
Cirkit Designer
Your all-in-one circuit design IDE
Home /
Component Documentation
How to Use vcc: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with vcc in Cirkit Designer
Design with vcc in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
- Vcc is the voltage supply reference point in a circuit, typically representing the positive supply voltage. It is a crucial concept in electronics, as it provides the necessary power for active components like transistors, integrated circuits (ICs), and microcontrollers to operate.
- Common applications include powering digital and analog circuits, serving as a reference voltage for logic levels, and acting as the primary supply voltage in microcontroller-based systems.
Explore Projects Built with vcc
High Voltage Generator with Push Switch Activation
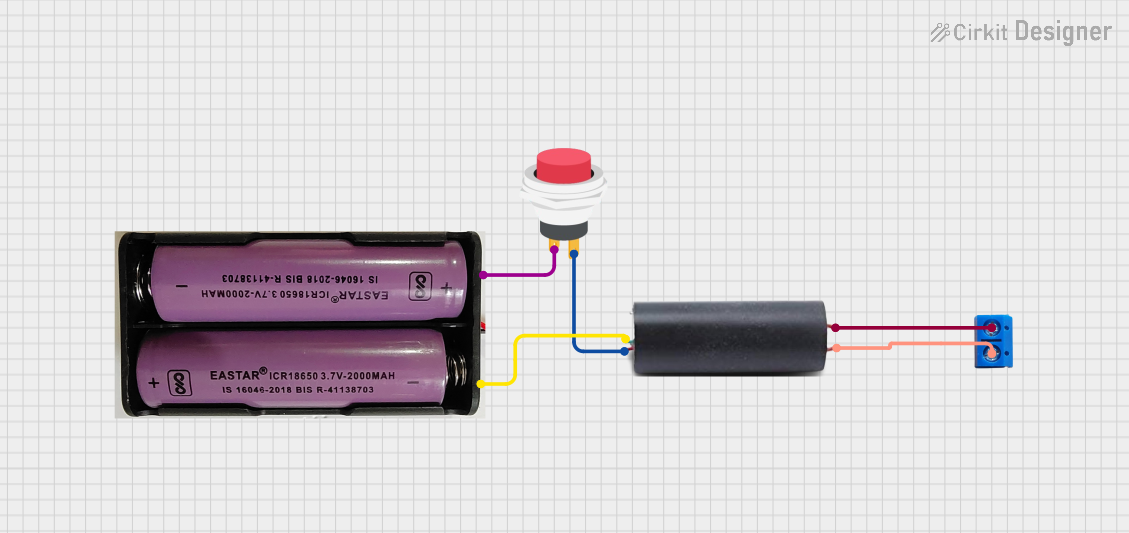
This circuit features a high voltage generator connected to a terminal PCB for output, with its power supply controlled by a 2-pin push switch. The high voltage generator's VCC is connected through the switch, allowing the user to turn the high voltage output on and off. The circuit is powered by a 7.4V battery, with the positive terminal connected to the switch and the negative terminal connected to the generator's ground.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerSolar Panel to 12V Battery Charging Circuit
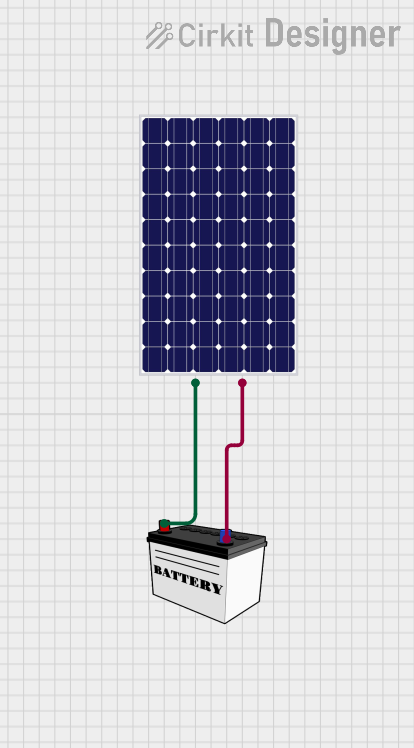
This circuit connects a solar panel to a 12V battery for charging purposes. The positive terminal of the solar panel is connected to the VCC of the battery, and the negative terminal is connected to the GND of the battery, allowing for energy transfer from the solar panel to the battery.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCellular-Enabled IoT Device with Real-Time Clock and Power Management

