
How to Use XY-MD02: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with XY-MD02 in Cirkit Designer
Design with XY-MD02 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The XY-MD02 is a wireless Bluetooth module designed for seamless communication between devices. It supports serial communication (UART) and operates using the Bluetooth 4.0 protocol, making it ideal for low-power and high-speed data transmission. This module is widely used in IoT applications, enabling microcontrollers to connect to smartphones, tablets, or other Bluetooth-enabled devices. Its compact size and ease of integration make it a popular choice for hobbyists and professionals alike.
Explore Projects Built with XY-MD02

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer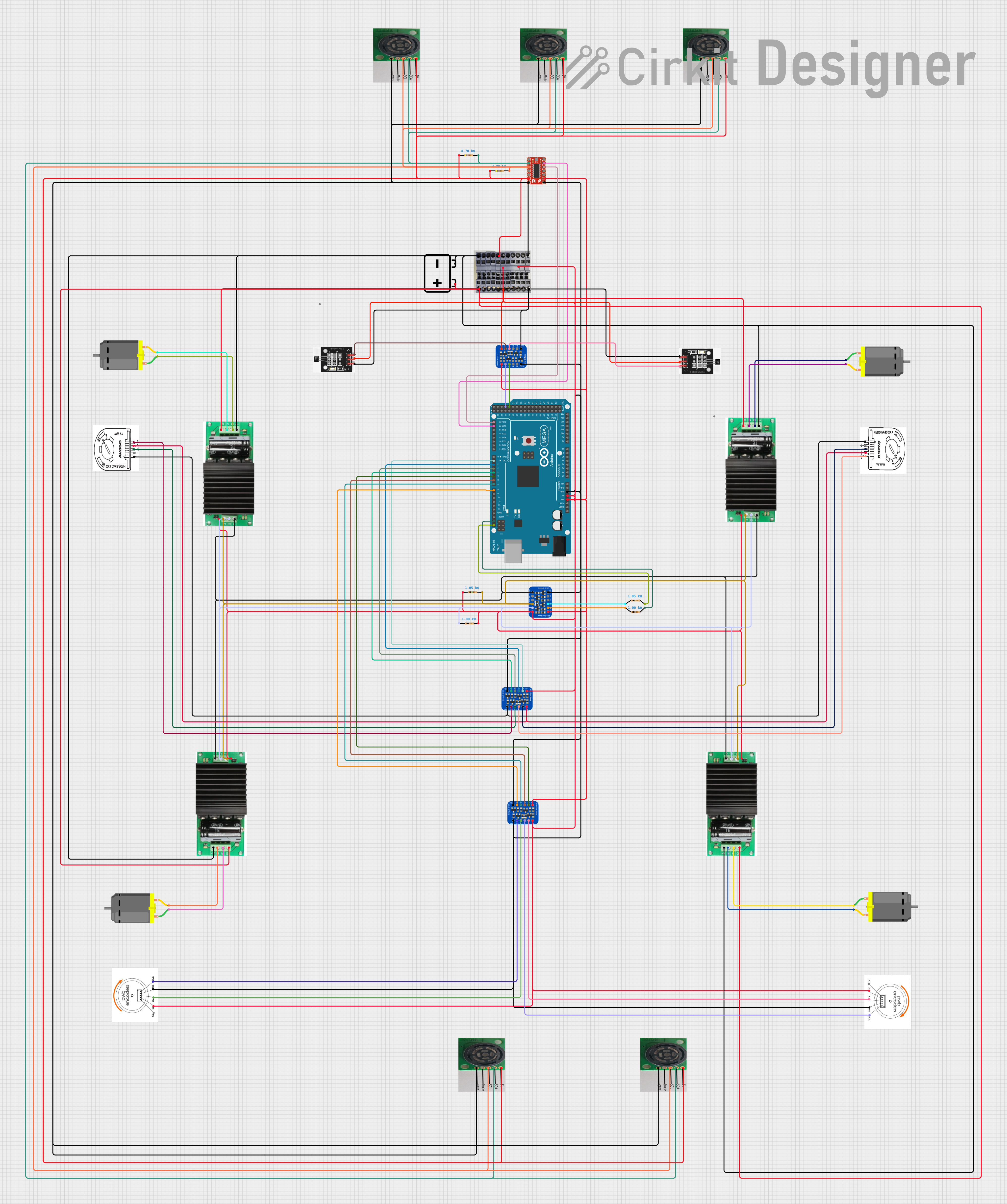
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer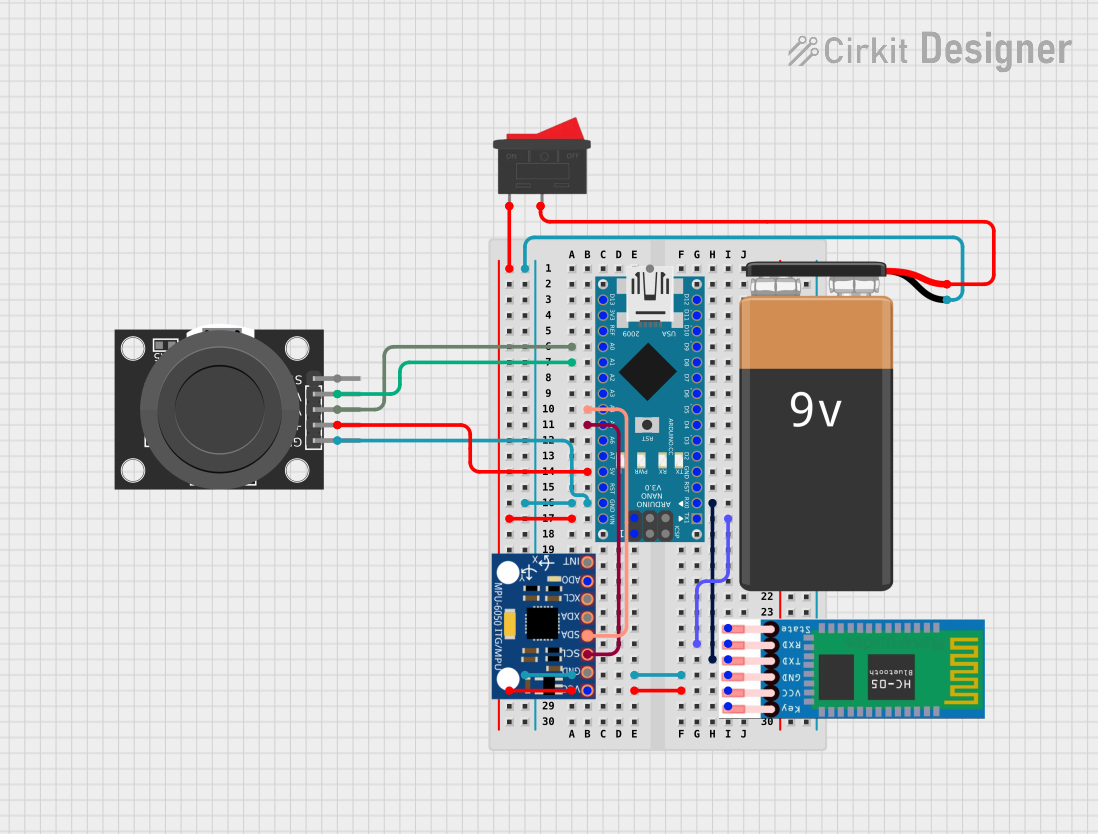
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer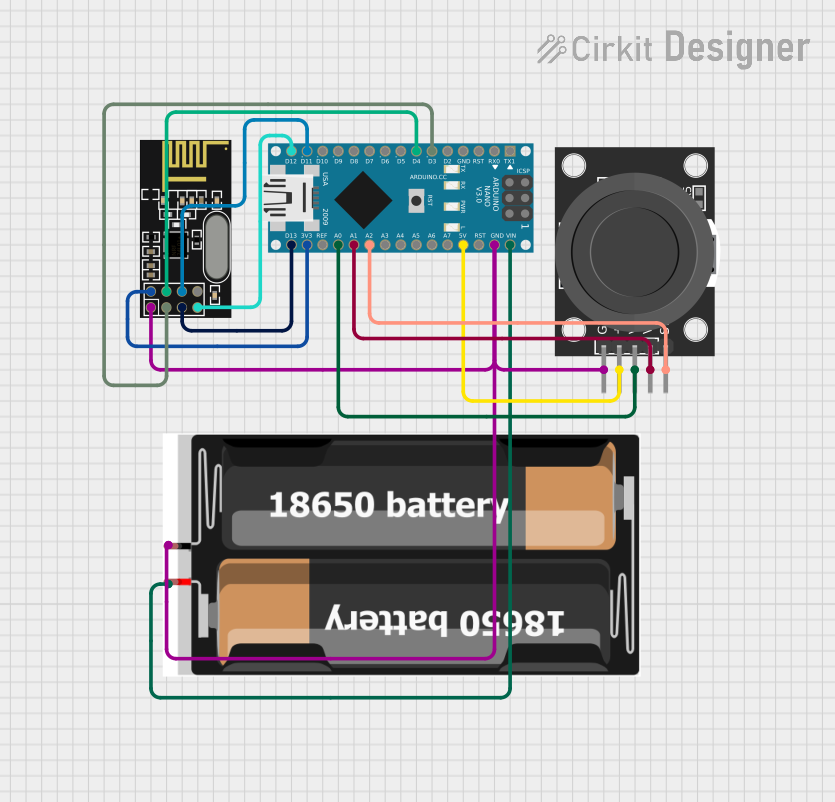
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with XY-MD02

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Wireless data transmission between microcontrollers and smartphones
- IoT devices and smart home automation
- Remote control systems
- Wireless sensor networks
- Robotics and industrial automation
Technical Specifications
The XY-MD02 module is designed to provide reliable and efficient Bluetooth communication. Below are its key technical specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Bluetooth Version | 4.0 (Low Energy) |
| Communication Protocol | UART (Serial Communication) |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 6V |
| Operating Current | 8mA (typical) |
| Baud Rate | 9600 bps (default, configurable) |
| Transmission Range | Up to 10 meters (line of sight) |
| Dimensions | 37mm x 15mm x 7mm |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to 70°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The XY-MD02 module has 6 pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (3.3V to 6V). Connect to the power source. |
| 2 | GND | Ground. Connect to the ground of the circuit. |
