.print(voltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
This code reads the output from an AC voltage sensor connected to the Arduino UNO and prints the measured voltage to the Serial Monitor. Note that this is a simplified example and actual implementation may require additional components and safety measures.
This documentation provides a comprehensive overview of Alternative Current (AC), including its technical specifications, usage instructions, troubleshooting tips, and an example code for interfacing with an Arduino UNO. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced user, this guide aims to help you understand and effectively use AC in your projects.