This circuit features a LilyGo-SIM7000G module for cellular communication and GPS functionality, interfaced with an RTC DS3231 for real-time clock capabilities. It includes voltage sensing through two voltage sensor modules, and uses an 8-channel opto-coupler for isolating different parts of the circuit. Power management is handled by a buck converter connected to a DC power source and batteries, with a fuse for protection and a rocker switch for on/off control. Additionally, there's an LED for indication purposes.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerDC-DC Converter and Relay Module Power Distribution System

This circuit consists of a DC-DC converter powering a 6-channel power module, which in turn supplies 5V to a 2-relay module. The power module distributes the converted voltage to the relay module, enabling it to control external devices.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with vcc

High Voltage Generator with Push Switch Activation
This circuit features a high voltage generator connected to a terminal PCB for output, with its power supply controlled by a 2-pin push switch. The high voltage generator's VCC is connected through the switch, allowing the user to turn the high voltage output on and off. The circuit is powered by a 7.4V battery, with the positive terminal connected to the switch and the negative terminal connected to the generator's ground.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Solar Panel to 12V Battery Charging Circuit
This circuit connects a solar panel to a 12V battery for charging purposes. The positive terminal of the solar panel is connected to the VCC of the battery, and the negative terminal is connected to the GND of the battery, allowing for energy transfer from the solar panel to the battery.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Cellular-Enabled IoT Device with Real-Time Clock and Power Management
This circuit features a LilyGo-SIM7000G module for cellular communication and GPS functionality, interfaced with an RTC DS3231 for real-time clock capabilities. It includes voltage sensing through two voltage sensor modules, and uses an 8-channel opto-coupler for isolating different parts of the circuit. Power management is handled by a buck converter connected to a DC power source and batteries, with a fuse for protection and a rocker switch for on/off control. Additionally, there's an LED for indication purposes.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
DC-DC Converter and Relay Module Power Distribution System
This circuit consists of a DC-DC converter powering a 6-channel power module, which in turn supplies 5V to a 2-relay module. The power module distributes the converted voltage to the relay module, enabling it to control external devices.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
- Voltage Range: Vcc can vary depending on the circuit design and components used. Common values include:
- 3.3V for low-power devices
- 5V for standard digital circuits
- 12V or higher for specific analog or power circuits
- Current Capacity: Determined by the power supply and the circuit's total load.
- Polarity: Vcc is typically the positive terminal in a circuit, with the negative terminal being ground (GND).
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Vcc is not a standalone component but rather a reference point in a circuit. However, in ICs and microcontrollers, Vcc is often labeled as a specific pin. Below is an example of how Vcc is represented in a typical microcontroller:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Vcc | Positive supply voltage input pin |
| GND | Ground or negative supply pin |
Usage Instructions
How to Use Vcc in a Circuit:
- Identify the required Vcc voltage for your circuit components. For example, a 5V microcontroller requires a 5V Vcc supply.
- Connect the positive terminal of your power supply to the Vcc pin or rail in your circuit.
- Ensure the ground (GND) of the power supply is connected to the circuit's ground.
Important Considerations and Best Practices:
- Always verify the voltage and current requirements of your components to avoid damage.
- Use decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1µF ceramic capacitors) near the Vcc pins of ICs to filter noise and stabilize the supply voltage.
- Avoid short circuits between Vcc and GND, as this can damage the power supply and components.
- If using a microcontroller like the Arduino UNO, ensure the Vcc voltage matches the board's operating voltage (e.g., 5V for Arduino UNO).
Example: Connecting Vcc to an Arduino UNO: Below is an example of how to power an Arduino UNO using its Vcc pin:
// Example code to blink an LED using Arduino UNO
// Ensure the Arduino is powered with 5V Vcc and GND is connected properly.
int ledPin = 13; // Pin 13 is connected to the onboard LED
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues:
- No power to the circuit:
- Check if the Vcc and GND connections are secure.
- Verify the power supply is functioning and providing the correct voltage.
- Overheating components:
- Ensure the Vcc voltage does not exceed the component's maximum rating.
- Check for short circuits or excessive current draw.
- Noise or instability in the circuit:
- Add decoupling capacitors near the Vcc pins of ICs.
- Use a regulated power supply to provide a stable Vcc.
- No power to the circuit:
FAQs:
- What does Vcc stand for?
- Vcc stands for "Voltage at the Common Collector," a term originating from transistor circuits. It generally refers to the positive supply voltage in a circuit.
- Can Vcc be negative?
- No, Vcc typically represents the positive supply voltage. For negative voltages, terms like Vee or Vss are used.
- How do I measure Vcc in a circuit?
- Use a multimeter to measure the voltage between the Vcc point and GND. Ensure the circuit is powered on during measurement.
- What does Vcc stand for?