| 3 | TXD | Transmit data pin. Sends serial data to the connected microcontroller. |
| 4 | RXD | Receive data pin. Receives serial data from the connected microcontroller. |
| 5 | EN (Key) | Enable pin. Used to switch between command and data modes. |
| 6 | STATE | Status indicator pin. High when connected to a device, low when disconnected. |
Usage Instructions
The XY-MD02 module is straightforward to use and can be easily integrated into a circuit. Below are the steps and best practices for using the module:
Connecting the XY-MD02 to a Microcontroller
- Power Supply: Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5V power source and theGNDpin to the ground. - Serial Communication:
- Connect the
TXDpin of the module to theRXpin of the microcontroller. - Connect the
RXDpin of the module to theTXpin of the microcontroller.
- Connect the
- Enable Pin: Leave the
ENpin unconnected for normal operation. Pull it high to enter AT command mode. - Status Pin: Optionally, connect the
STATEpin to an LED or microcontroller input to monitor the connection status.
Example: Using XY-MD02 with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the XY-MD02 module with an Arduino UNO to send and receive data via Bluetooth.
Circuit Diagram
- Connect
VCCto the 5V pin on the Arduino. - Connect
GNDto the GND pin on the Arduino. - Connect
TXDto pin 10 on the Arduino (software serial RX). - Connect
RXDto pin 11 on the Arduino (software serial TX).
Arduino Code
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define software serial pins for the XY-MD02 module
SoftwareSerial bluetooth(10, 11); // RX, TX
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
// Initialize Bluetooth module communication
bluetooth.begin(9600); // Default baud rate for XY-MD02
Serial.println("Bluetooth module ready. Waiting for connection...");
}
void loop() {
// Check if data is available from the Bluetooth module
if (bluetooth.available()) {
char received = bluetooth.read(); // Read the incoming data
Serial.print("Received: ");
Serial.println(received); // Print the received data to the serial monitor
}
// Check if data is available from the serial monitor
if (Serial.available()) {
char toSend = Serial.read(); // Read the data from the serial monitor
