
How to Use DIP - 14 pins: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with DIP - 14 pins in Cirkit Designer
Design with DIP - 14 pins in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The DIP-14 (Dual In-line Package with 14 pins) is a widely used packaging for integrated circuits (ICs). This package features two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins, with seven pins on each side. The DIP-14 package is designed for through-hole mounting on printed circuit boards (PCBs) and is commonly used in a variety of electronic devices due to its ease of handling and soldering.
Explore Projects Built with DIP - 14 pins
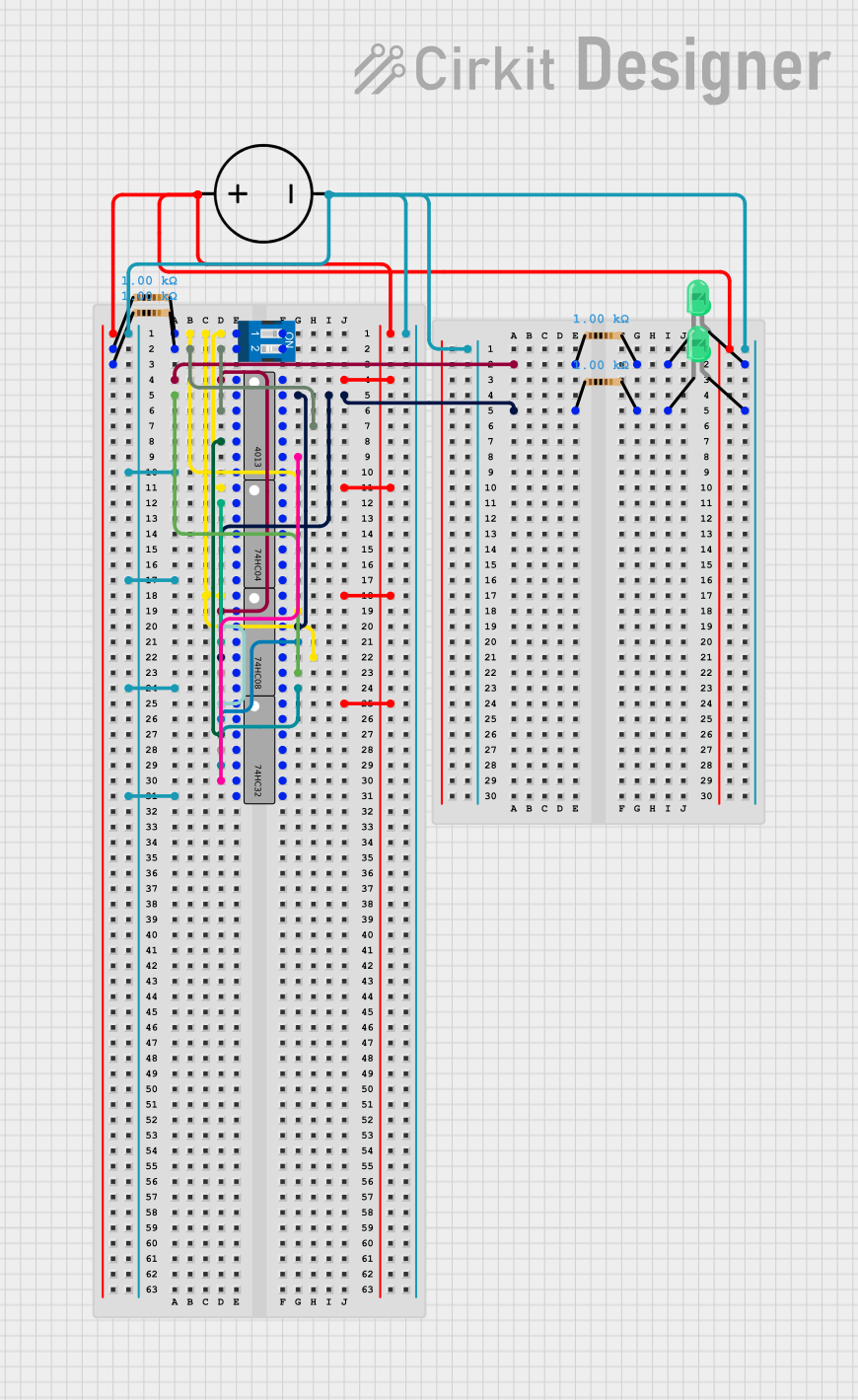
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer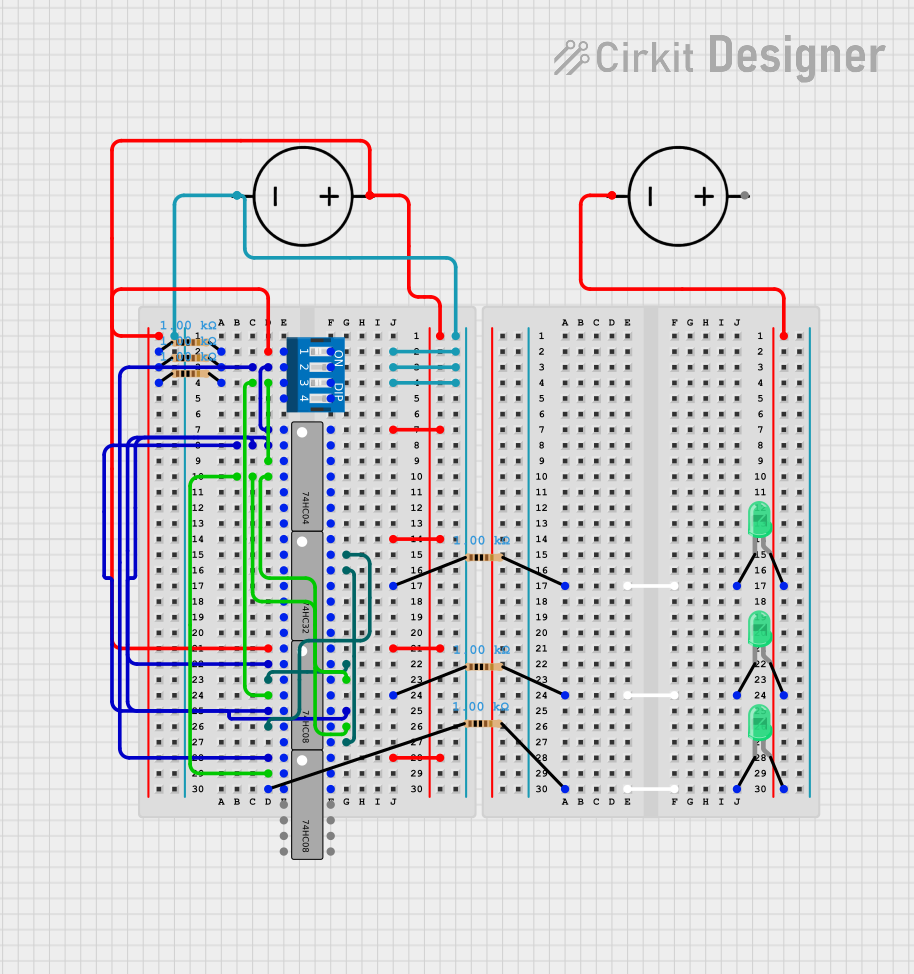
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer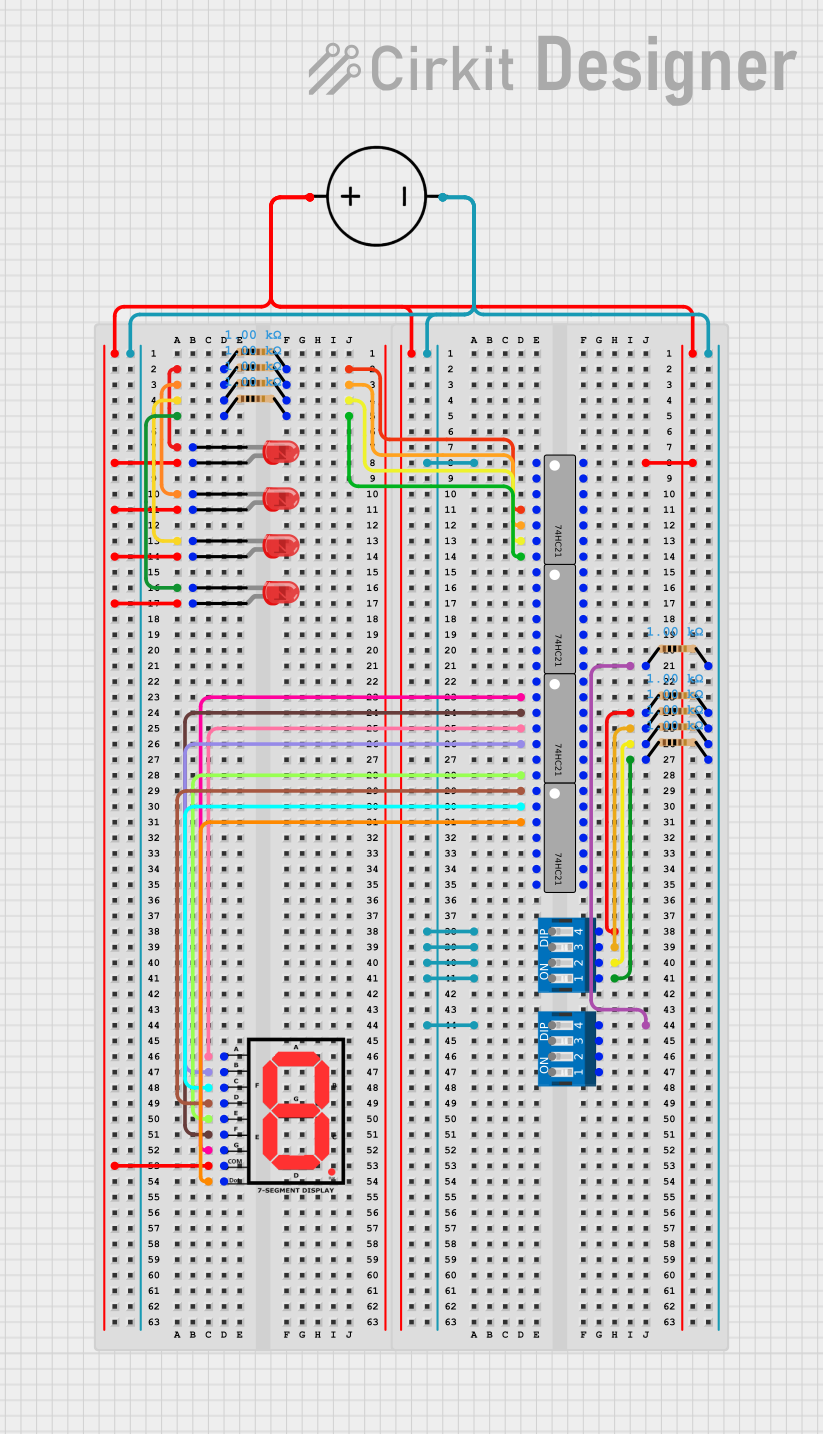
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer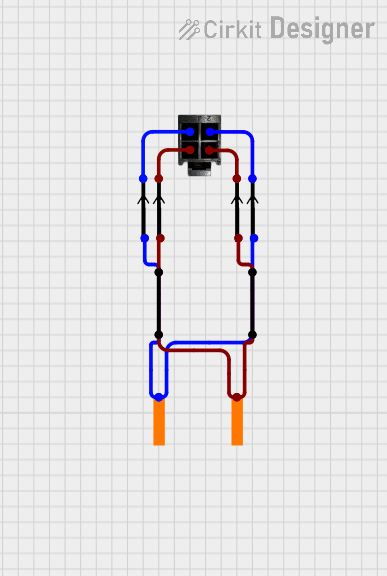
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with DIP - 14 pins

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Digital and analog circuits
- Timers and oscillators
- Logic gates and flip-flops
- Operational amplifiers
- Voltage regulators
- Audio processors
- Microcontrollers
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Package Type: Dual In-line Package (DIP)
- Number of Pins: 14
- Pin Pitch: 0.1 inches (2.54 mm)
- Body Width: 0.3 inches (7.62 mm)
- Mounting Type: Through-hole
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Function A Input/Output |
| 2 | Function B Input/Output |
| 3 | Function C Input/Output |
| 4 | Function D Input/Output |
| 5 | Function E Input/Output |
| 6 | Function F Input/Output |
| 7 | Ground (GND) |
| 8 | Function G Input/Output |
| 9 | Function H Input/Output |
| 10 | Function I Input/Output |
| 11 | Function J Input/Output |
| 12 | Function K Input/Output |
| 13 | Function L Input/Output |
| 14 | Positive Supply Voltage (Vcc) |
Note: The actual function of each pin depends on the specific IC housed in the DIP-14 package.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Identify the IC: Determine the specific IC and its function that is housed in the DIP-14 package.
- Check Orientation: Identify the notch or dot on the IC to ensure correct orientation in the circuit.
- Insertion: Carefully insert the IC into the PCB, aligning the pins with the corresponding through-hole pads.
- Soldering: Solder each pin to the PCB, ensuring good electrical contact and avoiding solder bridges between adjacent pins.
- Connection: Connect other components to the IC as per the circuit diagram, respecting the pin functions and electrical characteristics.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Static Discharge: Handle the IC with care to prevent damage from electrostatic discharge (ESD).
- Heat Sensitivity: Avoid prolonged exposure to heat when soldering to prevent damage to the IC.
- Power Supply: Ensure that the power supply voltage matches the IC's requirements.
- Decoupling Capacitors: Place a decoupling capacitor close to the Vcc pin to stabilize the power supply.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- IC Not Functioning: Ensure that the IC is correctly oriented and that all pins are properly soldered.
- Unexpected Behavior: Double-check the connections and the power supply voltage.
- Overheating: Verify that the current draw is within the IC's specified limits.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Visual Inspection: Look for cold solder joints, solder bridges, and correct pin connections.
- Multimeter Checks: Use a multimeter to check for continuity and correct voltage levels at the pins.
- Replacement: If the IC is suspected to be faulty, replace it with a new one, taking care to avoid damage during installation.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a socket for the DIP-14 IC? A: Yes, using a socket allows for easy replacement and prevents heat damage during soldering.
Q: What is the typical power supply voltage for DIP-14 ICs? A: It varies depending on the IC. Common voltages are 5V, 3.3V, or as specified by the manufacturer.
Q: How can I prevent damage to the IC from static electricity? A: Use an ESD wrist strap or mat, and handle the IC by the edges.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
If the DIP-14 component is a microcontroller or other device that can interface with an Arduino UNO, the following is an example code snippet for initializing communication:
// Example initialization code for a DIP-14 IC connected to an Arduino UNO
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication if the IC requires it
Serial.begin(9600);
// Set up the pin modes for the IC's digital pins
pinMode(2, OUTPUT); // Assuming pin 2 of the Arduino is connected to a relevant pin on the IC
pinMode(3, INPUT); // Assuming pin 3 of the Arduino is connected to another relevant pin on the IC
}
void loop() {
// Example logic for interacting with the IC
digitalWrite(2, HIGH); // Send a signal to the IC
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(2, LOW); // Turn off the signal
delay(1000); // Wait for another second
// Read a value from the IC
int sensorValue = digitalRead(3);
// Process the value read from the IC
}
Note: The actual code will vary based on the specific IC and its function within the DIP-14 package.