bluetooth.write(toSend); // Send the data to the Bluetooth module
Serial.print("Sent: ");
Serial.println(toSend); // Print the sent data to the serial monitor
}
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: Ensure the module operates within its voltage range (3.3V to 6V). If using a 3.3V microcontroller, use a level shifter for the
TXDandRXDpins. - Baud Rate: The default baud rate is 9600 bps. Use AT commands to change it if needed.
- Command Mode: Pull the
ENpin high to enter AT command mode for configuration. Use a serial terminal to send AT commands. - Antenna Placement: Avoid placing the module near metal objects or other RF sources to ensure optimal signal strength.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Module Not Responding
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or power supply.
- Solution: Double-check the connections and ensure the module is powered correctly.
No Data Transmission
- Cause: Baud rate mismatch between the module and microcontroller.
- Solution: Verify the baud rate settings and adjust if necessary using AT commands.
Unstable Connection
- Cause: Interference or poor signal strength.
- Solution: Ensure the module is within the specified range and away from interference sources.
Cannot Enter AT Command Mode
- Cause:
ENpin not pulled high. - Solution: Pull the
ENpin high and reset the module to enter command mode.
- Cause:
FAQs
Q1: Can the XY-MD02 module be used with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A1: Yes, the module supports 3.3V operation. However, ensure proper voltage level shifting for the TXD and RXD pins if needed.
Q2: How do I reset the module to factory settings?
A2: Enter AT command mode and send the AT+RESET command to reset the module.
Q3: What is the maximum data rate supported by the module?
A3: The module supports a maximum baud rate of 115200 bps, configurable via AT commands.
Q4: Can I use the module for audio transmission?
A4: No, the XY-MD02 is designed for data transmission only and does not support audio profiles.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate and use the XY-MD02 Bluetooth module in your projects.